+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ru2 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
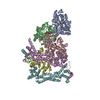
| Title | Structure of the F-actin barbed end bound by formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN /  actin / actin /  formin / Cdc12 / formin / Cdc12 /  profilin / profilin /  actin assembly actin assembly | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / MGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOB GTPase cycle / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOD GTPase cycle / RHOA GTPase cycle / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase ...negative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / MGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOB GTPase cycle / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOD GTPase cycle / RHOA GTPase cycle / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity / actin nucleation / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / neuron projection retraction / cellular response to cytochalasin B / DNA-methyltransferase activity / bBAF complex / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / npBAF complex / protein localization to microtubule / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization / regulation of transepithelial transport /  brahma complex / brahma complex /  nBAF complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / nBAF complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium /  profilin binding / cellular response to histamine / Formation of annular gap junctions / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein localization to adherens junction / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / Tat protein binding / DNA alkylation repair / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of double-strand break repair / profilin binding / cellular response to histamine / Formation of annular gap junctions / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein localization to adherens junction / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / Tat protein binding / DNA alkylation repair / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of double-strand break repair /  DNA ligation / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / regulation of microtubule-based process / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / DNA ligation / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / regulation of microtubule-based process / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol /  adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / axon midline choice point recognition / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / axon midline choice point recognition /  tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea /  SWI/SNF complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / SWI/SNF complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation /  NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / apical junction complex / regulation of cytoskeleton organization / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / apical junction complex / regulation of cytoskeleton organization / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance /  nitric-oxide synthase binding / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation / nitric-oxide synthase binding / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation /  brush border / brush border /  kinesin binding / kinesin binding /  calyx of Held / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / actin filament polymerization / Neutrophil degranulation / calyx of Held / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / actin filament polymerization / Neutrophil degranulation /  axonogenesis / negative regulation of protein binding / axonogenesis / negative regulation of protein binding /  actin filament / actin filament /  cell motility / cell motility /  methyltransferase activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / sensory perception of sound / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis methyltransferase activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / sensory perception of sound / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosisSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / ELECTRON MICROSCOPY /  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert, W. / Boiero Sanders, M. / Funk, J. / Prumbaum, D. / Raunser, S. / Bieling, P. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3items Germany, European Union, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular mechanism of actin filament elongation by formins. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Johanna Funk / Daniel Prumbaum / Stefan Raunser / Peter Bieling /  Abstract: Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action ...Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action remain unclear. In this work, we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin barbed ends bound by three distinct formins, revealing a common asymmetric formin conformation imposed by the filament. Formation of new intersubunit contacts during actin polymerization sterically displaces formin and triggers its translocation. This "undock-and-lock" mechanism explains how actin-filament growth is coordinated with formin movement. Filament elongation speeds are controlled by the positioning and stability of actin-formin interfaces, which distinguish fast and slow formins. Furthermore, we provide a structure of the actin-formin-profilin ring complex, which resolves how profilin is rapidly released from the barbed end during filament elongation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ru2.cif.gz 8ru2.cif.gz | 346.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ru2.ent.gz pdb8ru2.ent.gz | 271.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ru2.json.gz 8ru2.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/8ru2 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/8ru2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/8ru2 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ru/8ru2 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  19503MC  8rtyC  8ru0C  8rv2C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 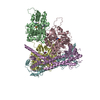
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein |  Mass: 41632.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Human beta-actin was recombinantly purified from BTI-Tnao38 cells. Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Plasmid: p2336 pFL_ACTB_C272A / Cell line (production host): BTI-Tnao38 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ACTB / Plasmid: p2336 pFL_ACTB_C272A / Cell line (production host): BTI-Tnao38 / Production host:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60709 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60709#2: Protein | Mass: 86469.258 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Has a N-terminal snap-tag. Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.) Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.)   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse)Gene: MGMT, Diaph1, Diap1 / Production host:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21 Star pRARE Escherichia coli (E. coli) / Strain (production host): BL21 Star pRAREReferences: UniProt: P16455, UniProt: O08808, methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase #3: Chemical |  Adenosine diphosphate Adenosine diphosphate#4: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  ELECTRON MICROSCOPY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method:  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied : NO / Vitrification applied : NO / Vitrification applied : YES : YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Details: 3 seconds, force 0. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS Details: 300 kV Titan Krios G2 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an in-column Cs-corrector. |
| Electron gun | Electron source : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs : 0.01 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm : 0.01 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 67.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 38913 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name : GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan energy filter. / Energyfilter slit width: 15 eV : GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan energy filter. / Energyfilter slit width: 15 eVSpherical aberration corrector  : Titan Krios G2 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an in-column Cs-corrector. : Titan Krios G2 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an in-column Cs-corrector. |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1963686 / Details: Particles picked using SPHIRE-crYOLO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry : C1 (asymmetric) : C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.49 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 150807 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: Refinement performed using phenix real-space refine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 115.26 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj





























