+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Molecular dissection of the glutamine synthetase-GlnR nitrogen regulatory circuitry in Gram-positive bacteria. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nat Commun, Vol. 13, Issue 1, Page 3793, Year 2022 |
| Publish date | Jul 1, 2022 |
 Authors Authors | Brady A Travis / Jared V Peck / Raul Salinas / Brandon Dopkins / Nicholas Lent / Viet D Nguyen / Mario J Borgnia / Richard G Brennan / Maria A Schumacher /  |
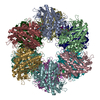
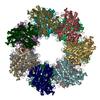
| PubMed Abstract | How bacteria sense and respond to nitrogen levels are central questions in microbial physiology. In Gram-positive bacteria, nitrogen homeostasis is controlled by an operon encoding glutamine ...How bacteria sense and respond to nitrogen levels are central questions in microbial physiology. In Gram-positive bacteria, nitrogen homeostasis is controlled by an operon encoding glutamine synthetase (GS), a dodecameric machine that assimilates ammonium into glutamine, and the GlnR repressor. GlnR detects nitrogen excess indirectly by binding glutamine-feedback-inhibited-GS (FBI-GS), which activates its transcription-repression function. The molecular mechanisms behind this regulatory circuitry, however, are unknown. Here we describe biochemical and structural analyses of GS and FBI-GS-GlnR complexes from pathogenic and non-pathogenic Gram-positive bacteria. The structures show FBI-GS binds the GlnR C-terminal domain within its active-site cavity, juxtaposing two GlnR monomers to form a DNA-binding-competent GlnR dimer. The FBI-GS-GlnR interaction stabilizes the inactive GS conformation. Strikingly, this interaction also favors a remarkable dodecamer to tetradecamer transition in some GS, breaking the paradigm that all bacterial GS are dodecamers. These data thus unveil unique structural mechanisms of transcription and enzymatic regulation. |
 External links External links |  Nat Commun / Nat Commun /  PubMed:35778410 / PubMed:35778410 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 1.96 - 3.5 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-25863, PDB-7tf6: EMDB-25864, PDB-7tf7: EMDB-25866, PDB-7tf9: EMDB-25867, PDB-7tfa: EMDB-25868, PDB-7tfb: EMDB-25869, PDB-7tfc: EMDB-25870, PDB-7tfd: EMDB-25871, PDB-7tfe: 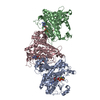 PDB-7tdp:  PDB-7tdv:  PDB-7tea: 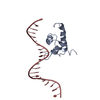 PDB-7tec: 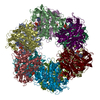 PDB-7ten: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-P3S:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-CA: 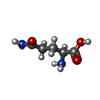 ChemComp-GLN: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / glutamate-ammonium ligase / GlnR / GS / feedback inhibition / transcription coregulator / glnRA / Glutamine synthetase / S. aureus / femC / DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / winged-HTH / transcription repressor / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex / listeria / repressor / transcription / LIGASE/INHIBITOR / glutamate ammonium ligase / Met-Sox / transition state / LIGASE-INHIBITOR complex / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / glutamine synthetase repressor dodecamer / glutamine synthetase dodecamer / glutamine synthetase repressor tetradecamer |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers