[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3kl4: Recognition of a signal peptide by the signal recognition particle -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3kl4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Recognition of a signal peptide by the signal recognition particle | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / signal recognition particle / SRP / SRP54 / Ffh / signal sequence / signal peptide / GTP-binding / Nucleotide-binding / Ribonucleoprotein / RNA-binding / Signal-anchor / Transmembrane | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationSynthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Dipeptidyl-peptidases and tripeptidyl-peptidases / signal recognition particle / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / dipeptidyl-peptidase activity / fungal-type vacuole membrane / aminopeptidase activity / protein processing ...Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Dipeptidyl-peptidases and tripeptidyl-peptidases / signal recognition particle / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / 7S RNA binding / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / dipeptidyl-peptidase activity / fungal-type vacuole membrane / aminopeptidase activity / protein processing / serine-type endopeptidase activity / GTPase activity / GTP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / proteolysis / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Sulfolobus solfataricus (archaea) Sulfolobus solfataricus (archaea) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MAD / Resolution: 3.5 Å MAD / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Janda, C.Y. / Nagai, K. / Li, J. / Oubridge, C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2010 Journal: Nature / Year: 2010Title: Recognition of a signal peptide by the signal recognition particle. Authors: Janda, C.Y. / Li, J. / Oubridge, C. / Hernandez, H. / Robinson, C.V. / Nagai, K. #1:  Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 1998 Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 1998Title: Crystal structure of the signal sequence binding subunit of the signal recognition particle. Authors: Keenan, R.J. / Freymann, D.M. / Walter, P. / Stroud, R.M. #2:  Journal: Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA / Year: 2003 Journal: Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA / Year: 2003Title: Crystal structure of the complete core of archaeal signal recognition particle and implications for interdomain communication. Authors: Rosendal, K.R. / Wild, K. / Montoya, G. / Sinning, I. #3:  Journal: Science / Year: 2000 Journal: Science / Year: 2000Title: Crystal structure of the ribonucleoprotein core of the signal recognition particle. Authors: Batey, R.T. / Rambo, R.P. / Lucast, L. / Rha, B. / Doudna, J.A. #4:  Journal: Structure / Year: 2000 Journal: Structure / Year: 2000Title: The crystal structure of the conserved GTPase of SRP54 from the archaeon Acidianus ambivalens and its comparison with related structures suggests a model for the SRP-SRP receptor complex. Authors: Montoya, G. / Kaat, K. / Moll, R. / Schafer, G. / Sinning, I. #5:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2006 Journal: Nature / Year: 2006Title: Following the signal sequence from ribosomal tunnel exit to signal recognition particle. Authors: Mario Halic / Michael Blau / Thomas Becker / Thorsten Mielke / Martin R Pool / Klemens Wild / Irmgard Sinning / Roland Beckmann /  Abstract: Membrane and secretory proteins can be co-translationally inserted into or translocated across the membrane. This process is dependent on signal sequence recognition on the ribosome by the signal ...Membrane and secretory proteins can be co-translationally inserted into or translocated across the membrane. This process is dependent on signal sequence recognition on the ribosome by the signal recognition particle (SRP), which results in targeting of the ribosome-nascent-chain complex to the protein-conducting channel at the membrane. Here we present an ensemble of structures at subnanometre resolution, revealing the signal sequence both at the ribosomal tunnel exit and in the bacterial and eukaryotic ribosome-SRP complexes. Molecular details of signal sequence interaction in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic complexes were obtained by fitting high-resolution molecular models. The signal sequence is presented at the ribosomal tunnel exit in an exposed position ready for accommodation in the hydrophobic groove of the rearranged SRP54 M domain. Upon ribosome binding, the SRP54 NG domain also undergoes a conformational rearrangement, priming it for the subsequent docking reaction with the NG domain of the SRP receptor. These findings provide the structural basis for improving our understanding of the early steps of co-translational protein sorting. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3kl4.cif.gz 3kl4.cif.gz | 96.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3kl4.ent.gz pdb3kl4.ent.gz | 74.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3kl4.json.gz 3kl4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kl/3kl4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kl/3kl4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kl/3kl4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kl/3kl4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 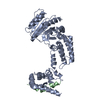
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Details | Biological unit is the same as asymmetric unit. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48503.363 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 2-432 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Sulfolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: P2 / Gene: srp54, SSO0971 / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host: Sulfolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: P2 / Gene: srp54, SSO0971 / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q97ZE7, signal-recognition-particle GTPase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4533.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 26-51 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  References: UniProt: P18962, Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Dipeptidyl-peptidases and tripeptidyl-peptidases |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 2 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 2 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.65 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 53.61 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295 K / Method: vapor diffusion / pH: 5.5 Details: 5-7 % PEG 4000, 100 mM Bis-Tris, 100 mM NaCl, 5-50 mM Mg(OAc)2, 2 % Polypropylene glycol P400. Crystals were obtained by seeding, pH 5.5, VAPOR DIFFUSION, temperature 295K |
-Data collection
| Diffraction |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Detector |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.5→58.42 Å / Num. all: 7683 / Num. obs: 7683 / % possible obs: 99.9 % / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 26.7 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 103.9 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.081 / Net I/σ(I): 29.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.5→3.69 Å / Redundancy: 27.1 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.762 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 5.1 / Num. unique all: 1098 / % possible all: 100 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MAD / Resolution: 3.5→58.42 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber MAD / Resolution: 3.5→58.42 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 151.852 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.5→58.42 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Total num. of bins used: 10
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj

