[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9b8o: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, Vo -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9b8o | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, Vo | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / Membrane / Synaptic / Complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation ...regulation of opioid receptor signaling pathway / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / negative regulation of autophagic cell death / Insulin receptor recycling / RHOA GTPase cycle / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / NURF complex / neuron spine / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / head morphogenesis / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / osteoclast development / neuron projection terminus / regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / vacuolar acidification / regulation of cellular pH / dendritic spine membrane / presynaptic active zone / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / syntaxin-1 binding / Neutrophil degranulation / cholesterol binding / response to amyloid-beta / ATPase activator activity / regulation of MAPK cascade / MLL1 complex / autophagosome membrane / excitatory synapse / cilium assembly / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / transporter activator activity / angiotensin maturation / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / axon terminus / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / SH2 domain binding / SNARE binding / neuromuscular junction / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / transmembrane transport / small GTPase binding / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / endocytosis / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / synaptic vesicle membrane / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / signaling receptor activity / presynapse / ATPase binding / presynaptic membrane / cell body / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / postsynaptic membrane / early endosome / lysosome / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / endosome / neuron projection / endosome membrane / postsynaptic density / cilium / apical plasma membrane / protein domain specific binding / axon / external side of plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / synapse / centrosome / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein-containing complex Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Coupland, C.E. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles. Authors: Claire E Coupland / Ryan Karimi / Stephanie A Bueler / Yingke Liang / Gautier M Courbon / Justin M Di Trani / Cassandra J Wong / Rayan Saghian / Ji-Young Youn / Lu-Yang Wang / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or ...Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) powers neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicles (SVs), with the V complex dissociating from the membrane region of the enzyme before exocytosis. We isolated SVs from rat brain using SidK, a V-ATPase-binding bacterial effector protein. Single-particle electron cryomicroscopy allowed high-resolution structure determination of V-ATPase within the native SV membrane. In the structure, regularly spaced cholesterol molecules decorate the enzyme's rotor and the abundant SV protein synaptophysin binds the complex stoichiometrically. ATP hydrolysis during vesicle loading results in a loss of the V region of V-ATPase from the SV membrane, suggesting that loading is sufficient to induce dissociation of the enzyme. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9b8o.cif.gz 9b8o.cif.gz | 633.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9b8o.ent.gz pdb9b8o.ent.gz | 506.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9b8o.json.gz 9b8o.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b8/9b8o https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b8/9b8o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b8/9b8o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b8/9b8o | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  44350MC 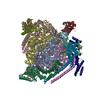 9b8pC  9b8qC  9brbC  9brcC  9brdC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 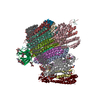
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules HUbfp
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28359.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 33331.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 21618.553 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 9502.132 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 39118.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-V-type proton ATPase ... , 6 types, 14 molecules PadeghijklmnoL
| #2: Protein | Mass: 51160.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 94950.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||
| #6: Protein | Mass: 40341.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9203.020 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||
| #9: Protein | Mass: 15815.833 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | | Mass: 13389.262 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Sugars , 3 types, 10 molecules 
| #12: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #13: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #16: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / | |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 46 molecules 






| #14: Chemical | ChemComp-PC1 / #15: Chemical | ChemComp-WJP / | #17: Chemical | ChemComp-LP3 / ( | #18: Chemical | ChemComp-PTY / #19: Chemical | ChemComp-CLR / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Synaptic vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, state 3, Vo Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1, #11, #3, #5-#6, #9-#10 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Grid type: Homemade |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 37.5 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: TFS FALCON 4i (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.21_5207 / Category: model refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 198533 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj