+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Mechanism of conductance control and neurosteroid binding in NMDA receptors. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 648, Issue 8092, Page 220-228, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Oct 29, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Hyunook Kang / Ruben Steigerwald / Elijah Z Ullman / Max Epstein / Srinu Paladugu / Dennis C Liotta / Stephen F Traynelis / Hiro Furukawa /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Ion-channel activity reflects a combination of open probability and unitary conductance. Many channels display subconductance states that modulate signalling strength, yet the structural mechanisms ...Ion-channel activity reflects a combination of open probability and unitary conductance. Many channels display subconductance states that modulate signalling strength, yet the structural mechanisms governing conductance levels remain incompletely understood. Here we report that conductance levels are controlled by the bending patterns of pore-forming transmembrane helices in the heterotetrameric neuronal channel GluN1a-2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). Our single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) analyses demonstrate that an endogenous neurosteroid and synthetic positive allosteric modulator (PAM), 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), binds to a juxtamembrane pocket in the GluN2B subunit and stabilizes the fully open-gate conformation, where GluN1a M3 and GluN2B M3' pore-forming helices are bent to dilate the channel pore. By contrast, EU1622-240 binds to the same GluN2B juxtamembrane pocket and a distinct juxtamembrane pocket in GluN1a to stabilize a sub-open state whereby only the GluN2B M3' helix is bent. Consistent with the varying extents of gate opening, the single-channel recordings predominantly show full-conductance and subconductance states in the presence of 24S-HC and EU1622-240, respectively. Another class of neurosteroid, pregnenolone sulfate, engages a similar GluN2B pocket, but two molecules bind simultaneously, revealing a diverse neurosteroid recognition pattern. Our study identifies that the juxtamembrane pockets are critical structural hubs for modulating conductance levels in NMDAR. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:41162707 PubMed:41162707 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.84 - 3.34 Å |
| Structure data |  EMDB-70644: Consensus map of open state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70645: ECD focused map of open state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70646: TMD focused refined open state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70647: Consensus map of Closed state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70648: TMD focus refined Closed state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70649: ECD focus refined map of Closed state Gly/Glu/24S-HC bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70650: Consensus map of Non-active state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70651: ECD focus refined map of Non-active state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70652: TMD focus refined map of Non-active state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70653: Consensus map of pre-active state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70654: ECD focus refined map of preactive state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR  EMDB-70655: TMD focus refined map of preactive state Gly/Glu/PS bound hGluN1a-2B NMDAR EMDB-70669, PDB-9ooq: EMDB-70670, PDB-9oor: EMDB-70671, PDB-9oos: EMDB-70672, PDB-9oot: EMDB-70673, PDB-9oou: |
| Chemicals | 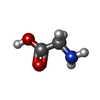 ChemComp-GLY:  ChemComp-POV: 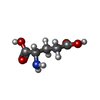 ChemComp-GLU:  PDB-1ce1:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-A8W:  PDB-1aft:  ChemComp-CLR: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor / Closed state / 24S-HC / GluN2B / Open state / Non-active / Pregnenolone Sulfate / pre-active / Ion Channels / NMDAR |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers













 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
