+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Biophysical investigation of type A PutAs reveals a conserved core oligomeric structure. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | FEBS J, Vol. 284, Issue 18, Page 3029-3049, Year 2017 |
| Publish date | Aug 1, 2017 |
 Authors Authors | David A Korasick / Harkewal Singh / Travis A Pemberton / Min Luo / Richa Dhatwalia / John J Tanner /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Many enzymes form homooligomers, yet the functional significance of self-association is seldom obvious. Herein, we examine the connection between oligomerization and catalytic function for proline ...Many enzymes form homooligomers, yet the functional significance of self-association is seldom obvious. Herein, we examine the connection between oligomerization and catalytic function for proline utilization A (PutA) enzymes. PutAs are bifunctional enzymes that catalyze both reactions of proline catabolism. Type A PutAs are the smallest members of the family, possessing a minimal domain architecture consisting of N-terminal proline dehydrogenase and C-terminal l-glutamate-γ-semialdehyde dehydrogenase modules. Type A PutAs form domain-swapped dimers, and in one case (Bradyrhizobium japonicum PutA), two of the dimers assemble into a ring-shaped tetramer. Whereas the dimer has a clear role in substrate channeling, the functional significance of the tetramer is unknown. To address this question, we performed structural studies of four-type A PutAs from two clades of the PutA tree. The crystal structure of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus PutA covalently inactivated by N-propargylglycine revealed a fold and substrate-channeling tunnel similar to other PutAs. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and analytical ultracentrifugation indicated that Bdellovibrio PutA is dimeric in solution, in contrast to the prediction from crystal packing of a stable tetrameric assembly. SAXS studies of two other type A PutAs from separate clades also suggested that the dimer predominates in solution. To assess whether the tetramer of B. japonicum PutA is necessary for catalytic function, a hot spot disruption mutant that cleanly produces dimeric protein was generated. The dimeric variant exhibited kinetic parameters similar to the wild-type enzyme. These results implicate the domain-swapped dimer as the core structural and functional unit of type A PutAs. ENZYMES: Proline dehydrogenase (EC 1.5.5.2); l-glutamate-γ-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.88). DATABASES: The atomic coordinates and structure factor amplitudes have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank under accession number 5UR2. The SAXS data have been deposited in the SASBDB under the following accession codes: SASDCP3 (BbPutA), SASDCQ3 (DvPutA 1.5 mg·mL ), SASDCX3 (DvPutA 3.0 mg·mL ), SASDCY3 (DvPutA 4.5 mg·mL ), SASDCR3 (LpPutA 3.0 mg·mL ), SASDCV3 (LpPutA 5.0 mg·mL ), SASDCW3 (LpPutA 8.0 mg·mL ), SASDCS3 (BjPutA 2.3 mg·mL ), SASDCT3 (BjPutA 4.7 mg·mL ), SASDCU3 (BjPutA 7.0 mg·mL ), SASDCZ3 (R51E 2.3 mg·mL ), SASDC24 (R51E 4.7 mg·mL ), SASDC34 (R51E 7.0 mg·mL ). |
 External links External links |  FEBS J / FEBS J /  PubMed:28710792 / PubMed:28710792 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | SAS (X-ray synchrotron) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.23 Å |
| Structure data | 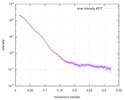 SASDC24: Proline utilization A from Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (formerly Bradyrhizobium japonicum) R51E mutant 4.7 mg/mL  SASDC34:  SASDCP3: 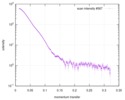 SASDCQ3: Proline utilization A from Desulfovibrio vulgaris 1.5 mg/mL 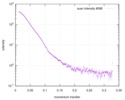 SASDCR3: Proline utilization A from Legionella pneumophila 3 mg/mL 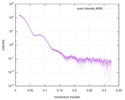 SASDCS3: Proline utilization A from Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (formerly Bradyrhizobium japonicum) 2.3 mg/mL 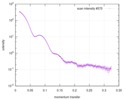 SASDCT3: Proline utilization A from Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (formerly Bradyrhizobium japonicum) 4.7 mg/mL  SASDCU3: 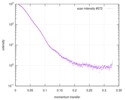 SASDCV3: Proline utilization A from Legionella pneumophila 5 mg/mL  SASDCW3:  SASDCX3: 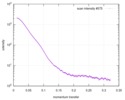 SASDCY3: Proline utilization A from Desulfovibrio vulgaris 4.5 mg/mL  SASDCZ3: Proline utilization A from Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (formerly Bradyrhizobium japonicum) R51E mutant 2.3 mg/mL  PDB-5ur2: |
| Chemicals | 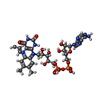 ChemComp-P5F:  ChemComp-HOH: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | OXIDOREDUCTASE / FLAVOENZYME / ROSSMANN FOLD / ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE / FLAVIN ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE / NICOTINAMIDE ADENINE DINUCLEOTIDE / PROLINE CATABOLISM / SUBSTRATE CHANNELING / BIFUNCTIONAL ENZYME / MECHANISM-BASED INACTIVATION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers



 Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (strain jcm 10833 / iam 13628 / nbrc 14792 / usda 110) (bacteria)
Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens (strain jcm 10833 / iam 13628 / nbrc 14792 / usda 110) (bacteria)