+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structure of apolipoprotein B100 bound to the low-density lipoprotein receptor. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 638, Issue 8051, Page 829-835, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Dec 11, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Mart Reimund / Altaira D Dearborn / Giorgio Graziano / Haotian Lei / Anthony M Ciancone / Ashish Kumar / Ronald Holewinski / Edward B Neufeld / Francis J O'Reilly / Alan T Remaley / Joseph Marcotrigiano /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial ...Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial hypercholesterolaemia, an autosomal dominant disease that is characterized by a marked increase in LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The structure of apoB100 on LDL and its interaction with LDLR are poorly understood. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of apoB100 on LDL bound to the LDLR and a nanobody complex, which can form a C-symmetric, higher-order complex. Using local refinement, we determined high-resolution structures of the interfaces between apoB100 and LDLR. One binding interface is formed between several small-ligand-binding modules of LDLR and a series of basic patches that are scattered along a β-belt formed by apoB100, encircling LDL. The other binding interface is formed between the β-propeller domain of LDLR and the N-terminal domain of apoB100. Our results reveal how both interfaces are involved in LDL dimer formation, and how LDLR cycles between LDL- and self-bound conformations. In addition, known mutations in either apoB100 or LDLR, associated with high levels of LDL-C, are located at the LDL-LDLR interface. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:39663455 PubMed:39663455 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.73 - 8.6 Å |
| Structure data | 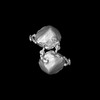 EMDB-44442: Dimeric form of LDL, LDL receptor and Legobody EMDB-44443, PDB-9bd1: EMDB-44446, PDB-9bd8: EMDB-44450, PDB-9bde: EMDB-44469, PDB-9bdt: EMDB-45787, PDB-9coo: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-CA: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID TRANSPORT / Apolipoprotien B 100 / alpha/beta 1 region / LDL / Low density lipoprotein / LDL receptor / Apolipoprotein B 100 / ApoB100 / LDLreceptor |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers











 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)

