+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
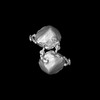
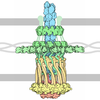
| Title | Apolipoprotein B 100 bound to LDL receptor and legobody | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | LocScale | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LDL / ApoB100 / LDL receptor / LIPID TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmature chylomicron / Scavenging by Class H Receptors / triglyceride mobilization / positive regulation of cholesterol storage / VLDL assembly / receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport / regulation of phosphatidylcholine catabolic process / plasma lipoprotein particle clearance / LDL remodeling / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process ...mature chylomicron / Scavenging by Class H Receptors / triglyceride mobilization / positive regulation of cholesterol storage / VLDL assembly / receptor-mediated endocytosis involved in cholesterol transport / regulation of phosphatidylcholine catabolic process / plasma lipoprotein particle clearance / LDL remodeling / regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / Scavenging by Class B Receptors / positive regulation of lysosomal protein catabolic process / lipase binding / negative regulation of astrocyte activation / VLDL clearance / negative regulation of microglial cell activation / very-low-density lipoprotein particle assembly / triglyceride catabolic process / very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity / PCSK9-LDLR complex / cholesterol import / low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / positive regulation of triglyceride biosynthetic process / negative regulation of receptor recycling / clathrin heavy chain binding / intestinal cholesterol absorption / chylomicron remnant / intermediate-density lipoprotein particle / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor activity / Chylomicron clearance / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / Chylomicron remodeling / low-density lipoprotein particle binding / cellular response to lipoprotein particle stimulus / regulation of protein metabolic process / Chylomicron assembly / response to caloric restriction / LDL clearance / high-density lipoprotein particle clearance / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / chylomicron / phospholipid transport / lipoprotein catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid storage / low-density lipoprotein particle / flagellated sperm motility / lipoprotein biosynthetic process / cholesterol transfer activity / cholesterol transport / very-low-density lipoprotein particle / low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling / cellular response to fatty acid / negative regulation of amyloid fibril formation / positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / fertilization / endolysosome membrane / negative regulation of low-density lipoprotein particle clearance / IgG binding / cholesterol efflux / regulation of cholesterol metabolic process / artery morphogenesis / negative regulation of protein metabolic process / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / lipoprotein transport / Platelet sensitization by LDL / sorting endosome / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / lipoprotein particle binding / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / amyloid-beta clearance / cellular response to low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / maltose binding / maltose transport / maltodextrin transmembrane transport / long-term memory / phagocytosis / retinoid metabolic process / Retinoid metabolism and transport / cholesterol metabolic process / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex, substrate-binding subunit-containing / somatodendritic compartment / lipid droplet / clathrin-coated pit / endocytic vesicle lumen / lysosomal lumen / receptor-mediated endocytosis / cholesterol homeostasis / endosome lumen / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / post-embryonic development / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / establishment of localization in cell / clathrin-coated endocytic vesicle membrane / Heme signaling / phospholipid binding / lipid metabolic process / response to virus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /    | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dearborn AD / Reimund M / Graziano G / Lei H / Kumar A / Neufeld EB / Remaley AT / Marcotrigiano J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Structure of apolipoprotein B100 bound to the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Authors: Mart Reimund / Altaira D Dearborn / Giorgio Graziano / Haotian Lei / Anthony M Ciancone / Ashish Kumar / Ronald Holewinski / Edward B Neufeld / Francis J O'Reilly / Alan T Remaley / Joseph Marcotrigiano /  Abstract: Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial ...Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB100) is a structural component of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a ligand for the LDL receptor (LDLR). Mutations in apoB100 or in LDLR cause familial hypercholesterolaemia, an autosomal dominant disease that is characterized by a marked increase in LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. The structure of apoB100 on LDL and its interaction with LDLR are poorly understood. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of apoB100 on LDL bound to the LDLR and a nanobody complex, which can form a C-symmetric, higher-order complex. Using local refinement, we determined high-resolution structures of the interfaces between apoB100 and LDLR. One binding interface is formed between several small-ligand-binding modules of LDLR and a series of basic patches that are scattered along a β-belt formed by apoB100, encircling LDL. The other binding interface is formed between the β-propeller domain of LDLR and the N-terminal domain of apoB100. Our results reveal how both interfaces are involved in LDL dimer formation, and how LDLR cycles between LDL- and self-bound conformations. In addition, known mutations in either apoB100 or LDLR, associated with high levels of LDL-C, are located at the LDL-LDLR interface. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44469.map.gz emd_44469.map.gz | 71 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44469-v30.xml emd-44469-v30.xml emd-44469.xml emd-44469.xml | 29.4 KB 29.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44469_fsc.xml emd_44469_fsc.xml | 11.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44469.png emd_44469.png | 61.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44469.cif.gz emd-44469.cif.gz | 12.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44469_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44469_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44469_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44469_half_map_2.map.gz | 134.1 MB 134.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44469 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44469 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44469 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44469 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
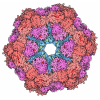
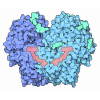
| Related structure data |  9bdtMC 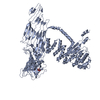 9bd1C 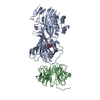 9bd8C  9bdeC  9cooC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44469.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 144.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44469.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 144.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | LocScale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.66 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half Map A
| File | emd_44469_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44469_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Apoliprotein B 100 from LDL bound to LDL receptor and Legobody
| Entire | Name: Apoliprotein B 100 from LDL bound to LDL receptor and Legobody |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Apoliprotein B 100 from LDL bound to LDL receptor and Legobody
| Supramolecule | Name: Apoliprotein B 100 from LDL bound to LDL receptor and Legobody type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #2-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Apolipoprotein B-100
| Macromolecule | Name: Apolipoprotein B-100 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 516.167469 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MDPPRPALLA LLALPALLLL LLAGARAEEE MLENVSLVCP KDATRFKHLR KYTYNYEAES SSGVPGTADS RSATRINCKV ELEVPQLCS FILKTSQCTL KEVYGFNPEG KALLKKTKNS EEFAAAMSRY ELKLAIPEGK QVFLYPEKDE PTYILNIKRG I ISALLVPP ...String: MDPPRPALLA LLALPALLLL LLAGARAEEE MLENVSLVCP KDATRFKHLR KYTYNYEAES SSGVPGTADS RSATRINCKV ELEVPQLCS FILKTSQCTL KEVYGFNPEG KALLKKTKNS EEFAAAMSRY ELKLAIPEGK QVFLYPEKDE PTYILNIKRG I ISALLVPP ETEEAKQVLF LDTVYGNCST HFTVKTRKGN VATEISTERD LGQCDRFKPI RTGISPLALI KGMTRPLSTL IS SSQSCQY TLDAKRKHVA EAICKEQHLF LPFSYKNKYG MVAQVTQTLK LEDTPKINSR FFGEGTKKMG LAFESTKSTS PPK QAEAVL KTLQELKKLT ISEQNIQRAN LFNKLVTELR GLSDEAVTSL LPQLIEVSSP ITLQALVQCG QPQCSTHILQ WLKR VHANP LLIDVVTYLV ALIPEPSAQQ LREIFNMARD QRSRATLYAL SHAVNNYHKT NPTGTQELLD IANYLMEQIQ DDCTG DEDY TYLILRVIGN MGQTMEQLTP ELKSSILKCV QSTKPSLMIQ KAAIQALRKM EPKDKDQEVL LQTFLDDASP GDKRLA AYL MLMRSPSQAD INKIVQILPW EQNEQVKNFV ASHIANILNS EELDIQDLKK LVKEALKESQ LPTVMDFRKF SRNYQLY KS VSLPSLDPAS AKIEGNLIFD PNNYLPKESM LKTTLTAFGF ASADLIEIGL EGKGFEPTLE ALFGKQGFFP DSVNKALY W VNGQVPDGVS KVLVDHFGYT KDDKHEQDMV NGIMLSVEKL IKDLKSKEVP EARAYLRILG EELGFASLHD LQLLGKLLL MGARTLQGIP QMIGEVIRKG SKNDFFLHYI FMENAFELPT GAGLQLQISS SGVIAPGAKA GVKLEVANMQ AELVAKPSVS VEFVTNMGI IIPDFARSGV QMNTNFFHES GLEAHVALKA GKLKFIIPSP KRPVKLLSGG NTLHLVSTTK TEVIPPLIEN R QSWSVCKQ VFPGLNYCTS GAYSNASSTD SASYYPLTGD TRLELELRPT GEIEQYSVSA TYELQREDRA LVDTLKFVTQ AE GAKQTEA TMTFKYNRQS MTLSSEVQIP DFDVDLGTIL RVNDESTEGK TSYRLTLDIQ NKKITEVALM GHLSCDTKEE RKI KGVISI PRLQAEARSE ILAHWSPAKL LLQMDSSATA YGSTVSKRVA WHYDEEKIEF EWNTGTNVDT KKMTSNFPVD LSDY PKSLH MYANRLLDHR VPQTDMTFRH VGSKLIVAMS SWLQKASGSL PYTQTLQDHL NSLKEFNLQN MGLPDFHIPE NLFLK SDGR VKYTLNKNSL KIEIPLPFGG KSSRDLKMLE TVRTPALHFK SVGFHLPSRE FQVPTFTIPK LYQLQVPLLG VLDLST NVY SNLYNWSASY SGGNTSTDHF SLRARYHMKA DSVVDLLSYN VQGSGETTYD HKNTFTLSCD GSLRHKFLDS NIKFSHV EK LGNNPVSKGL LIFDASSSWG PQMSASVHLD SKKKQHLFVK EVKIDGQFRV SSFYAKGTYG LSCQRDPNTG RLNGESNL R FNSSYLQGTN QITGRYEDGT LSLTSTSDLQ SGIIKNTASL KYENYELTLK SDTNGKYKNF ATSNKMDMTF SKQNALLRS EYQADYESLR FFSLLSGSLN SHGLELNADI LGTDKINSGA HKATLRIGQD GISTSATTNL KCSLLVLENE LNAELGLSGA SMKLTTNGR FREHNAKFSL DGKAALTELS LGSAYQAMIL GVDSKNIFNF KVSQEGLKLS NDMMGSYAEM KFDHTNSLNI A GLSLDFSS KLDNIYSSDK FYKQTVNLQL QPYSLVTTLN SDLKYNALDL TNNGKLRLEP LKLHVAGNLK GAYQNNEIKH IY AISSAAL SASYKADTVA KVQGVEFSHR LNTDIAGLAS AIDMSTNYNS DSLHFSNVFR SVMAPFTMTI DAHTNGNGKL ALW GEHTGQ LYSKFLLKAE PLAFTFSHDY KGSTSHHLVS RKSISAALEH KVSALLTPAE QTGTWKLKTQ FNNNEYSQDL DAYN TKDKI GVELTGRTLA DLTLLDSPIK VPLLLSEPIN IIDALEMRDA VEKPQEFTIV AFVKYDKNQD VHSINLPFFE TLQEY FERN RQTIIVVLEN VQRNLKHINI DQFVRKYRAA LGKLPQQAND YLNSFNWERQ VSHAKEKLTA LTKKYRITEN DIQIAL DDA KINFNEKLSQ LQTYMIQFDQ YIKDSYDLHD LKIAIANIID EIIEKLKSLD EHYHIRVNLV KTIHDLHLFI ENIDFNK SG SSTASWIQNV DTKYQIRIQI QEKLQQLKRH IQNIDIQHLA GKLKQHIEAI DVRVLLDQLG TTISFERIND ILEHVKHF V INLIGDFEVA EKINAFRAKV HELIERYEVD QQIQVLMDKL VELAHQYKLK ETIQKLSNVL QQVKIKDYFE KLVGFIDDA VKKLNELSFK TFIEDVNKFL DMLIKKLKSF DYHQFVDETN DKIREVTQRL NGEIQALELP QKAEALKLFL EETKATVAVY LESLQDTKI TLIINWLQEA LSSASLAHMK AKFRETLEDT RDRMYQMDIQ QELQRYLSLV GQVYSTLVTY ISDWWTLAAK N LTDFAEQY SIQDWAKRMK ALVEQGFTVP EIKTILGTMP AFEVSLQALQ KATFQTPDFI VPLTDLRIPS VQINFKDLKN IK IPSRFST PEFTILNTFH IPSFTIDFVE MKVKIIRTID QMLNSELQWP VPDIYLRDLK VEDIPLARIT LPDFRLPEIA IPE FIIPTL NLNDFQVPDL HIPEFQLPHI SHTIEVPTFG KLYSILKIQS PLFTLDANAD IGNGTTSANE AGIAASITAK GESK LEVLN FDFQANAQLS NPKINPLALK ESVKFSSKYL RTEHGSEMLF FGNAIEGKSN TVASLHTEKN TLELSNGVIV KINNQ LTLD SNTKYFHKLN IPKLDFSSQA DLRNEIKTLL KAGHIAWTSS GKGSWKWACP RFSDEGTHES QISFTIEGPL TSFGLS NKI NSKHLRVNQN LVYESGSLNF SKLEIQSQVD SQHVGHSVLT AKGMALFGEG KAEFTGRHDA HLNGKVIGTL KNSLFFS AQ PFEITASTNN EGNLKVRFPL RLTGKIDFLN NYALFLSPSA QQASWQVSAR FNQYKYNQNF SAGNNENIME AHVGINGE A NLDFLNIPLT IPEMRLPYTI ITTPPLKDFS LWEKTGLKEF LKTTKQSFDL SVKAQYKKNK HRHSITNPLA VLCEFISQS IKSFDRHFEK NRNNALDFVT KSYNETKIKF DKYKAEKSHD ELPRTFQIPG YTVPVVNVEV SPFTIEMSAF GYVFPKAVSM PSFSILGSD VRVPSYTLIL PSLELPVLHV PRNLKLSLPD FKELCTISHI FIPAMGNITY DFSFKSSVIT LNTNAELFNQ S DIVAHLLS SSSSVIDALQ YKLEGTTRLT RKRGLKLATA LSLSNKFVEG SHNSTVSLTT KNMEVSVATT TKAQIPILRM NF KQELNGN TKSKPTVSSS MEFKYDFNSS MLYSTAKGAV DHKLSLESLT SYFSIESSTK GDVKGSVLSR EYSGTIASEA NTY LNSKST RSSVKLQGTS KIDDIWNLEV KENFAGEATL QRIYSLWEHS TKNHLQLEGL FFTNGEHTSK ATLELSPWQM SALV QVHAS QPSSFHDFPD LGQEVALNAN TKNQKIRWKN EVRIHSGSFQ SQVELSNDQE KAHLDIAGSL EGHLRFLKNI ILPVY DKSL WDFLKLDVTT SIGRRQHLRV STAFVYTKNP NGYSFSIPVK VLADKFIIPG LKLNDLNSVL VMPTFHVPFT DLQVPS CKL DFREIQIYKK LRTSSFALNL PTLPEVKFPE VDVLTKYSQP EDSLIPFFEI TVPESQLTVS QFTLPKSVSD GIAALDL NA VANKIADFEL PTIIVPEQTI EIPSIKFSVP AGIVIPSFQA LTARFEVDSP VYNATWSASL KNKADYVETV LDSTCSST V QFLEYELNVL GTHKIEDGTL ASKTKGTFAH RDFSAEYEED GKYEGLQEWE GKAHLNIKSP AFTDLHLRYQ KDKKGISTS AASPAVGTVG MDMDEDDDFS KWNFYYSPQS SPDKKLTIFK TELRVRESDE ETQIKVNWEE EAASGLLTSL KDNVPKATGV LYDYVNKYH WEHTGLTLRE VSSKLRRNLQ NNAEWVYQGA IRQIDDIDVR FQKAASGTTG TYQEWKDKAQ NLYQELLTQE G QASFQGLK DNVFDGLVRV TQEFHMKVKH LIDSLIDFLN FPRFQFPGKP GIYTREELCT MFIREVGTVL SQVYSKVHNG SE ILFSYFQ DLVITLPFEL RKHKLIDVIS MYRELLKDLS KEAQEVFKAI QSLKTTEVLR NLQDLLQFIF QLIEDNIKQL KEM KFTYLI NYIQDEINTI FSDYIPYVFK LLKENLCLNL HKFNEFIQNE LQEASQELQQ IHQYIMALRE EYFDPSIVGW TVKY YELEE KIVSLIKNLL VALKDFHSEY IVSASNFTSQ LSSQVEQFLH RNIQEYLSIL TDPDGKGKEK IAELSATAQE IIKSQ AIAT KKIISDYHQQ FRYKLQDFSD QLSDYYEKFI AESKRLIDLS IQNYHTFLIY ITELLKKLQS TTVMNPYMKL APGELT IIL UniProtKB: Apolipoprotein B-100 |
-Macromolecule #2: Legobody 8D3 Fab Heavy Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Legobody 8D3 Fab Heavy Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.252217 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DVQLVESGGG LVQPGKSLRL SCAASGFTFS NFGMHWVRQA PEMGLEWVAY ISSGSTTKYY GDTVKGRFTI SRDNPKNTLY LQMNSLRSE DTAMYYCARR PLYDGDYGYP MDYWGQGTSV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA ...String: DVQLVESGGG LVQPGKSLRL SCAASGFTFS NFGMHWVRQA PEMGLEWVAY ISSGSTTKYY GDTVKGRFTI SRDNPKNTLY LQMNSLRSE DTAMYYCARR PLYDGDYGYP MDYWGQGTSV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK STSGGTAALG CLVKDYFPEP V TVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV NHKPSNTKVD KKVEPKSCGS HHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #3: Legobody 8D3 Fab Light Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Legobody 8D3 Fab Light Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.095852 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: NIMLTQSPSS LAVSAGERVT MSCKSTQSIL YNSNQKTYLA WYQQKPGQSP KLLIYWASTR ASGVPDRFTG SGSGTDFTLT INSVQPEDL AVYYCHQYLS AWTFGGGTKL EIKRTVAAPS VFIFPPSDEQ LKSGTASVVC LLNNFYPREA KVQWKVDNAL Q SGNSQESV ...String: NIMLTQSPSS LAVSAGERVT MSCKSTQSIL YNSNQKTYLA WYQQKPGQSP KLLIYWASTR ASGVPDRFTG SGSGTDFTLT INSVQPEDL AVYYCHQYLS AWTFGGGTKL EIKRTVAAPS VFIFPPSDEQ LKSGTASVVC LLNNFYPREA KVQWKVDNAL Q SGNSQESV TEQDSKDSTY SLSSTLTLSK ADYEKHKVYA CEVTHQGLSS PVTKSFNRGE C |
-Macromolecule #4: Maltodextrin-binding protein,Immunoglobulin G-binding protein A,I...
| Macromolecule | Name: Maltodextrin-binding protein,Immunoglobulin G-binding protein A,Immunoglobulin G-binding protein G type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.233246 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKIEEGKLVI WINGDKGYNG LAEVGKKFEK DTGIKVTVEH PDKLEEKFPQ VAATGDGPDI IFWAHDRFGG YAQSGLLAEI TPDKAFQDK LYPFTWDAVR YNGKLIAYPI AVEALSLIYN KDLLPNPPKT WEEIPALDKE LKAKGKSALM FNLQEPYFTW P LIAADGGY ...String: MKIEEGKLVI WINGDKGYNG LAEVGKKFEK DTGIKVTVEH PDKLEEKFPQ VAATGDGPDI IFWAHDRFGG YAQSGLLAEI TPDKAFQDK LYPFTWDAVR YNGKLIAYPI AVEALSLIYN KDLLPNPPKT WEEIPALDKE LKAKGKSALM FNLQEPYFTW P LIAADGGY AFKYENGKYD IKDVGVDNAG AKAGLTFLVD LIKNKHMNAD TDYSIAEAAF NKGETAMTIN GPWAWSNIDT SK VNYGVTV LPTFKGQPSK PFVGVLSAGI NAASPNKELA KEFLENYLLT DEGLEAVNKD KPLGAVALKS YEEELAKDPR IAA TMENAQ KGEIMPNIPQ MSAFWYAVRT AVINAASGRQ TVDQALAFAQ ILIMPNLTEE QRNGFIQSLK DDPSVSKEIL AEAK KLNEH QAPKGGSGGA GSGDQQSAFY EILNMPNLNE AQRNGFIQSL KDDPSQSTNV LGEAKKLNES QAGGGSGGGS GGSAV TTYK LVINGKTLKG ETTTKAVDAE TAEKAFKQYA NDNGVDGVWT YDDATKTFTV TEGSGHHHHH H UniProtKB: Maltodextrin-binding protein, Immunoglobulin G-binding protein A, Immunoglobulin G-binding protein G |
-Macromolecule #5: Low-density lipoprotein receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Low-density lipoprotein receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 95.477023 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGPWGWKLRW TVALLLAAAG TAVGDRCERN EFQCQDGKCI SYKWVCDGSA ECQDGSDESQ ETCLSVTCKS GDFSCGGRVN RCIPQFWRC DGQVDCDNGS DEQGCPPKTC SQDEFRCHDG KCISRQFVCD SDRDCLDGSD EASCPVLTCG PASFQCNSST C IPQLWACD ...String: MGPWGWKLRW TVALLLAAAG TAVGDRCERN EFQCQDGKCI SYKWVCDGSA ECQDGSDESQ ETCLSVTCKS GDFSCGGRVN RCIPQFWRC DGQVDCDNGS DEQGCPPKTC SQDEFRCHDG KCISRQFVCD SDRDCLDGSD EASCPVLTCG PASFQCNSST C IPQLWACD NDPDCEDGSD EWPQRCRGLY VFQGDSSPCS AFEFHCLSGE CIHSSWRCDG GPDCKDKSDE ENCAVATCRP DE FQCSDGN CIHGSRQCDR EYDCKDMSDE VGCVNVTLCE GPNKFKCHSG ECITLDKVCN MARDCRDWSD EPIKECGTNE CLD NNGGCS HVCNDLKIGY ECLCPDGFQL VAQRRCEDID ECQDPDTCSQ LCVNLEGGYK CQCEEGFQLD PHTKACKAVG SIAY LFFTN RHEVRKMTLD RSEYTSLIPN LRNVVALDTE VASNRIYWSD LSQRMICSTQ LDRAHGVSSY DTVISRDIQA PDGLA VDWI HSNIYWTDSV LGTVSVADTK GVKRKTLFRE NGSKPRAIVV DPVHGFMYWT DWGTPAKIKK GGLNGVDIYS LVTENI QWP NGITLDLLSG RLYWVDSKLH SISSIDVNGG NRKTILEDEK RLAHPFSLAV FEDKVFWTDI INEAIFSANR LTGSDVN LL AENLLSPEDM VLFHNLTQPR GVNWCERTTL SNGGCQYLCL PAPQINPHSP KFTCACPDGM LLARDMRSCL TEAEAAVA T QETSTVRLKV SSTAVRTQHT TTRPVPDTSR LPGATPGLTT VEIVTMSHQA LGDVAGRGNE KKPSSVRALS IVLPIVLLV FLCLGVFLLW KNWRLKNINS INFDNPVYQK TTEDEVHICH NQDGYSYPSR QMVSLEDDVA UniProtKB: Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
-Macromolecule #6: ApoB100 nanobody 4
| Macromolecule | Name: ApoB100 nanobody 4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.322896 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QVQLQESGGG LVQAGGSLRL SCVASGYTDG AVNMGWFRQA PGKDRDWVAA ISPGGGLTYY ADSVKGRFTI SQDKAKNTVY LQMNSLKPE DTAIYYCAAA RSLAHFKLSQ YNYWGQGTQV TVSSLEHHHH HH |
-Macromolecule #8: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #9: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 9 / Number of copies: 7 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOCONTINUUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 51.38 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)