+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9bd8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
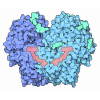
| Title | ApoB 100 beta barrel bound to LDLR beta propeller | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID TRANSPORT / LDL / Low density lipoprotein / LDL receptor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmature chylomicron / Scavenging by Class H Receptors / triglyceride mobilization / positive regulation of cholesterol storage / VLDL assembly / receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport / regulation of phosphatidylcholine catabolic process / plasma lipoprotein particle clearance / LDL remodeling / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process ...mature chylomicron / Scavenging by Class H Receptors / triglyceride mobilization / positive regulation of cholesterol storage / VLDL assembly / receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport / regulation of phosphatidylcholine catabolic process / plasma lipoprotein particle clearance / LDL remodeling / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / Scavenging by Class B Receptors / positive regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process / lipase binding / negative regulation of astrocyte activation / VLDL clearance / negative regulation of microglial cell activation / very-low-density lipoprotein particle assembly / triglyceride catabolic process / very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity / PCSK9-LDLR complex / cholesterol import / low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process / negative regulation of receptor recycling / clathrin heavy chain binding / intestinal cholesterol absorption / chylomicron remnant / intermediate-density lipoprotein particle / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity / Chylomicron clearance / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / Chylomicron remodeling / low-density lipoprotein particle binding / cellular response to lipoprotein particle stimulus / regulation of protein metabolic process / Chylomicron assembly / response to caloric restriction / LDL clearance / high-density lipoprotein particle clearance / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / chylomicron / phospholipid transport / lipoprotein catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid storage / low-density lipoprotein particle / flagellated sperm motility / lipoprotein biosynthetic process / cholesterol transfer activity / cholesterol transport / very-low-density lipoprotein particle / low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling / cellular response to fatty acid / negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation / positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / fertilization / endolysosome membrane / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / cholesterol efflux / regulation of cholesterol metabolic process / artery morphogenesis / negative regulation of protein metabolic process / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / lipoprotein transport / Platelet sensitization by LDL / sorting endosome / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / lipoprotein particle binding / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / amyloid-beta clearance / cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus / long-term memory / phagocytosis / retinoid metabolic process / Retinoid metabolism and transport / cholesterol metabolic process / somatodendritic compartment / lipid droplet / clathrin-coated pit / endocytic vesicle lumen / lysosomal lumen / receptor-mediated endocytosis / cholesterol homeostasis / endosome lumen / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / post-embryonic development / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / establishment of localization in cell / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / Heme signaling / phospholipid binding / lipid metabolic process / response to virus / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / endocytosis / apical part of cell / positive regulation of inflammatory response / late endosome / nervous system development Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dearborn, A.D. / Reimund, M. / Graziano, G. / Lei, H. / Kumar, A. / Neufeld, E.B. / Remaley, A.T. / Marcotrigiano, J. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Structure of apolipoprotein B100 bound to the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Authors: Mart Reimund / Altaira D Dearborn / Giorgio Graziano / Haotian Lei / Anthony M Ciancone / Ashish Kumar / Ronald Holewinski / Edward B Neufeld / Francis J O'Reilly / Alan T Remaley / Joseph Marcotrigiano /  Abstract: Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial ...Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial hypercholesterolaemia, an autosomal dominant disease that is characterized by a marked increase in LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The structure of apoB100 on LDL and its interaction with LDLR are poorly understood. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of apoB100 on LDL bound to the LDLR and a nanobody complex, which can form a C-symmetric, higher-order complex. Using local refinement, we determined high-resolution structures of the interfaces between apoB100 and LDLR. One binding interface is formed between several small-ligand-binding modules of LDLR and a series of basic patches that are scattered along a β-belt formed by apoB100, encircling LDL. The other binding interface is formed between the β-propeller domain of LDLR and the N-terminal domain of apoB100. Our results reveal how both interfaces are involved in LDL dimer formation, and how LDLR cycles between LDL- and self-bound conformations. In addition, known mutations in either apoB100 or LDLR, associated with high levels of LDL-C, are located at the LDL-LDLR interface. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9bd8.cif.gz 9bd8.cif.gz | 255.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9bd8.ent.gz pdb9bd8.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9bd8.json.gz 9bd8.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bd/9bd8 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bd/9bd8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bd/9bd8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bd/9bd8 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44446MC  9bd1C  9bdeC  9bdtC  9cooC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 516167.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04114 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P04114 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 95477.023 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LDLR / Cell line (production host): HEK293 GnTI- / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LDLR / Cell line (production host): HEK293 GnTI- / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01130 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01130 |
| #3: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51.38 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOCONTINUUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21_5207 / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3689076 / Details: Topaz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 522863 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 279.1 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj