+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Science, Vol. 385, Issue 6705, Page 168-174, Year 2024 |
| Publish date | Jul 12, 2024 |
 Authors Authors | Claire E Coupland / Ryan Karimi / Stephanie A Bueler / Yingke Liang / Gautier M Courbon / Justin M Di Trani / Cassandra J Wong / Rayan Saghian / Ji-Young Youn / Lu-Yang Wang / John L Rubinstein /  |
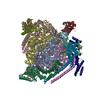
| PubMed Abstract | Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or ...Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) powers neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicles (SVs), with the V complex dissociating from the membrane region of the enzyme before exocytosis. We isolated SVs from rat brain using SidK, a V-ATPase-binding bacterial effector protein. Single-particle electron cryomicroscopy allowed high-resolution structure determination of V-ATPase within the native SV membrane. In the structure, regularly spaced cholesterol molecules decorate the enzyme's rotor and the abundant SV protein synaptophysin binds the complex stoichiometrically. ATP hydrolysis during vesicle loading results in a loss of the V region of V-ATPase from the SV membrane, suggesting that loading is sufficient to induce dissociation of the enzyme. |
 External links External links |  Science / Science /  PubMed:38900912 PubMed:38900912 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 3.2 - 3.9 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-44350, PDB-9b8o: EMDB-44351, PDB-9b8p: EMDB-44352, PDB-9b8q: EMDB-44353, PDB-9brd: EMDB-44354, PDB-9brc: EMDB-44355, PDB-9brb: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-PC1:  ChemComp-WJP:  ChemComp-NAG:  ChemComp-LP3:  ChemComp-PTY:  ChemComp-CLR:  ChemComp-ADP: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / Membrane / Synaptic / Complex / Mmebrane / Native / Vesicle |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About EMN Papers
About EMN Papers














 legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. philadelphia 1 (bacteria)
legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. philadelphia 1 (bacteria)