7A0O
 
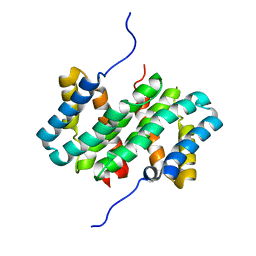 | | NMR structure of flagelliform spidroin (FlagSp) N-terminal domain from Trichonephila clavipes at pH 5.5 | | Descriptor: | Flagelliform spidroin variant 1 | | Authors: | Sarr, M, Kitoka, K, Walsh-White, K.-A, Kaldmae, M, Landreh, M, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Jaudzems, K, Kronqvist, N. | | Deposit date: | 2020-08-10 | | Release date: | 2021-08-18 | | Last modified: | 2024-06-19 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | The dimerization mechanism of the N-terminal domain of spider silk proteins is conserved despite extensive sequence divergence.
J.Biol.Chem., 298, 2022
|
|
7A0I
 
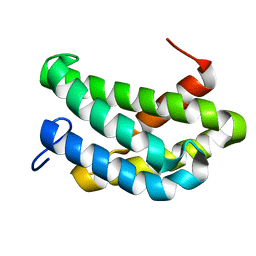 | | NMR structure of flagelliform spidroin (FlagSp) N-terminal domain from Trichonephila clavipes at pH 7.2 | | Descriptor: | Flagelliform spidroin variant 1 | | Authors: | Sarr, M, Kitoka, K, Walsh-White, K.-A, Kaldmae, M, Landreh, M, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Jaudzems, K, Kronqvist, N. | | Deposit date: | 2020-08-09 | | Release date: | 2021-08-18 | | Last modified: | 2024-06-19 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | The dimerization mechanism of the N-terminal domain of spider silk proteins is conserved despite extensive sequence divergence.
J.Biol.Chem., 298, 2022
|
|
4FBS
 
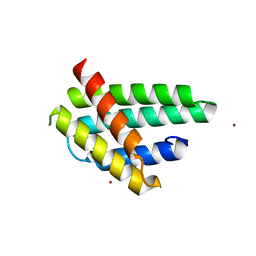 | | Structure of monomeric NT from Euprosthenops australis Major Ampullate Spidroin 1 (MaSp1) | | Descriptor: | BROMIDE ION, Major ampullate spidroin 1 | | Authors: | Askarieh, G, Hedhammar, M, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Knight, S.D. | | Deposit date: | 2012-05-23 | | Release date: | 2012-08-01 | | Last modified: | 2024-04-03 | | Method: | X-RAY DIFFRACTION (1.7 Å) | | Cite: | pH-Dependent Dimerization of Spider Silk N-Terminal Domain Requires Relocation of a Wedged Tryptophan Side Chain
J.Mol.Biol., 2012
|
|
5NDA
 
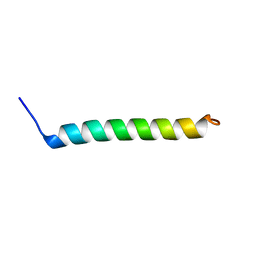 | | NMR Structural Characterisation of Pharmaceutically Relevant Proteins Obtained Through a Novel Recombinant Production: The Case of The Pulmonary Surfactant Polypeptide C Analogue rSP-C33Leu. | | Descriptor: | rSP-C33Leu -RECOMBINANT PULMONARY SURFACTANT-ASSOCIATED POLYPEPTIDE C ANALOGUE- | | Authors: | Venturi, L, Pioselli, B, Johansson, J, Rising, A, Kronqvist, N, Nordling, K. | | Deposit date: | 2017-03-08 | | Release date: | 2017-06-07 | | Last modified: | 2024-06-19 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | Efficient protein production inspired by how spiders make silk.
Nat Commun, 8, 2017
|
|
3LR2
 
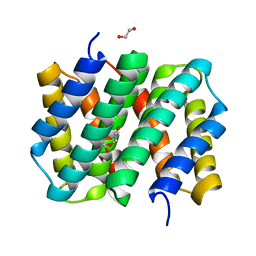 | | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay | | Descriptor: | 1,2-ETHANEDIOL, DI(HYDROXYETHYL)ETHER, Major ampullate spidroin 1 | | Authors: | Askarieh, G, Hedhammar, H, Nordling, K, Johansson, J, Knight, S.D, Rising, A, Casals, C, Saenz, A. | | Deposit date: | 2010-02-10 | | Release date: | 2010-05-12 | | Last modified: | 2024-02-21 | | Method: | X-RAY DIFFRACTION (1.7 Å) | | Cite: | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay.
Nature, 465, 2010
|
|
3LR6
 
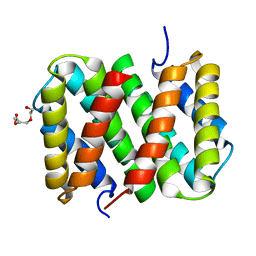 | | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay | | Descriptor: | Major ampullate spidroin 1, TRIETHYLENE GLYCOL | | Authors: | Askarieh, G, Hedhammar, H, Nordling, K, Saenz, A, Casals, C, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Knight, S.D. | | Deposit date: | 2010-02-10 | | Release date: | 2010-05-12 | | Last modified: | 2024-02-21 | | Method: | X-RAY DIFFRACTION (2.2 Å) | | Cite: | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay.
Nature, 465, 2010
|
|
3LRD
 
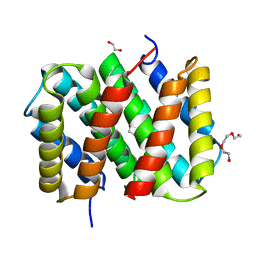 | | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay | | Descriptor: | 1,2-ETHANEDIOL, Major ampullate spidroin 1, TRIETHYLENE GLYCOL | | Authors: | Askarieh, G, Hedhammar, H, Nordling, K, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Knight, S.D, Saenz, A, Casals, C. | | Deposit date: | 2010-02-11 | | Release date: | 2010-05-12 | | Last modified: | 2024-04-03 | | Method: | X-RAY DIFFRACTION (2.15 Å) | | Cite: | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay.
Nature, 465, 2010
|
|
3LR8
 
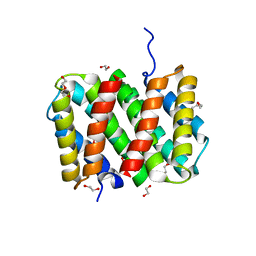 | | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay | | Descriptor: | 1,2-ETHANEDIOL, DI(HYDROXYETHYL)ETHER, Major ampullate spidroin 1, ... | | Authors: | Askarieh, G, Hedhammar, H, Nordling, K, Rising, A, Johansson, J, Knight, S.D. | | Deposit date: | 2010-02-10 | | Release date: | 2010-05-12 | | Last modified: | 2024-04-03 | | Method: | X-RAY DIFFRACTION (2.3 Å) | | Cite: | Self-assembly of spider silk proteins is controlled by a pH-sensitive relay.
Nature, 465, 2010
|
|
2MX9
 
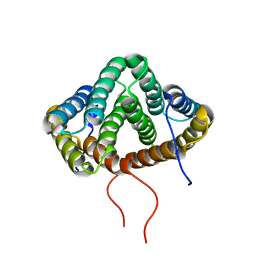 | | NMR structure of N-terminal domain from A. ventricosus minor ampullate spidroin (MiSp) at pH 5.5 | | Descriptor: | Minor ampullate spidroin | | Authors: | Otikovs, M, Jaudzems, K, Chen, G, Nordling, K, Rising, A, Johansson, J. | | Deposit date: | 2014-12-17 | | Release date: | 2015-08-19 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | Diversified Structural Basis of a Conserved Molecular Mechanism for pH-Dependent Dimerization in Spider Silk N-Terminal Domains.
Chembiochem, 16, 2015
|
|
2MX8
 
