+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDEZ6 |
|---|---|
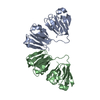
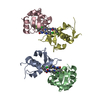
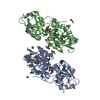
 Sample Sample | Gamma-crystallin S disulfide-linked dimer
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstructural constituent of eye lens / lens development in camera-type eye / visual perception / morphogenesis of an epithelium Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2019Title: The Structure and Stability of the Disulfide-Linked γS-Crystallin Dimer Provide Insight into Oxidation Products Associated with Lens Cataract Formation. Authors: David C Thorn / Aidan B Grosas / Peter D Mabbitt / Nicholas J Ray / Colin J Jackson / John A Carver /  Abstract: The reducing environment in the eye lens diminishes with age, leading to significant oxidative stress. Oxidation of lens crystallin proteins is the major contributor to their destabilization and ...The reducing environment in the eye lens diminishes with age, leading to significant oxidative stress. Oxidation of lens crystallin proteins is the major contributor to their destabilization and deleterious aggregation that scatters visible light, obscures vision, and ultimately leads to cataract. However, the molecular basis for oxidation-induced aggregation is unknown. Using X-ray crystallography and small-angle X-ray scattering, we describe the structure of a disulfide-linked dimer of human γS-crystallin that was obtained via oxidation of C24. The γS-crystallin dimer is stable at glutathione concentrations comparable to those in aged and cataractous lenses. Moreover, dimerization of γS-crystallin significantly increases the protein's propensity to form large insoluble aggregates owing to non-cooperative domain unfolding, as is observed in crystallin variants associated with early-onset cataract. These findings provide insight into how oxidative modification of crystallins contributes to cataract and imply that early-onset and age-related forms of the disease share comparable development pathways. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDEZ6 SASDEZ6 |
|---|
-Related structure data
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
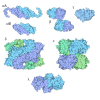
| Model #2528 |  Type: dummy / Radius of dummy atoms: 2.25 A / Chi-square value: 1.356 / P-value: 0.648769  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|---|
| Model #2569 |  Type: atomic / Chi-square value: 4.792  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Gamma-crystallin S disulfide-linked dimer / Specimen concentration: 6 mg/ml |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM sodium phosphate / pH: 7 |
| Entity #1339 | Type: protein / Description: Gamma-crystallin S / Formula weight: 21.007 / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P22914 Sequence: MSKTGTKITF YEDKNFQGRR YDCDCDCADF HTYLSRCNSI KVEGGTWAVY ERPNFAGYMY ILPQGEYPEY QRWMGLNDRL SSCRAVHLPS GGQYKIQIFE KGDFSGQMYE TTEDCPSIME QFHMREIHSC KVLEGVWIFY ELPNYRGRQY LLDKKEYRKP IDWGAASPAV QSFRRIVE |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation/Australian Centre for Neutron Scattering Bruker Nanostar II City: Sydney / 国: Australia  / Type of source: X-ray in house / Wavelength: 0.1541 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 0.73 mm / Type of source: X-ray in house / Wavelength: 0.1541 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 0.73 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: Bruker Hi-Star / Type: multiwire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller