+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
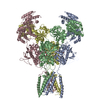
| Title | Glycine/Glutamate/EU 1622-240 rGluN1a-2B NMDAR | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Membrane Protein / Ion Channels / NMDAR | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / pons maturation / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / regulation of cell communication ...cellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / pons maturation / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / regulation of cell communication / auditory behavior / positive regulation of Schwann cell migration / sensitization / olfactory learning / conditioned taste aversion / response to other organism / dendritic branch / fear response / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / response to methylmercury / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / apical dendrite / regulation of ARF protein signal transduction / response to manganese ion / response to carbohydrate / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / suckling behavior / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / interleukin-1 receptor binding / cellular response to dsRNA / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / cellular response to lipid / response to growth hormone / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / heterocyclic compound binding / response to amine / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / response to glycoside / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / regulation of axonogenesis / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / neuromuscular process / response to morphine / regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein heterotetramerization / male mating behavior / regulation of synapse assembly / glycine binding / small molecule binding / receptor clustering / startle response / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / behavioral response to pain / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / regulation of MAPK cascade / monoatomic ion channel complex / cellular response to glycine / response to magnesium ion / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / response to electrical stimulus / action potential / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / associative learning / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / social behavior / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / monoatomic cation transport / glutamate receptor binding / response to mechanical stimulus / prepulse inhibition / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / long-term memory / neuron development / multicellular organismal response to stress / phosphatase binding / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / behavioral fear response / response to fungicide / monoatomic cation channel activity / synaptic cleft / calcium ion homeostasis / glutamate-gated receptor activity / cellular response to manganese ion / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / D2 dopamine receptor binding / response to cytokine / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.34 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Steigerwald R / Furukawa H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Mechanism of conductance control and neurosteroid binding in NMDA receptors. Authors: Hyunook Kang / Ruben Steigerwald / Elijah Z Ullman / Max Epstein / Srinu Paladugu / Dennis C Liotta / Stephen F Traynelis / Hiro Furukawa /  Abstract: Ion-channel activity reflects a combination of open probability and unitary conductance. Many channels display subconductance states that modulate signalling strength, yet the structural mechanisms ...Ion-channel activity reflects a combination of open probability and unitary conductance. Many channels display subconductance states that modulate signalling strength, yet the structural mechanisms governing conductance levels remain incompletely understood. Here we report that conductance levels are controlled by the bending patterns of pore-forming transmembrane helices in the heterotetrameric neuronal channel GluN1a-2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR). Our single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) analyses demonstrate that an endogenous neurosteroid and synthetic positive allosteric modulator (PAM), 24S-hydroxycholesterol (24S-HC), binds to a juxtamembrane pocket in the GluN2B subunit and stabilizes the fully open-gate conformation, where GluN1a M3 and GluN2B M3' pore-forming helices are bent to dilate the channel pore. By contrast, EU1622-240 binds to the same GluN2B juxtamembrane pocket and a distinct juxtamembrane pocket in GluN1a to stabilize a sub-open state whereby only the GluN2B M3' helix is bent. Consistent with the varying extents of gate opening, the single-channel recordings predominantly show full-conductance and subconductance states in the presence of 24S-HC and EU1622-240, respectively. Another class of neurosteroid, pregnenolone sulfate, engages a similar GluN2B pocket, but two molecules bind simultaneously, revealing a diverse neurosteroid recognition pattern. Our study identifies that the juxtamembrane pockets are critical structural hubs for modulating conductance levels in NMDAR. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_70673.map.gz emd_70673.map.gz | 306.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-70673-v30.xml emd-70673-v30.xml emd-70673.xml emd-70673.xml | 21.2 KB 21.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_70673_fsc.xml emd_70673_fsc.xml | 14.5 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_70673.png emd_70673.png | 71.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-70673.cif.gz emd-70673.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_70673_half_map_1.map.gz emd_70673_half_map_1.map.gz emd_70673_half_map_2.map.gz emd_70673_half_map_2.map.gz | 300.2 MB 300.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70673 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70673 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70673 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70673 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9oouMC  9ooqC  9oorC  9oosC  9ootC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_70673.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_70673.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.827 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_70673_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_70673_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Di-heteromeric GluN1a-2B NMDA receptor
| Entire | Name: Di-heteromeric GluN1a-2B NMDA receptor |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Di-heteromeric GluN1a-2B NMDA receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: Di-heteromeric GluN1a-2B NMDA receptor / type: cell / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 95.225883 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSTMHLLTFA LLFSCSFARA ASDPKIVNIG AVLSTRKHEQ MFREAVNQAN KRHGSWKIQL QATSVTHKPN AIQMALSVCE DLISSQVYA ILVSHPPTPN DHFTPTPVSY TAGFYRIPVL GLTTRMSIYS DKSIHLSFLR TVPPYSHQSS VWFEMMRVYN W NHIILLVS ...String: MSTMHLLTFA LLFSCSFARA ASDPKIVNIG AVLSTRKHEQ MFREAVNQAN KRHGSWKIQL QATSVTHKPN AIQMALSVCE DLISSQVYA ILVSHPPTPN DHFTPTPVSY TAGFYRIPVL GLTTRMSIYS DKSIHLSFLR TVPPYSHQSS VWFEMMRVYN W NHIILLVS DDHEGRAAQK RLETLLEERE SKAEKVLQFD PGTKNVTALL MEARELEARV IILSASEDDA ATVYRAAAML DM TGSGYVW LVGEREISGN ALRYAPDGII GLQLINGKNE SAHISDAVGV VAQAVHELLE KENITDPPRG CVGNTNIWKT GPL FKRVLM SSKYADGVTG RVEFNEDGDR KFAQYSIMNL QNRKLVQVGI YNGTHVIPND RKIIWPGGET EKPRGYQMST RLKI VTIHQ EPFVYVKPTM SDGTCKEEFT VNGDPVKKVI CTGPNDTSPG SPRHTVPQCC YGFCIDLLIK LARTMQFTYE VHLVA DGKF GTQERVQNSN KKEWNGMMGE LLSGQADMIV APLTINNERA QYIEFSKPFK YQGLTILVKK EIPRSTLDSF MQPFQS TLW LLVGLSVHVV AVMLYLLDRF SPFGRFKVNS EEEEEDALTL SSAMWFSWGV LLNSGIGEGA PRSFSARILG MVWAGFA MI IVASYTANLA AFLVLDRPEE RITGINDPRL RNPSDKFIYA TVKQSSVDIY FRRQVELSTM YRHMEKHNYE SAAEAIQA V RDNKLHAFIW DSAVLEFEAS QKCDLVTTGE LFFRSGFGIG MRKDSPWKQQ VSLSILKSHE NGFMEDLDKT WVRYQECDS RSNAPATLTF ENMAGVFMLV AGGIVAGIFL IFIEIAYKRH KDANGAQ UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.498977 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKG ALVPRGRSQK SPPSIGIAVI LVGTSDEVAI KDAHEKDDFH HLSVVPRVEL VAMNETDPK SIITRICDLM SDRKIQGVVF ADDTDQEAIA QILDFISAQT LTPILGIHGG SSMIMADKDE SSMFFQFGPS I EQQASVML ...String: GWSHPQFEKG GGSGGGSGGS AWSHPQFEKG ALVPRGRSQK SPPSIGIAVI LVGTSDEVAI KDAHEKDDFH HLSVVPRVEL VAMNETDPK SIITRICDLM SDRKIQGVVF ADDTDQEAIA QILDFISAQT LTPILGIHGG SSMIMADKDE SSMFFQFGPS I EQQASVML NIMEEYDWYI FSIVTTYFPG YQDFVNKIRS TIENSFVGWE LEEVLLLDMS LDDGDSKIQN QLKKLQSPII LL YCTKEEA TYIFEVANSV GLTGYGYTWI VPSLVAGDTD TVPSEFPTGL ISVSYDEWDY GLPARVRDGI AIITTAASDM LSE HSFIPE PKSSCYNTHE KRIYQSNMLN RYLINVTFEG RNLSFSEDGY QMHPKLVIIL LNKERKWERV GKWKDKSLQM KYYV WPRMC PETEEQEDDH LSIVTLEEAP FVIVESVDPL SGTCMRNTVP CQKRIISENK TDEEPGYIKK CCKGFCIDIL KKISK SVKF TYDLYLVTNG KHGKKINGTW NGMIGEVVMK RAYMAVGSLT INEERSEVVD FSVPFIETGI SVMVSRSNGT VSPSAF LEP FSADVWVMMF VMLLIVSAVA VFVFEYFSPV GYNRCLADGR EPGGPSFTIG KAIWLLWGLV FNNSVPVQNP KGTTSKI MV SVWAFFAVIF LASYTANLAA FMIQEEYVDQ VSGLSDKKFQ RPNDFSPPFR FGTVPNGSTE RNIRNNYAEM HAYMGKFN Q RGVDDALLSL KTGKLDAFIY DAAVLNYMAG RDEGCKLVTI GSGKVFASTG YGIAIQKDSG WKRQVDLAIL QLFGDGEME ELEALWLTGI CHNEKNEVMS SQLDIDNMAG VFYMLGAAMA LSLITFICEH LFYWQFRHSF MG UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B |
-Macromolecule #3: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #4: (5M)-5-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-6-ethynyl-3-[2-(3-fluoro-3-methyl...
| Macromolecule | Name: (5M)-5-(3-bromo-4-fluorophenyl)-6-ethynyl-3-[2-(3-fluoro-3-methylazetidin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl]thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-one type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: A1AFT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 478.31 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: CHOLESTEROL
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CLR |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 386.654 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CLR: |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 18 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 58.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller
























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)