+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP-AMP. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 567, Issue 7748, Page 389-393, Year 2019 |
| Publish date | Mar 6, 2019 |
 Authors Authors | Guijun Shang / Conggang Zhang / Zhijian J Chen / Xiao-Chen Bai / Xuewu Zhang /  |
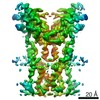
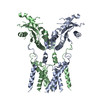
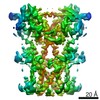
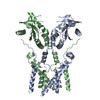
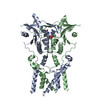
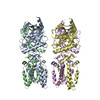
| PubMed Abstract | Infections by pathogens that contain DNA trigger the production of type-I interferons and inflammatory cytokines through cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which produces 2'3'-cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) that binds ...Infections by pathogens that contain DNA trigger the production of type-I interferons and inflammatory cytokines through cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, which produces 2'3'-cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) that binds to and activates stimulator of interferon genes (STING; also known as TMEM173, MITA, ERIS and MPYS). STING is an endoplasmic-reticulum membrane protein that contains four transmembrane helices followed by a cytoplasmic ligand-binding and signalling domain. The cytoplasmic domain of STING forms a dimer, which undergoes a conformational change upon binding to cGAMP. However, it remains unclear how this conformational change leads to STING activation. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length STING from human and chicken in the inactive dimeric state (about 80 kDa in size), as well as cGAMP-bound chicken STING in both the dimeric and tetrameric states. The structures show that the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions interact to form an integrated, domain-swapped dimeric assembly. Closure of the ligand-binding domain, induced by cGAMP, leads to a 180° rotation of the ligand-binding domain relative to the transmembrane domain. This rotation is coupled to a conformational change in a loop on the side of the ligand-binding-domain dimer, which leads to the formation of the STING tetramer and higher-order oligomers through side-by-side packing. This model of STING oligomerization and activation is supported by our structure-based mutational analyses. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:30842659 / PubMed:30842659 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
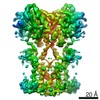
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 4.0 - 6.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-0502, PDB-6nt5: EMDB-0503, PDB-6nt6: |
| Chemicals | 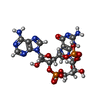 ChemComp-1SY: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / ER / membrane / adaptor |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
