[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-19522: Structure of the formin INF2 bound to the barbed end of F-actin. -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
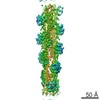
| Title | Structure of the formin INF2 bound to the barbed end of F-actin. | ||||||||||||
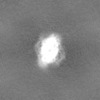
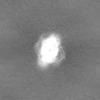
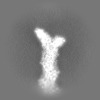
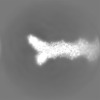
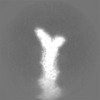
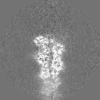
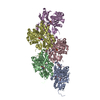
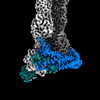
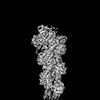
 Map data Map data | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of the formin INF2 bound to the barbed end of actin filaments. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords |  actin / actin /  formin / INF2 / actin end / barbed end / formin / INF2 / actin end / barbed end /  STRUCTURAL PROTEIN STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity /  regulation of mitochondrial fission / regulation of mitochondrial fission /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity /  regulation of mitochondrial fission / regulation of mitochondrial fission /  tropomyosin binding / tropomyosin binding /  myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration / myosin heavy chain binding / mesenchyme migration /  troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / troponin I binding / actin filament bundle / filamentous actin / actin filament bundle assembly / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development /  stress fiber / stress fiber /  titin binding / actin filament polymerization / titin binding / actin filament polymerization /  filopodium / filopodium /  actin filament / actin filament /  Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement /  small GTPase binding / calcium-dependent protein binding / small GTPase binding / calcium-dependent protein binding /  lamellipodium / lamellipodium /  cell body / cell body /  actin binding / actin binding /  hydrolase activity / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / protein domain specific binding /  calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / magnesium ion binding / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / magnesium ion binding /  ATP binding / identical protein binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding /  cytoplasm cytoplasmSimilarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) /   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
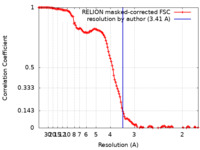
| Method |  single particle reconstruction / single particle reconstruction /  cryo EM / Resolution: 3.41 Å cryo EM / Resolution: 3.41 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Oosterheert W / Boiero Sanders M / Funk J / Prumbaum D / Raunser S / Bieling P | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3 items Germany, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2024 Journal: Science / Year: 2024Title: Molecular mechanism of actin filament elongation by formins. Authors: Wout Oosterheert / Micaela Boiero Sanders / Johanna Funk / Daniel Prumbaum / Stefan Raunser / Peter Bieling /  Abstract: Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action ...Formins control the assembly of actin filaments (F-actin) that drive cell morphogenesis and motility in eukaryotes. However, their molecular interaction with F-actin and their mechanism of action remain unclear. In this work, we present high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of F-actin barbed ends bound by three distinct formins, revealing a common asymmetric formin conformation imposed by the filament. Formation of new intersubunit contacts during actin polymerization sterically displaces formin and triggers its translocation. This "undock-and-lock" mechanism explains how actin-filament growth is coordinated with formin movement. Filament elongation speeds are controlled by the positioning and stability of actin-formin interfaces, which distinguish fast and slow formins. Furthermore, we provide a structure of the actin-formin-profilin ring complex, which resolves how profilin is rapidly released from the barbed end during filament elongation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_19522.map.gz emd_19522.map.gz | 106.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-19522-v30.xml emd-19522-v30.xml emd-19522.xml emd-19522.xml | 40.2 KB 40.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
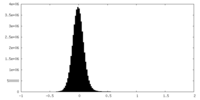
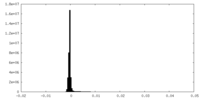
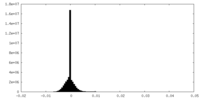
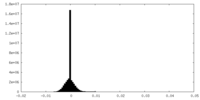
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_19522_fsc.xml emd_19522_fsc.xml | 12.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_19522.png emd_19522.png | 94.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_19522_msk_1.map emd_19522_msk_1.map emd_19522_msk_2.map emd_19522_msk_2.map | 178 MB 178 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-19522.cif.gz emd-19522.cif.gz | 8.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_19522_additional_1.map.gz emd_19522_additional_1.map.gz emd_19522_additional_2.map.gz emd_19522_additional_2.map.gz emd_19522_additional_3.map.gz emd_19522_additional_3.map.gz emd_19522_additional_4.map.gz emd_19522_additional_4.map.gz emd_19522_additional_5.map.gz emd_19522_additional_5.map.gz emd_19522_additional_6.map.gz emd_19522_additional_6.map.gz emd_19522_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19522_half_map_1.map.gz emd_19522_half_map_2.map.gz emd_19522_half_map_2.map.gz | 88.9 MB 165.3 MB 165.3 MB 140.4 MB 168.2 MB 105.4 MB 141.2 MB 141.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19522 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19522 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19522 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-19522 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8rv2MC  8rtyC  8ru0C  8ru2C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_19522.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_19522.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened, local-resolution filtered cryo-EM density map of the formin INF2 bound to the barbed end of actin filaments. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.9 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
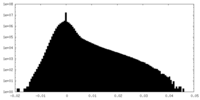
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
+Mask #1
+Mask #2
+Additional map: 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of INF2 bound...
+Additional map: Unfiltered half map 1 of the formin INF2...
+Additional map: Unfiltered half map 2 of the formin INF2...
+Additional map: 3D-refined, unsharpened cryo-EM density map of the formin...
+Additional map: Sharpened cryo-EM density map of the formin INF2...
+Additional map: Composite map computed with the main map of...
+Half map: Unfiltered half map 1 of the formin INF2...
+Half map: Unfiltered half map 2 of the formin INF2...
