[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0505: Cryo-EM structure of full-length chicken STING in the cGAMP-bound... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0505 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
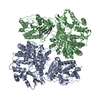
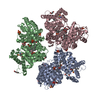
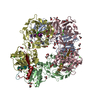
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of full-length chicken STING in the cGAMP-bound tetrameric state | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | primary map | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ER / membrane / adaptor / IMMUNE SYSTEM | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSTING mediated induction of host immune responses / 2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP binding / cyclic-di-GMP binding / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / proton channel activity / reticulophagy / protein complex oligomerization / autophagosome membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / autophagosome assembly ...STING mediated induction of host immune responses / 2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP binding / cyclic-di-GMP binding / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / proton channel activity / reticulophagy / protein complex oligomerization / autophagosome membrane / positive regulation of macroautophagy / autophagosome assembly / positive regulation of type I interferon production / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / activation of innate immune response / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / autophagosome / Neutrophil degranulation / cytoplasmic vesicle / defense response to virus / Golgi membrane / innate immune response / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein homodimerization activity / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shang G / Zhang C | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP-AMP. Authors: Guijun Shang / Conggang Zhang / Zhijian J Chen / Xiao-Chen Bai / Xuewu Zhang /  Abstract: Infections by pathogens that contain DNA trigger the production of type-I interferons and inflammatory cytokines through cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which produces 2'3'-cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) that binds ...Infections by pathogens that contain DNA trigger the production of type-I interferons and inflammatory cytokines through cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which produces 2'3'-cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) that binds to and activates stimulator of interferon genes (STING; also known as TMEM173, MITA, ERIS and MPYS). STING is an endoplasmic-reticulum membrane protein that contains four transmembrane helices followed by a cytoplasmic ligand-binding and signalling domain. The cytoplasmic domain of STING forms a dimer, which undergoes a conformational change upon binding to cGAMP. However, it remains unclear how this conformational change leads to STING activation. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length STING from human and chicken in the inactive dimeric state (about 80 kDa in size), as well as cGAMP-bound chicken STING in both the dimeric and tetrameric states. The structures show that the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions interact to form an integrated, domain-swapped dimeric assembly. Closure of the ligand-binding domain, induced by cGAMP, leads to a 180° rotation of the ligand-binding domain relative to the transmembrane domain. This rotation is coupled to a conformational change in a loop on the side of the ligand-binding-domain dimer, which leads to the formation of the STING tetramer and higher-order oligomers through side-by-side packing. This model of STING oligomerization and activation is supported by our structure-based mutational analyses. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0505.map.gz emd_0505.map.gz | 35.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0505-v30.xml emd-0505-v30.xml emd-0505.xml emd-0505.xml | 12.1 KB 12.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_0505_fsc.xml emd_0505_fsc.xml | 7.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_0505.png emd_0505.png | 129.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0505.cif.gz emd-0505.cif.gz | 5.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0505 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0505 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0505 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0505 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6nt8MC  0502C  0503C 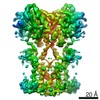 0504C  6nt5C  6nt6C  6nt7C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0505.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0505.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | primary map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.84 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : full-length chicken STING
| Entire | Name: full-length chicken STING |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: full-length chicken STING
| Supramolecule | Name: full-length chicken STING / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Stimulator of interferon genes protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Stimulator of interferon genes protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.20707 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPQDPSTRSS PARLLIPEPR AGRARHAACV LLAVCFVVLF LSGEPLAPII RSVCTQLAAL QLGVLLKGCC CLAEEIFHLH SRHHGSLWQ VLCSCFPPRW YLALLLVGGS AYLDPPEDNG HSPRLALTLS CLCQLLVLAL GLQKLSAVEV SELTESSKKN V AHGLAWSY ...String: MPQDPSTRSS PARLLIPEPR AGRARHAACV LLAVCFVVLF LSGEPLAPII RSVCTQLAAL QLGVLLKGCC CLAEEIFHLH SRHHGSLWQ VLCSCFPPRW YLALLLVGGS AYLDPPEDNG HSPRLALTLS CLCQLLVLAL GLQKLSAVEV SELTESSKKN V AHGLAWSY YIGYLKVVLP RLKECMEELS RTNPMLRAHR DTWKLHILVP LGCDIWDDLE KADSNIQYLA DLPETILTRA GI KRRVYKH SLYVIRDKDN KLRPCVLEFA SPLQTLCAMS QDDCAAFSRE QRLEQARLFY RSLRDILGSS KECAGLYRLI AYE EPAEPE SHFLSGLILW HLQQQQREEY MVQEELPLGT SSVELSLQVS SSDLPQPLRS DCPGIHRPDY KDDDDK UniProtKB: Stimulator of interferon genes protein |
-Macromolecule #2: cGAMP
| Macromolecule | Name: cGAMP / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 1SY |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 674.411 Da |
| Chemical component information | 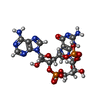 ChemComp-1SY: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Grid | Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6nt8: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















