[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2722: Conformational Snapshots of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2722 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Conformational Snapshots of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Single-particle reconstruction of iNOS: Group I, Conformation v | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | heterogeneity / random conical tilt / nitric oxide synthase / calmodulin / heme / electron transfer / flavin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationNitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Peroxisomal protein import / prostaglandin secretion / tetrahydrobiopterin binding / arginine binding / peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation / superoxide metabolic process / cortical cytoskeleton / cellular response to cytokine stimulus ...Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Peroxisomal protein import / prostaglandin secretion / tetrahydrobiopterin binding / arginine binding / peptidyl-cysteine S-nitrosylation / superoxide metabolic process / cortical cytoskeleton / cellular response to cytokine stimulus / regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / Fc-gamma receptor signaling pathway involved in phagocytosis / : / nitric-oxide synthase (NADPH) / nitric-oxide synthase activity / arginine catabolic process / nitric oxide biosynthetic process / regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / response to bacterium / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / cellular response to type II interferon / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / circadian rhythm / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / FMN binding / peroxisome / NADP binding / flavin adenine dinucleotide binding / regulation of cell population proliferation / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / response to lipopolysaccharide / response to hypoxia / calmodulin binding / defense response to bacterium / inflammatory response / iron ion binding / negative regulation of gene expression / heme binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / protein homodimerization activity / metal ion binding / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 66.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Campbell MG / Smith BC / Potter CS / Carragher B / Marletta MA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2014Title: Molecular architecture of mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Authors: Melody G Campbell / Brian C Smith / Clinton S Potter / Bridget Carragher / Michael A Marletta /  Abstract: NOSs are homodimeric multidomain enzymes responsible for producing NO. In mammals, NO acts as an intercellular messenger in a variety of signaling reactions, as well as a cytotoxin in the innate ...NOSs are homodimeric multidomain enzymes responsible for producing NO. In mammals, NO acts as an intercellular messenger in a variety of signaling reactions, as well as a cytotoxin in the innate immune response. Mammals possess three NOS isoforms--inducible, endothelial, and neuronal NOS--that are composed of an N-terminal oxidase domain and a C-terminal reductase domain. Calmodulin (CaM) activates NO synthesis by binding to the helical region connecting these two domains. Although crystal structures of isolated domains have been reported, no structure is available for full-length NOS. We used high-throughput single-particle EM to obtain the structures and higher-order domain organization of all three NOS holoenzymes. The structures of inducible, endothelial, and neuronal NOS with and without CaM bound are similar, consisting of a dimerized oxidase domain flanked by two separated reductase domains. NOS isoforms adopt many conformations enabled by three flexible linkers. These conformations represent snapshots of the continuous electron transfer pathway from the reductase domain to the oxidase domain, which reveal that only a single reductase domain participates in electron transfer at a time, and that CaM activates NOS by constraining rotational motions and by directly binding to the oxidase domain. Direct visualization of these large conformational changes induced during electron transfer provides significant insight into the molecular underpinnings governing NO formation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2722.map.gz emd_2722.map.gz | 54.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2722-v30.xml emd-2722-v30.xml emd-2722.xml emd-2722.xml | 10 KB 10 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_2722.png emd_2722.png | 29.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2722 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2722 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2722 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2722 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_2722_validation.pdf.gz emd_2722_validation.pdf.gz | 198.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_2722_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_2722_full_validation.pdf.gz | 197.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_2722_validation.xml.gz emd_2722_validation.xml.gz | 7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-2722 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-2722 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-2722 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-2722 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2718C  2719C  2720C  2721C  2723C  2724C  2725C  2726C  2727C  2728C  2729C  2730C  2731C  2732C  2733C  2734C  2735C  2736C  2737C  2738C  2739C  2740C  2741C 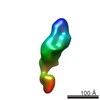 2742C  2743C 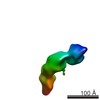 2744C  2745C 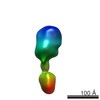 2746C  2747C  2748C  2749C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2722.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 162.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2722.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 162.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Single-particle reconstruction of iNOS: Group I, Conformation v | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.36 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Murine Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
| Entire | Name: Murine Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Murine Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
| Supramolecule | Name: Murine Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Details: Sample is highly flexible / Oligomeric state: Homodimer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 260 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase
| Macromolecule | Name: Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: iNOS / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Homodimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 260 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Nitric oxide synthase, inducible GO: nitric oxide biosynthetic process, FMN binding, NADP binding, calmodulin binding, flavin adenine dinucleotide binding, heme binding, iron ion binding, nitric-oxide synthase activity InterPro: Ser/Thr protein kinase, TGFB receptor |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 / Details: 50 mM TEA pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, and 5 mM DTT |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE Details: 3 microliters of sample were applied to grid. The specimen was stained twice with 2% uranyl formate, then allowed to air-dry. |
| Grid | Details: Glow discharged C-flat grid with 2-micron-diameter holes overlaid by thin 1.5 nm continuous carbon |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Date | Mar 6, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F416 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 2226 / Average electron dose: 37 e/Å2 Details: Each area is imaged twice: once at 55 degrees and again with no tilt. |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 114705 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 62000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: SIDE ENTRY, EUCENTRIC / Tilt angle max: 55 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | See publication. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each Image |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 66.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Appion, Spider / Details: See publication. / Number images used: 260 |
| Final two d classification | Number classes: 1 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






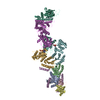
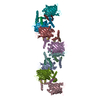


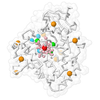
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