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of the formin INF2 dimer that binds to the actin subunits...
| Entire | Name: Complex of the formin INF2 dimer that binds to the actin subunits at the barbed end of actin filaments. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of the formin INF2 dimer that binds to the actin subunits...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of the formin INF2 dimer that binds to the actin subunits at the barbed end of actin filaments. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Alpha actin was purified from rabbit skeletal muscle. INF2 was purified from E. coli. Actin filaments were co-polymerized in the presence of the formin INF2 prior to cryo-EM grid preparation. |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Actin filament barbed end
| Supramolecule | Name: Actin filament barbed end / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: Complex of the actin subunits that form the barbed end of actin filaments. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Tissue: Skeletal muscle Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Tissue: Skeletal muscle |
-Supramolecule #3: INF2 dimer
| Supramolecule | Name: INF2 dimer / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 Details: This dimer is composed of the FH2 domain of the formin INF2. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Rabbit skeletal alpha actin purified from frozen rabbit muscle acetone powder. Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Tissue: Skeletal muscle Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) / Tissue: Skeletal muscle |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.875633 KDa |
| Sequence | String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GII TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSG DG VTHNVPIYEG ...String: DEDETTALVC DNGSGLVKAG FAGDDAPRAV FPSIVGRPRH QGVMVGMGQK DSYVGDEAQS KRGILTLKYP IE(HIC)GII TNW DDMEKIWHHT FYNELRVAPE EHPTLLTEAP LNPKANREKM TQIMFETFNV PAMYVAIQAV LSLYASGRTT GIVLDSG DG VTHNVPIYEG YALPHAIMRL DLAGRDLTDY LMKILTERGY SFVTTAEREI VRDIKEKLCY VALDFENEMA TAASSSSL E KSYELPDGQV ITIGNERFRC PETLFQPSFI GMESAGIHET TYNSIMKCDI DIRKDLYANN VMSGGTTMYP GIADRMQKE ITALAPSTMK IKIIAPPERK YSVWIGGSIL ASLSTFQQMW ITKQEYDEAG PSIVHRKCF UniProtKB:  Actin, alpha skeletal muscle Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #2: Isoform 2 of Inverted formin-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Isoform 2 of Inverted formin-2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: INF2 FH1FH2C nonCAAX isoform was recombinantly expressed in E. coli BL21 Star pRARE cells and purified. This compound consists of the formin homology 1 and 2 domains, as well as the C- ...Details: INF2 FH1FH2C nonCAAX isoform was recombinantly expressed in E. coli BL21 Star pRARE cells and purified. This compound consists of the formin homology 1 and 2 domains, as well as the C-terminal region of the human formin INF2 isoform nonCAAX. Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 84.453711 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:   Escherichia coli (E. coli) Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Sequence | String: GGGGGMAPPA PPLPPPLPGS CEFLSPPPPP LPGLGCPPPP PPLLPGMGWG PPPPPPPLLP CTCSPPVAGG MEEVIVAQVD HGLGSAWVP SHRRVNPPTL RMKKLNWQKL PSNVAREHNS MWASLSSPDA EAVEPDFSSI ERLFSFPAAK PKEPTMVAPR A RKEPKEIT ...String: GGGGGMAPPA PPLPPPLPGS CEFLSPPPPP LPGLGCPPPP PPLLPGMGWG PPPPPPPLLP CTCSPPVAGG MEEVIVAQVD HGLGSAWVP SHRRVNPPTL RMKKLNWQKL PSNVAREHNS MWASLSSPDA EAVEPDFSSI ERLFSFPAAK PKEPTMVAPR A RKEPKEIT FLDAKKSLNL NIFLKQFKCS NEEVAAMIRA GDTTKFDVEV LKQLLKLLPE KHEIENLRAF TEERAKLASA DH FYLLLLA IPCYQLRIEC MLLCEGAAAV LDMVRPKAQL VLAACESLLT SRQLPIFCQL ILRIGNFLNY GSHTGDADGF KIS TLLKLT ETKSQQNRVT LLHHVLEEAE KSHPDLLQLP RDLEQPSQAA GINLEIIRSE ASSNLKKLLE TERKVSASVA EVQE QYTER LQASISAFRA LDELFEAIEQ KQRELADYLC EDAQQLSLED TFSTMKAFRD LFLRALKENK DRKEQAAKAE RRKQQ LAEE EARRPRGEDG KPVRKGPGKQ EEVCVIDALL ADIRKGFQLR KTARGRGDTD GGSKAASMDP PRATEPVATS NPAGDP VGS TRCPASEPGL DATTASESRG WDLVDAVTPG PQPTLEQLEE GGPRPLERRS SWYVDASDVL TTEDPQCPQP LEGAWPV TL GDAQALKPLK FSSNQPPAAG SSRQDAKDPT SLLGVLQAEA DSTSEGLEDA VHSRGARPPA AGPGGDEDED EEDTAPES A LDTSLDKSFS EDAVTDSSGS GTLPRARGRA SKGTGKRRKK RPSRSQEGLR PRPKAK UniProtKB: Inverted formin-2 |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: PHOSPHATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 94.971 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PO4: |
-Macromolecule #6: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method |  cryo EM cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing |  single particle reconstruction single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.1 Component:
Details: 12 mM HEPES pH 7.1, 100 mM KCl, 2.1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM TCEP, 0.2 mM ATP | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 90 sec. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: 3 seconds, force 0.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 Bright-field microscopy / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.9 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Specialist optics | Spherical aberration corrector: 300 kV Titan Krios G3 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 15 eV / Details: Gatan energy filter. |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Details | 300 kV Titan Krios G3 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific). |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 20305 / Average electron dose: 60.6 e/Å2 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Real Space Refinement in Phenix. | |||||||||
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT | |||||||||
| Output model |  PDB-8rv2: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 Z
Z Y
Y X
X