+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
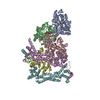
| Title | Structure of the F-actin barbed end bound by formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened cryo-EM density map of the F-actin barbed end bound by the formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  actin / actin /  formin / Cdc12 / formin / Cdc12 /  profilin / profilin /  actin assembly / actin assembly /  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / MGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOB GTPase cycle / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOD GTPase cycle / RHOA GTPase cycle / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase ...negative regulation of neuron projection regeneration / multicellular organismal locomotion / MGMT-mediated DNA damage reversal / RHOF GTPase cycle / RHOB GTPase cycle / ERBB2 Regulates Cell Motility / RHOC GTPase cycle / RHOD GTPase cycle / RHOA GTPase cycle / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase / methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase activity / actin nucleation / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / neuron projection retraction / cellular response to cytochalasin B / DNA-methyltransferase activity / bBAF complex / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / npBAF complex / protein localization to microtubule / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton organization / regulation of transepithelial transport /  brahma complex / brahma complex /  nBAF complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / nBAF complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium /  profilin binding / cellular response to histamine / Formation of annular gap junctions / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein localization to adherens junction / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / Tat protein binding / DNA alkylation repair / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of double-strand break repair / profilin binding / cellular response to histamine / Formation of annular gap junctions / GBAF complex / Gap junction degradation / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein localization to adherens junction / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / Tat protein binding / DNA alkylation repair / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / regulation of double-strand break repair /  DNA ligation / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / regulation of microtubule-based process / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / DNA ligation / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / regulation of microtubule-based process / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol /  adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / axon midline choice point recognition / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / axon midline choice point recognition /  tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea /  SWI/SNF complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / SWI/SNF complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / positive regulation of T cell differentiation /  NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / apical junction complex / regulation of cytoskeleton organization / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / apical junction complex / regulation of cytoskeleton organization / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance /  nitric-oxide synthase binding / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation / nitric-oxide synthase binding / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / negative regulation of cell differentiation /  brush border / brush border /  kinesin binding / kinesin binding /  calyx of Held / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / actin filament polymerization / Neutrophil degranulation / calyx of Held / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / actin filament polymerization / Neutrophil degranulation /  axonogenesis / negative regulation of protein binding / axonogenesis / negative regulation of protein binding /  actin filament / actin filament /  cell motility / cell motility /  methyltransferase activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / sensory perception of sound / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosis methyltransferase activity / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / positive regulation of cell differentiation / sensory perception of sound / FCGR3A-mediated phagocytosisSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.49 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert W / Boiero Sanders M / Funk J / Prumbaum D / Raunser S / Bieling P | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3 items Germany, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular mechanism of actin filament elongation by formins. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Johanna Funk / Daniel Prumbaum / Stefan Raunser / Peter Bieling /  Abstract: Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action ...Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action remain unclear. In this work, we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin barbed ends bound by three distinct formins, revealing a common asymmetric formin conformation imposed by the filament. Formation of new intersubunit contacts during actin polymerization sterically displaces formin and triggers its translocation. This "undock-and-lock" mechanism explains how actin-filament growth is coordinated with formin movement. Filament elongation speeds are controlled by the positioning and stability of actin-formin interfaces, which distinguish fast and slow formins. Furthermore, we provide a structure of the actin-formin-profilin ring complex, which resolves how profilin is rapidly released from the barbed end during filament elongation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19503.map.gz emd_19503.map.gz | 398.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19503-v30.xml emd-19503-v30.xml emd-19503.xml emd-19503.xml | 27.3 KB 27.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19503_fsc.xml emd_19503_fsc.xml | 15.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19503.png emd_19503.png | 95.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_19503_msk_1.map emd_19503_msk_1.map | 421.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19503.cif.gz emd-19503.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19503_additional_1.map.gz emd_19503_additional_1.map.gz emd_19503_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19503_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19503_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19503_half_map_2.map.gz | 209.9 MB 390.9 MB 390.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19503 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19503 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19503 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19503 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8ru2MC  8rtyC  8ru0C  8rv2C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19503.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19503.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened cryo-EM density map of the F-actin barbed end bound by the formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.88 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_19503_msk_1.map emd_19503_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
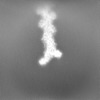
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
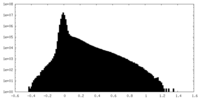
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of the F-actin...
| File | emd_19503_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of the F-actin barbed end bound by the formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
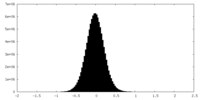
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 1 of the F-actin barbed...
| File | emd_19503_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 1 of the F-actin barbed end bound by the formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map 2 of the F-actin barbed...
| File | emd_19503_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map 2 of the F-actin barbed end bound by the formin mDia1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
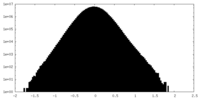
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : mDia1-bound F-actin barbed end.
| Entire | Name: mDia1-bound F-actin barbed end. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: mDia1-bound F-actin barbed end.
| Supramolecule | Name: mDia1-bound F-actin barbed end. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Human beta-actin and mouse mDia1 were purified separately. Both proteins were mixed to assemble the complex prior to cryo-EM grid preparation. |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Actin filament
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Mouse mDia1 (FH1FH2C domain)
| Supramolecule | Name: Mouse mDia1 (FH1FH2C domain) / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, cytoplasmic 1, N-terminally processed / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Human beta-actin was recombinantly purified from BTI-Tnao38 cells. Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.632422 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: DDDIAALVVD NGSGMCKAGF AGDDAPRAVF PSIVGRPRHQ GVMVGMGQKD SYVGDEAQSK RGILTLKYPI E(HIC)GIVT NWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGD GV THTVPIYEGY ...String: DDDIAALVVD NGSGMCKAGF AGDDAPRAVF PSIVGRPRHQ GVMVGMGQKD SYVGDEAQSK RGILTLKYPI E(HIC)GIVT NWD DMEKIWHHTF YNELRVAPEE HPVLLTEAPL NPKANREKMT QIMFETFNTP AMYVAIQAVL SLYASGRTTG IVMDSGD GV THTVPIYEGY ALPHAILRLD LAGRDLTDYL MKILTERGYS FTTTAEREIV RDIKEKLCYV ALDFEQEMAT AASSSSLE K SYELPDGQVI TIGNERFRCP EALFQPSFLG MESAGIHETT FNSIMKCDVD IRKDLYANTV LSGGTTMYPG IADRMQKEI TALAPSTMKI KIIAPPERKY SVWIGGSILA SLSTFQQMWI SKQEYDESGP SIVHRKCF UniProtKB:  Actin, cytoplasmic 1 Actin, cytoplasmic 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase,Protein diapha...
| Macromolecule | Name: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase,Protein diaphanous homolog 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: Has a N-terminal snap-tag. / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: methylated-DNA-[protein]-cysteine S-methyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Mus musculus (house mouse) Mus musculus (house mouse) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 86.469258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: MASTMDIKLT GEFAMDKDCE MKRTTLDSPL GKLELSGCEQ GLHEIKLLGK GTSAADAVEV PAPAAVLGGP EPLMQATAWL NAYFHQPEA IEEFPVPALH HPVFQQESFT RQVLWKLLKV VKFGEVISYQ QLAALAGNPA ATAAVKTALS GNPVPILIPC H RVVSSSGA ...String: MASTMDIKLT GEFAMDKDCE MKRTTLDSPL GKLELSGCEQ GLHEIKLLGK GTSAADAVEV PAPAAVLGGP EPLMQATAWL NAYFHQPEA IEEFPVPALH HPVFQQESFT RQVLWKLLKV VKFGEVISYQ QLAALAGNPA ATAAVKTALS GNPVPILIPC H RVVSSSGA VGGYEGGLAV KEWLLAHEGH RLGKPGLGPA GGSPGGGSGG SEMASLSAVV VAPSVSSSAA VPPAPPLPGD SG TVIPPPP PGMGVPPPPP FGFGVPAAPV LPFGLTPKKV YKPEVQLRRP NWSKFVAEDL SQDCFWTKVK EDRFENNELF AKL TLAFSA QTKTSKAKKD QEGGEEKKSV QKKKVKELKV LDSKTAQNLS IFLGSFRMPY QEIKNVILEV NEAVLTESMI QNLI KQMPE PEQLKMLSEL KEEYDDLAES EQFGVVMGTV PRLRPRLNAI LFKLQFSEQV ENIKPEIVSV TAACEELRKS ENFSS LLEL TLLVGNYMNA GSRNAGAFGF NISFLCKLRD TKSADQKMTL LHFLAELCEN DHPEVLKFPD ELAHVEKASR VSAENL QKS LDQMKKQIAD VERDVQNFPA ATDEKDKFVE KMTSFVKDAQ EQYNKLRMMH SNMETLYKEL GDYFVFDPKK LSVEEFF MD LHNFRNMFLQ AVKENQKRRE TEEKMRRAKL AKEKAEKERL EKQQKREQLI DMNAEGDETG VMDSLLEALQ SGAAFRRK R GPRQVNRKAG CAVTSLLASE LTKDDAMAPG PVKVPKKSEG VPTILEEAKE LVGRASHHHH HH UniProtKB: Methylated-DNA--protein-cysteine methyltransferase, Protein diaphanous homolog 1, Protein diaphanous homolog 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.1 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 90 sec. | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 3 seconds, force 0.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 0.01 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 0.01 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Specialist optics | Spherical aberration corrector: Titan Krios G2 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an in-column Cs-corrector. Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 15 eV / Details: Gatan energy filter. |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Details | 300 kV Titan Krios G2 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with an in-column Cs-corrector. |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 38913 / Average electron dose: 67.6 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Refinement performed using phenix real-space refine | |||||||||
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | |||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-8ru2: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

































 Z
Z Y
Y X
X