+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Cryo-EM architecture of a near-native stretch-sensitive membrane microdomain. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 632, Issue 8025, Page 664-671, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Jul 24, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Jennifer M Kefauver / Markku Hakala / Luoming Zou / Josephine Alba / Javier Espadas / Maria G Tettamanti / Jelena Gajić / Caroline Gabus / Pablo Campomanes / Leandro F Estrozi / Nesli E Sen / Stefano Vanni / Aurélien Roux / Ambroise Desfosses / Robbie Loewith /    |
| PubMed Abstract | Biological membranes are partitioned into functional zones termed membrane microdomains, which contain specific lipids and proteins. The composition and organization of membrane microdomains remain ...Biological membranes are partitioned into functional zones termed membrane microdomains, which contain specific lipids and proteins. The composition and organization of membrane microdomains remain controversial because few techniques are available that allow the visualization of lipids in situ without disrupting their native behaviour. The yeast eisosome, composed of the BAR-domain proteins Pil1 and Lsp1 (hereafter, Pil1/Lsp1), scaffolds a membrane compartment that senses and responds to mechanical stress by flattening and releasing sequestered factors. Here we isolated near-native eisosomes as helical tubules made up of a lattice of Pil1/Lsp1 bound to plasma membrane lipids, and solved their structures by helical reconstruction. Our structures reveal a striking organization of membrane lipids, and, using in vitro reconstitutions and molecular dynamics simulations, we confirmed the positioning of individual PI(4,5)P, phosphatidylserine and sterol molecules sequestered beneath the Pil1/Lsp1 coat. Three-dimensional variability analysis of the native-source eisosomes revealed a dynamic stretching of the Pil1/Lsp1 lattice that affects the sequestration of these lipids. Collectively, our results support a mechanism in which stretching of the Pil1/Lsp1 lattice liberates lipids that would otherwise be anchored by the Pil1/Lsp1 coat, and thus provide mechanistic insight into how eisosome BAR-domain proteins create a mechanosensitive membrane microdomain. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:39048819 / PubMed:39048819 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / EM (helical sym.) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 3.86 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-18307: Native eisosome lattice bound to plasma membrane microdomain EMDB-18308, PDB-8qb9: EMDB-18309, PDB-8qbb: EMDB-18310, PDB-8qbd: EMDB-18311: Compact state - Native eisosome lattice bound to plasma membrane microdomain EMDB-18312: Stretched state - Native eisosome lattice bound to plasma membrane microdomain  EMDB-19822: Helical reconstruction of yeast eisosome protein Pil1 bound to membrane composed of lipid mixture +PIP2/+bromosterol (DOPC, DOPE, DOPS, bromo-ergosterol, PI(4,5)P2 35:20:20:15:10) |
| Chemicals | 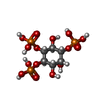 ChemComp-I3P:  ChemComp-P5S:  ChemComp-SEP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID BINDING PROTEIN / BAR domain / plasma membrane microdomain / membrane curvature / native biochemistry / lipid reconstitution / membrane microdomain |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers