+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-32046 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human KCNQ4-ML213 complex in digitonin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | KCNQ4 / ML213 / cryo-EM / digitonin / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationVoltage gated Potassium channels / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction ...Voltage gated Potassium channels / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / positive regulation of cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / protein phosphatase activator activity / : / adenylate cyclase binding / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / catalytic complex / potassium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / detection of calcium ion / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / : / titin binding / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / sperm midpiece / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / sarcomere / regulation of heart rate / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / basal plasma membrane / regulation of cytokinesis / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / spindle microtubule / sensory perception of sound / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / potassium ion transport / spindle pole / response to calcium ion / calcium-dependent protein binding / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / myelin sheath / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / vesicle / transmembrane transporter binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / centrosome / calcium ion binding / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu F / Zheng Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Neuron / Year: 2022 Journal: Neuron / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into the lipid and ligand regulation of a human neuronal KCNQ channel. Authors: You Zheng / Heng Liu / Yuxin Chen / Shaowei Dong / Fang Wang / Shengyi Wang / Geng-Lin Li / Yilai Shu / Fei Xu /  Abstract: The KCNQ family (KCNQ1-KCNQ5) of voltage-gated potassium channels plays critical roles in many physiological and pathological processes. It is known that the channel opening of all KCNQs relies on ...The KCNQ family (KCNQ1-KCNQ5) of voltage-gated potassium channels plays critical roles in many physiological and pathological processes. It is known that the channel opening of all KCNQs relies on the signaling lipid molecule phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). However, the molecular mechanism of PIP2 in modulating the opening of the four neuronal KCNQ channels (KCNQ2-KCNQ5), which are essential for regulating neuronal excitability, remains largely elusive. Here, we report the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human KCNQ4 determined in complex with the activator ML213 in the absence or presence of PIP2. Two PIP2 molecules are identified in the open-state structure of KCNQ4, which act as a bridge to couple the voltage-sensing domain (VSD) and pore domain (PD) of KCNQ4 leading to the channel opening. Our findings reveal the binding sites and activation mechanisms of ML213 and PIP2 for neuronal KCNQ channels, providing a framework for therapeutic intervention targeting on these important channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32046.map.gz emd_32046.map.gz | 62.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32046-v30.xml emd-32046-v30.xml emd-32046.xml emd-32046.xml | 12.4 KB 12.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_32046.png emd_32046.png | 75.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-32046.cif.gz emd-32046.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32046 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32046 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32046 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32046 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_32046_validation.pdf.gz emd_32046_validation.pdf.gz | 481.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_32046_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_32046_full_validation.pdf.gz | 481.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_32046_validation.xml.gz emd_32046_validation.xml.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_32046_validation.cif.gz emd_32046_validation.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32046 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32046 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32046 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-32046 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vnrMC  7vnpC  7vnqC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32046.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32046.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : KCNQ4-ML213 complex in digitonin
| Entire | Name: KCNQ4-ML213 complex in digitonin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: KCNQ4-ML213 complex in digitonin
| Supramolecule | Name: KCNQ4-ML213 complex in digitonin / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4,Maltodextr...
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4,Maltodextrin-binding protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: The fusion protein of Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4, linker, and Maltodextrin-binding protein Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 116.541383 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDYKDDDDKA EAPPRRLGLG PPPGDAPRAE LVALTAVQSE QGEAGGGGSP RRLGLLGSPL PPGAPLPGPG SGSGSACGQR SSAAHKRYR RLQNWVYNVL ERPRGWAFVY HVFIFLLVFS CLVLSVLSTI QEHQELANEC LLILEFVMIV VFGLEYIVRV W SAGCCCRY ...String: MDYKDDDDKA EAPPRRLGLG PPPGDAPRAE LVALTAVQSE QGEAGGGGSP RRLGLLGSPL PPGAPLPGPG SGSGSACGQR SSAAHKRYR RLQNWVYNVL ERPRGWAFVY HVFIFLLVFS CLVLSVLSTI QEHQELANEC LLILEFVMIV VFGLEYIVRV W SAGCCCRY RGWQGRFRFA RKPFCVIDFI VFVASVAVIA AGTQGNIFAT SALRSMRFLQ ILRMVRMDRR GGTWKLLGSV VY AHSKELI TAWYIGFLVL IFASFLVYLA EKDANSDFSS YADSLWWGTI TLTTIGYGDK TPHTWLGRVL AAGFALLGIS FFA LPAGIL GSGFALKVQE QHRQKHFEKR RMPAANLIQA AWRLYSTDMS RAYLTATWYY YDSILPSFRE LALLFEHVQR ARNG GLRPL EVRRAPVPDG APSRYPPVAT CHRPGSTSFC PGESSRMGIK DRIRMGSSQR RTGPSKQHLA PPTMPTSPSS EQVGE ATSP TKVQKSWSFN DRTRFRASLR LKPRTSAEDA PSEEVAEEKS YQCELTVDDI MPAVKTVIRS IRILKFLVAK RKFKET LRP YDVKDVIEQY SAGHLDMLGR IKSLQTRVDQ IVGRGPGDRK AREKGDKGPS DAEVVDEISM MGRVVKVEKQ VQSIEHK LD LLLGFYSRCL RSGTSALEVL FQGPMAKIEE GKLVIWINGD KGYNGLAEVG KKFEKDTGIK VTVEHPDKLE EKFPQVAA T GDGPDIIFWA HDRFGGYAQS GLLAEITPDK AFQDKLYPFT WDAVRYNGKL IAYPIAVEAL SLIYNKDLLP NPPKTWEEI PALDKELKAK GKSALMFNLQ EPYFTWPLIA ADGGYAFKYE NGKYDIKDVG VDNAGAKAGL TFLVDLIKNK HMNADTDYSI AEAAFNKGE TAMTINGPWA WSNIDTSKVN YGVTVLPTFK GQPSKPFVGV LSAGINAASP NKELAKEFLE NYLLTDEGLE A VNKDKPLG AVALKSYEEE LAKDPRIAAT MENAQKGEIM PNIPQMSAFW YAVRTAVINA ASGRQTVDEA LKDAQTNAAA EH HHHHHHH HH UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4, Maltodextrin-binding protein |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-3 |
-Macromolecule #3: (1S,2S,4R)-N-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxamid
| Macromolecule | Name: (1S,2S,4R)-N-(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2-carboxamid type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: 7YV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 257.371 Da |
| Chemical component information | 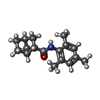 ChemComp-7YV: |
-Macromolecule #4: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.8 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 45 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 16.8 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 126225 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)