[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0246: Leucine-zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain with single bo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0246 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Leucine-zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain with single bound insulin - "lower" membrane-proximal part | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | insulin bound to insulin receptor ectodomain - "lower" membrane-proximal part | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | insulin / insulin receptor ectodomain / signal transdution / SIGNALING PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / regulation of female gonad development / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / insulin-like growth factor II binding ...FCERI mediated MAPK activation / protein localization to nuclear periphery / regulation of female gonad development / Activation of the AP-1 family of transcription factors / positive regulation of meiotic cell cycle / response to amino acid starvation / negative regulation of ribosomal protein gene transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of cellular response to amino acid starvation / mediator complex binding / insulin-like growth factor II binding / positive regulation of developmental growth / male sex determination / insulin receptor complex / insulin-like growth factor I binding / positive regulation of protein-containing complex disassembly / insulin receptor activity / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / exocrine pancreas development / dendritic spine maintenance / cargo receptor activity / insulin binding / adrenal gland development / PTB domain binding / neuronal cell body membrane / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / positive regulation of respiratory burst / amyloid-beta clearance / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / amino acid biosynthetic process / insulin receptor substrate binding / regulation of embryonic development / positive regulation of receptor internalization / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / epidermis development / protein kinase activator activity / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / cellular response to nutrient levels / heart morphogenesis / transport across blood-brain barrier / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / Insulin receptor recycling / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / neuron projection maintenance / dendrite membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / receptor-mediated endocytosis / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / cellular response to amino acid starvation / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / learning / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / caveola / receptor internalization / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / male gonad development / memory / cellular response to insulin stimulus / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / late endosome / glucose homeostasis / amyloid-beta binding / protein autophosphorylation / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / protein tyrosine kinase activity / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / lysosome / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / receptor complex / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / endosome membrane / intracellular signal transduction / positive regulation of cell migration / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein domain specific binding / axon / external side of plasma membrane / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / chromatin binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / symbiont entry into host cell / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / extracellular exosome / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Weis F / Menting JG | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, Australia,  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2018Title: The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Authors: Felix Weis / John G Menting / Mai B Margetts / Shu Jin Chan / Yibin Xu / Norbert Tennagels / Paulus Wohlfart / Thomas Langer / Christoph W Müller / Matthias K Dreyer / Michael C Lawrence /    Abstract: Understanding the structural biology of the insulin receptor and how it signals is of key importance in the development of insulin analogs to treat diabetes. We report here a cryo-electron microscopy ...Understanding the structural biology of the insulin receptor and how it signals is of key importance in the development of insulin analogs to treat diabetes. We report here a cryo-electron microscopy structure of a single insulin bound to a physiologically relevant, high-affinity version of the receptor ectodomain, the latter generated through attachment of C-terminal leucine zipper elements to overcome the conformational flexibility associated with ectodomain truncation. The resolution of the cryo-electron microscopy maps is 3.2 Å in the insulin-binding region and 4.2 Å in the membrane-proximal region. The structure reveals how the membrane proximal domains of the receptor come together to effect signalling and how insulin's negative cooperativity of binding likely arises. Our structure further provides insight into the high affinity of certain super-mitogenic insulins. Together, these findings provide a new platform for insulin analog investigation and design. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0246.map.gz emd_0246.map.gz | 2.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0246-v30.xml emd-0246-v30.xml emd-0246.xml emd-0246.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_0246.png emd_0246.png | 110.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0246.cif.gz emd-0246.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0246 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0246 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_0246_validation.pdf.gz emd_0246_validation.pdf.gz | 334.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_0246_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_0246_full_validation.pdf.gz | 334.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_0246_validation.xml.gz emd_0246_validation.xml.gz | 6.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_0246_validation.cif.gz emd_0246_validation.cif.gz | 7.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0246 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0246 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0246 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6hn4MC  0247C  6hn5C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0246.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0246.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | insulin bound to insulin receptor ectodomain - "lower" membrane-proximal part | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Leucine zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain (IR-A isoform,...
| Entire | Name: Leucine zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain (IR-A isoform, "deltabeta" mutant) in complex with insulin and two Fv 83-7 modules : "lower" membrane-proximal part |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Leucine zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain (IR-A isoform,...
| Supramolecule | Name: Leucine zippered human insulin receptor ectodomain (IR-A isoform, "deltabeta" mutant) in complex with insulin and two Fv 83-7 modules : "lower" membrane-proximal part type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: Note: Attached to the leucine-zippered insulin receptor ectodomain are two Fv 83-7 modules. One of these is present within this map volume but it is very poorly ordered and thus left ...Details: Note: Attached to the leucine-zippered insulin receptor ectodomain are two Fv 83-7 modules. One of these is present within this map volume but it is very poorly ordered and thus left completely unmodelled. See the manuscript for further details. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin receptor,Insulin receptor,General control protein GCN4
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin receptor,Insulin receptor,General control protein GCN4 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: receptor protein-tyrosine kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 106.728211 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: HLYPGEVCPG MDIRNNLTRL HELENCSVIE GHLQILLMFK TRPEDFRDLS FPKLIMITDY LLLFRVYGLE SLKDLFPNLT VIRGSRLFF NYALVIFEMV HLKELGLYNL MNITRGSVRI EKNNELCYLA TIDWSRILDS VEDNHIVLNK DDNEECGDIC P GTAKGKTN ...String: HLYPGEVCPG MDIRNNLTRL HELENCSVIE GHLQILLMFK TRPEDFRDLS FPKLIMITDY LLLFRVYGLE SLKDLFPNLT VIRGSRLFF NYALVIFEMV HLKELGLYNL MNITRGSVRI EKNNELCYLA TIDWSRILDS VEDNHIVLNK DDNEECGDIC P GTAKGKTN CPATVINGQF VERCWTHSHC QKVCPTICKS HGCTAEGLCC HSECLGNCSQ PDDPTKCVAC RNFYLDGRCV ET CPPPYYH FQDWRCVNFS FCQDLHHKCK NSRRQGCHQY VIHNNKCIPE CPSGYTMNSS NLLCTPCLGP CPKVCHLLEG EKT IDSVTS AQELRGCTVI NGSLIINIRG GNNLAAELEA NLGLIEEISG YLKIRRSYAL VSLSFFRKLR LIRGETLEIG NYSF YALDN QNLRQLWDWS KHNLTTTQGK LFFHYNPKLC LSEIHKMEEV SGTKGRQERN DIALKTNGDK ASCENELLKF SYIRT SFDK ILLRWEPYWP PDFRDLLGFM LFYKEAPYQN VTEFDGQDAC GSNSWTVVDI DPPLRSNDPK SQNHPGWLMR GLKPWT QYA IFVKTLVTFS DERRTYGAKS DIIYVQTDAT NPSVPLDPIS VSNSSSQIIL KWKPPSDPNG NITHYLVFWE RQAEDSE LF ELDYCLKGLK LPSRTWSPPF ESEDSQKHNQ SEYEDSAGEC CSCPKTDSQI LKELEESSFR KTFEDYLHNV VFVPRPSR K RRSLGDVGNA GNNEEHRPFE KVVNKESLVI SGLRHFTGYR IELQACNQDT PEERCSVAAY VSARTMPEAK ADDIVGPVT HEIFENNVVH LMWQEPKEPN GLIVLYEVSY RRYGDEELHL CVSRKHFALE RGCRLRGLSP GNYSVRIRAT SLAGNGSWTE PTYFYVTDY LDVPSNIARM KQLEDKVEEL LSKNYHLENE VARLKKLVGE R UniProtKB: Insulin receptor, Insulin receptor, General control transcription factor GCN4 |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.094 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-20 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 2287 / Average exposure time: 16.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.85 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 130000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Source name: PDB / Chain - Initial model type: experimental model |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
| Output model |  PDB-6hn4: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





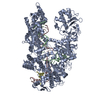
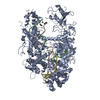















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)