[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-44351: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Mmebrane / Synaptic / Complex / PROTON TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIon channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / Insulin receptor recycling / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels ...Ion channel transport / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / symbiont-mediated suppression of host phagosome acidification / Insulin receptor recycling / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / extrinsic component of synaptic vesicle membrane / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / protein localization to cilium / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar acidification / regulation of cellular pH / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Neutrophil degranulation / ATPase complex / microvillus / cilium assembly / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / ruffle / proton transmembrane transport / secretory granule / synaptic vesicle membrane / melanosome / ATPase binding / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / endosome / cilium / apical plasma membrane / centrosome / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. Philadelphia 1 (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. Philadelphia 1 (bacteria) | |||||||||
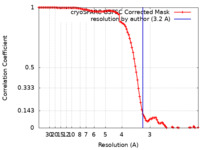
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Coupland EM / Rubinstein JL | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1 items Canada, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: High-resolution electron cryomicroscopy of V-ATPase in native synaptic vesicles. Authors: Claire E Coupland / Ryan Karimi / Stephanie A Bueler / Yingke Liang / Gautier M Courbon / Justin M Di Trani / Cassandra J Wong / Rayan Saghian / Ji-Young Youn / Lu-Yang Wang / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or ...Intercellular communication in the nervous system occurs through the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between neurons. In the presynaptic neuron, the proton pumping vesicular- or vacuolar-type ATPase (V-ATPase) powers neurotransmitter loading into synaptic vesicles (SVs), with the V complex dissociating from the membrane region of the enzyme before exocytosis. We isolated SVs from rat brain using SidK, a V-ATPase-binding bacterial effector protein. Single-particle electron cryomicroscopy allowed high-resolution structure determination of V-ATPase within the native SV membrane. In the structure, regularly spaced cholesterol molecules decorate the enzyme's rotor and the abundant SV protein synaptophysin binds the complex stoichiometrically. ATP hydrolysis during vesicle loading results in a loss of the V region of V-ATPase from the SV membrane, suggesting that loading is sufficient to induce dissociation of the enzyme. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_44351.map.gz emd_44351.map.gz | 97.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-44351-v30.xml emd-44351-v30.xml emd-44351.xml emd-44351.xml | 22.3 KB 22.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_44351_fsc.xml emd_44351_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_44351.png emd_44351.png | 39.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-44351.cif.gz emd-44351.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_44351_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44351_half_map_1.map.gz emd_44351_half_map_2.map.gz emd_44351_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.5 MB 95.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44351 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44351 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44351 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-44351 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 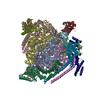 9b8pMC  9b8oC  9b8qC  9brbC  9brcC  9brdC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_44351.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_44351.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_44351_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
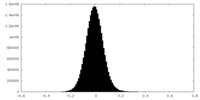
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_44351_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1
| Entire | Name: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1
| Supramolecule | Name: Synaptic Vesicle V-ATPase with synaptophysin and SidK, State 3, V1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#7 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase
| Macromolecule | Name: H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 71.483438 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCFKFKSDRA SGSGLGTDSA LRARAGKFST MDFSKLPKIR DEDKESTFGY VHGVSGPVVT ACDMAGAAMY ELVRVGHSEL VGEIIRLEG DMATIQVYEE TSGVSVGDPV LRTGKPLSVE LGPGIMGAIF DGIQRPLSDI SSQTQSIYIP RGVNVSALSR D IKWEFIPS ...String: MCFKFKSDRA SGSGLGTDSA LRARAGKFST MDFSKLPKIR DEDKESTFGY VHGVSGPVVT ACDMAGAAMY ELVRVGHSEL VGEIIRLEG DMATIQVYEE TSGVSVGDPV LRTGKPLSVE LGPGIMGAIF DGIQRPLSDI SSQTQSIYIP RGVNVSALSR D IKWEFIPS KNLRVGSHIT GGDIYGIVNE NSLIKHKIML PPRSRGSVTY IAPPGNYDAS DVVLELEFEG VKEKLSMVQV WP VRQVRPV TEKLPANHPL LTGQRVLDAL FPCVQGGTTA IPGAFGCGKT VISQSLSKYS NSDVIIYVGC GERGNEMSEV LRD FPELTM EVDGKVESIM KRTALVANTS NMPVAAREAS IYTGITLSEY FRDMGYHVSM MADSTSRWAE ALREISGRLA EMPA DSGYP AYLGARLASF YERAGRVKCL GNPEREGSVS IVGAVSPPGG DFSDPVTSAT LGIVQVFWGL DKKLAQRKHF PSVNW LISY SKYMRALDEY YDKHFTEFVP LRTKAKEILQ EEEDLAEIVQ LVGKASLAET DKITLEVAKL IKDDFLQQNG YTPYDR FCP FYKTVGMLSN MISFYDMARR AVETTAQSDN KITWSIIREH MGEILYKLSS MKFKDPVKDG EAKIKADYAQ LLEDMQN AF RSLED UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A |
-Macromolecule #2: V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 56.61157 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MALRAMRGIV NGAAPELPVP TGGPMAGARE QALAVSRNYL SQPRLTYKTV SGVNGPLVIL DHVKFPRYAE IVHLTLPDGT KRSGQVLEV SGSKAVVQVF EGTSGIDAKK TSCEFTGDIL RTPVSEDMLG RVFNGSGKPI DRGPVVLAED FLDIMGQPIN P QCRIYPEE ...String: MALRAMRGIV NGAAPELPVP TGGPMAGARE QALAVSRNYL SQPRLTYKTV SGVNGPLVIL DHVKFPRYAE IVHLTLPDGT KRSGQVLEV SGSKAVVQVF EGTSGIDAKK TSCEFTGDIL RTPVSEDMLG RVFNGSGKPI DRGPVVLAED FLDIMGQPIN P QCRIYPEE MIQTGISAID GMNSIARGQK IPIFSAAGLP HNEIAAQICR QAGLVKKSKD VVDYSEENFA IVFAAMGVNM ET ARFFKSD FEENGSMDNV CLFLNLANDP TIERIITPRL ALTTAEFLAY QCEKHVLVIL TDMSSYAEAL REVSAAREEV PGR RGFPGY MYTDLATIYE RAGRVEGRNG SITQIPILTM PNDDITHPIP DLTGYITEGQ IYVDRQLHNR QIYPPINVLP SLSR LMKSA IGEGMTRKDH ADVSNQLYAC YAIGKDVQAM KAVVGEEALT SDDLLYLEFL QKFEKNFITQ GPYENRTVYE TLDIG WQLL RIFPKEMLKR IPQSTLSEFY PRDSAKH UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit B, brain isoform |
-Macromolecule #3: ATPase H+-transporting V1 subunit D
| Macromolecule | Name: ATPase H+-transporting V1 subunit D / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 28.35902 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSGKDRIEIF PSRMAQTIMK ARLKGAQTGR NLLKKKSDAL TLRFRQILKK IIETKMLMGE VMREAAFSLA EAKFTAGDFS TTVIQNVNK AQVKIRAKKD NVAGVTLPVF EHYHEGTDSY ELTGLARGGE QLAKLKRNYA KAVELLVELA SLQTSFVTLD E AIKITNRR ...String: MSGKDRIEIF PSRMAQTIMK ARLKGAQTGR NLLKKKSDAL TLRFRQILKK IIETKMLMGE VMREAAFSLA EAKFTAGDFS TTVIQNVNK AQVKIRAKKD NVAGVTLPVF EHYHEGTDSY ELTGLARGGE QLAKLKRNYA KAVELLVELA SLQTSFVTLD E AIKITNRR VNAIEHVIIP RIERTLAYII TELDEREREE FYRLKKIQEK KKIIKEKSEK DLERRRAAGE VMEPANLLAE EK DEDLLFE UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit D |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.167453 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MALSDADVQK QIKHMMAFIE QEANEKAEEI DAKAEEEFNI EKGRLVQTQR LKIMEYYEKK EKQIEQQKKI QMSNLMNQAR LKVLRARDD LITDLLNEAK QRLSKVVKDT TRYQVLLDGL VLQGLYQLLE PRMIVRCRKQ DFPLVKAAVQ KAIPMYKIAT K KDVDVQID ...String: MALSDADVQK QIKHMMAFIE QEANEKAEEI DAKAEEEFNI EKGRLVQTQR LKIMEYYEKK EKQIEQQKKI QMSNLMNQAR LKVLRARDD LITDLLNEAK QRLSKVVKDT TRYQVLLDGL VLQGLYQLLE PRMIVRCRKQ DFPLVKAAVQ KAIPMYKIAT K KDVDVQID LEAYLPEDIA GGVEIYNGDR KIKVSNTLES RLDLIAQQMM PEVRGALFGA NANRKFLD UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit E 1 |
-Macromolecule #5: V-type proton ATPase subunit F
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit F / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.389262 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAGRGKLIAV IGDEDTVTGF LLGGIGELNK NRHPNFLVVE KDTTINEIED TFRQFLNRDD IGIILINQYI AEMVRHALDA HQRSIPAVL EIPSKEHPYD AAKDSILRRA KGMFTAEDLR UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit F |
-Macromolecule #6: V-type proton ATPase subunit G
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type proton ATPase subunit G / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.690476 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MASQSQGIQQ LLQAEKRAAE KVADARKRKA RRLKQAKEEA QMEVEQYRRE REQEFQSKQQ AAMGSQGNLS AEVEQATRRQ VQGMQSSQQ RNRERVLTQL LGMVCDVRPQ VHPNYRITV UniProtKB: V-type proton ATPase subunit G |
-Macromolecule #7: SidK
| Macromolecule | Name: SidK / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. Philadelphia 1 (bacteria) Legionella pneumophila subsp. pneumophila str. Philadelphia 1 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.505297 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSFIKVGIKM GGLTSEQYHS QVVGKIGYIA RCMQTIDPEN NLKKIREDYQ DVLIWAEKNY RFEEILEASK SGKCPNDLDA LSRRSLILQ ELLRLVSSIS PFKMKLDLIE SQYEKMKQHV NLWKSDYHVK LNQLNQLTDY LKNAAPTPKN NFLRAMTSVL Q MQIAQYGI ...String: MSFIKVGIKM GGLTSEQYHS QVVGKIGYIA RCMQTIDPEN NLKKIREDYQ DVLIWAEKNY RFEEILEASK SGKCPNDLDA LSRRSLILQ ELLRLVSSIS PFKMKLDLIE SQYEKMKQHV NLWKSDYHVK LNQLNQLTDY LKNAAPTPKN NFLRAMTSVL Q MQIAQYGI TEDNEGINQL FKLGLHLLAM ANEKIDEQYH LFKGYVKDQP EESPFEGILP AEDQKILVKT MIDYAMPKLS SK VLQDKLS ALSSSDVLTK TLLDSIDRIV KENEKLNALS KVKLGKFGLD IREIEVIYSQ ALKISPQDAL QYTAQQCDAQ LLS MAFPDS QNYIIESISN KKVKTIAELI HSKEFIYQII KTEVFKQVDP NEKIRLQAAT ELYQLLGRIM DKQINLFTKM NLEQ INEYI QTKTKAILDK IPERVELLTF MGFEIPTFKG IETLMTDISH SQDNETLAIA QEFYTNIKNA KNQLLGDKLI EDITP QDVE KFFNQCSQYG SEAAEKLADN RPVLTKIADI LTAIARWAIS LIGFNTPPQF LAPTRTCVDQ VSDEITKIKL KLEDTL GSL QKVQEESLSL UniProtKB: Type IV secretion protein Dot |
-Macromolecule #8: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: TFS FALCON 4i (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 37.5 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.9000000000000001 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)