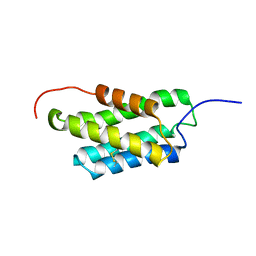 | | NMR structure of N-terminal domain from A. ventricosus minor ampullate spidroin (MiSp) at pH 7.2 | | Descriptor: | Minor ampullate spidroin | | Authors: | Otikovs, M, Jaudzems, K, Chen, G, Nordling, K, Rising, A, Johansson, J. | | Deposit date: | 2014-12-17 | | Release date: | 2015-08-19 | | Last modified: | 2024-10-09 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | Diversified Structural Basis of a Conserved Molecular Mechanism for pH-Dependent Dimerization in Spider Silk N-Terminal Domains.
Chembiochem, 16, 2015
|
|
2MFZ
 
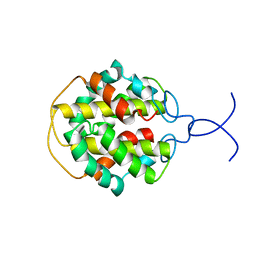 | | NMR structure of C-terminal domain from A. ventricosus minor ampullate spidroin (MiSp) | | Descriptor: | Minor ampullate spidroin | | Authors: | Otikovs, M, Jaudzems, K, Andersson, M, Chen, G, Landreh, M, Nordling, K, Kronqvist, N, Westermark, P, Jornvall, H, Knight, S, Ridderstrale, Y, Holm, L, Meng, Q, Chesler, M, Johansson, J, Rising, A. | | Deposit date: | 2013-10-24 | | Release date: | 2014-08-20 | | Last modified: | 2024-05-01 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | Carbonic Anhydrase Generates CO2 and H+ That Drive Spider Silk Formation Via Opposite Effects on the Terminal Domains
Plos Biol., 12, 2014
|
|
2LPI
 
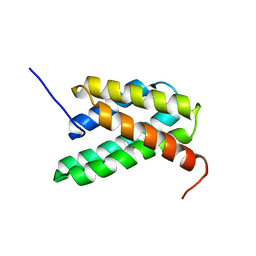 | | NMR structure of a monomeric mutant (A72R) of major ampullate spidroin 1 N-terminal domain | | Descriptor: | Major ampullate spidroin 1 | | Authors: | Jaudzems, K, Nordling, K, Landreh, M, Rising, A, Askarieh, G, Knight, S.D, Johansson, J. | | Deposit date: | 2012-02-14 | | Release date: | 2012-06-27 | | Last modified: | 2024-05-15 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | pH-Dependent Dimerization of Spider Silk N-Terminal Domain Requires Relocation of a Wedged Tryptophan Side Chain.
J.Mol.Biol., 422, 2012
|
|
2LTH
 
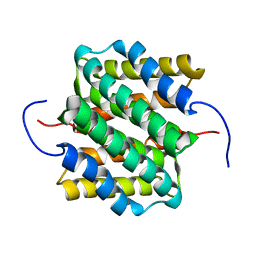 | | NMR structure of major ampullate spidroin 1 N-terminal domain at pH 5.5 | | Descriptor: | Major ampullate spidroin 1 | | Authors: | Otikovs, M, Jaudzems, K, Nordling, K, Landreh, M, Rising, A, Askarieh, G, Knight, S, Johansson, J. | | Deposit date: | 2012-05-25 | | Release date: | 2013-11-27 | | Last modified: | 2024-05-15 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | Sequential pH-driven dimerization and stabilization of the N-terminal domain enables rapid spider silk formation.
Nat Commun, 5, 2014
|
|
2LPJ
 
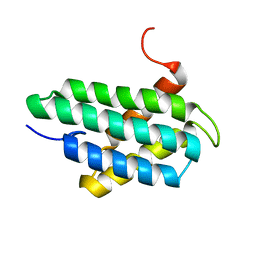 | | NMR structure of major ampullate spidroin 1 N-terminal domain at pH 7.2 | | Descriptor: | Major ampullate spidroin 1 | | Authors: | Jaudzems, K, Nordling, K, Landreh, M, Rising, A, Askarieh, G, Knight, S.D, Johansson, J. | | Deposit date: | 2012-02-14 | | Release date: | 2012-06-27 | | Last modified: | 2024-05-15 | | Method: | SOLUTION NMR | | Cite: | pH-Dependent Dimerization of Spider Silk N-Terminal Domain Requires Relocation of a Wedged Tryptophan Side Chain.
J.Mol.Biol., 422, 2012
|
|
