+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3uro | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
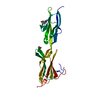
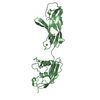
| Title | Poliovirus receptor CD155 D1D2 | |||||||||
 Components Components | Poliovirus receptor | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / poliovirus receptor ectodomain / Immunoglobulin Super Family / Cell adhesion / Cell membrane / Glycoprotein / Host-virus interaction / Immunoglobulin domain / Membrane / Receptor / Secreted / Transmembrane | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsusceptibility to T cell mediated cytotoxicity / susceptibility to natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / Nectin/Necl trans heterodimerization / positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / heterophilic cell-cell adhesion / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / homophilic cell-cell adhesion / cell adhesion molecule binding ...susceptibility to T cell mediated cytotoxicity / susceptibility to natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / Nectin/Necl trans heterodimerization / positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity directed against tumor cell target / positive regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / negative regulation of natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / heterophilic cell-cell adhesion / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / homophilic cell-cell adhesion / cell adhesion molecule binding / adherens junction / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / signaling receptor activity / virus receptor activity / receptor ligand activity / focal adhesion / cell surface / extracellular space / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  SIRAS / Resolution: 3.5005 Å SIRAS / Resolution: 3.5005 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, P. / Mueller, S. / Morais, M.C. / Bator, C.M. / Bowman, V.D. / Hafenstein, S. / Wimmer, E. / Rossmann, M.G. | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2008 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2008Title: Crystal structure of CD155 and electron microscopic studies of its complexes with polioviruses. Authors: Ping Zhang / Steffen Mueller / Marc C Morais / Carol M Bator / Valorie D Bowman / Susan Hafenstein / Eckard Wimmer / Michael G Rossmann /  Abstract: When poliovirus (PV) recognizes its receptor, CD155, the virus changes from a 160S to a 135S particle before releasing its genome into the cytoplasm. CD155 is a transmembrane protein with 3 Ig-like ...When poliovirus (PV) recognizes its receptor, CD155, the virus changes from a 160S to a 135S particle before releasing its genome into the cytoplasm. CD155 is a transmembrane protein with 3 Ig-like extracellular domains, D1-D3, where D1 is recognized by the virus. The crystal structure of D1D2 has been determined to 3.5-A resolution and fitted into approximately 8.5-A resolution cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of the virus-receptor complexes for the 3 PV serotypes. These structures show that, compared with human rhinoviruses, the virus-receptor interactions for PVs have a greater dependence on hydrophobic interactions, as might be required for a virus that can inhabit environments of different pH. The pocket factor was shown to remain in the virus during the first recognition stage. The present structures, when combined with earlier mutational investigations, show that in the subsequent entry stage the receptor moves further into the canyon when at a physiological temperature, thereby expelling the pocket factor and separating the viral subunits to form 135S particles. These results provide a detailed analysis of how a nonenveloped virus can enter its host cell. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3uro.cif.gz 3uro.cif.gz | 55.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3uro.ent.gz pdb3uro.ent.gz | 39.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3uro.json.gz 3uro.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/3uro https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/3uro ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/3uro ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ur/3uro | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1562C  1563C  1570C  3epcC  3epdC  3epfC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24355.645 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Fragment: poliovirus receptor CD155 D1D2 (UNP Residues 29-243) Mutation: N105D, N120S, N188Q, N218Q, N237S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PVR, PVS / Cell line (production host): HEK 293 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PVR, PVS / Cell line (production host): HEK 293 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P15151 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P15151 |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 3 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 3 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 4.28 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 71.23 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 8.5 Details: 100 mM MgSO4, 6.8 M NH4NO3, 100 mM Tris buffer, pH 8.5, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 298K |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 23-ID-D / Wavelength: 1.07 Å / Beamline: 23-ID-D / Wavelength: 1.07 Å |
| Detector | Type: KODAK / Detector: CCD / Date: Feb 23, 2007 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.07 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.5→40 Å / Num. all: 5800 / Num. obs: 5700 / % possible obs: 98 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 2 / Observed criterion σ(I): 2 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  SIRAS / Resolution: 3.5005→35.892 Å / SU ML: 0.76 / σ(F): 1.48 / Phase error: 36.73 / Stereochemistry target values: ML SIRAS / Resolution: 3.5005→35.892 Å / SU ML: 0.76 / σ(F): 1.48 / Phase error: 36.73 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL / Bsol: 292.848 Å2 / ksol: 0.373 e/Å3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.5005→35.892 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj