+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Inhibition of M. tuberculosis and human ATP synthase by BDQ and TBAJ-587. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Nature, Vol. 631, Issue 8020, Page 409-414, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Jul 3, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Yuying Zhang / Yuezheng Lai / Shan Zhou / Ting Ran / Yue Zhang / Ziqing Zhao / Ziyan Feng / Long Yu / Jinxu Xu / Kun Shi / Jianyun Wang / Yu Pang / Liang Li / Hongming Chen / Luke W Guddat / Yan Gao / Fengjiang Liu / Zihe Rao / Hongri Gong /   |
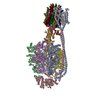
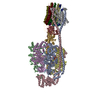
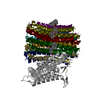
| PubMed Abstract | Bedaquiline (BDQ), a first-in-class diarylquinoline anti-tuberculosis drug, and its analogue, TBAJ-587, prevent the growth and proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by inhibiting ATP synthase. ...Bedaquiline (BDQ), a first-in-class diarylquinoline anti-tuberculosis drug, and its analogue, TBAJ-587, prevent the growth and proliferation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by inhibiting ATP synthase. However, BDQ also inhibits human ATP synthase. At present, how these compounds interact with either M. tuberculosis ATP synthase or human ATP synthase is unclear. Here we present cryogenic electron microscopy structures of M. tuberculosis ATP synthase with and without BDQ and TBAJ-587 bound, and human ATP synthase bound to BDQ. The two inhibitors interact with subunit a and the c-ring at the leading site, c-only sites and lagging site in M. tuberculosis ATP synthase, showing that BDQ and TBAJ-587 have similar modes of action. The quinolinyl and dimethylamino units of the compounds make extensive contacts with the protein. The structure of human ATP synthase in complex with BDQ reveals that the BDQ-binding site is similar to that observed for the leading site in M. tuberculosis ATP synthase, and that the quinolinyl unit also interacts extensively with the human enzyme. This study will improve researchers' understanding of the similarities and differences between human ATP synthase and M. tuberculosis ATP synthase in terms of the mode of BDQ binding, and will allow the rational design of novel diarylquinolines as anti-tuberculosis drugs. |
 External links External links |  Nature / Nature /  PubMed:38961288 PubMed:38961288 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.58 - 3.95 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-35909, PDB-8j0s: EMDB-35911, PDB-8j0t: EMDB-35982, PDB-8j57: EMDB-35983, PDB-8j58:  EMDB-36015: Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase Peripheral Stalk in the apo-form  EMDB-36017: Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase Peripheral Stalk in complex with bedaquiline(BDQ)  EMDB-36028: Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase F1 in the apo-form  EMDB-36031: Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase F1 in complex with bedaquiline(BDQ) EMDB-36589, PDB-8jr0: EMDB-36590, PDB-8jr1:  EMDB-36631: Cryo-EM structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase F1 in complex with TBAJ-587  EMDB-36632: Cryo-EM structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ATP synthase Peripheral Stalk in complex with TBAJ-587 EMDB-37243, PDB-8khf:  EMDB-37244: Structure of the human ATP synthase bound to bedaquiline  EMDB-37245: Structure of the human ATP synthase bound to bedaquiline (peripheral stalk domain) EMDB-37251, PDB-8ki3: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-ATP:  ChemComp-MG:  ChemComp-ADP:  ChemComp-BQ1: 
ChemComp-UTI: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ATP synthase / Mycobacterium tuberculosis / cryo-EM / Human |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers

















 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)