+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9o65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
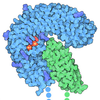
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of SHOC2-KRAS-PP1CA (SKP) complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / KRAS / SHOC2 / PP1CA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to growth hormone stimulus / regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of termination of RNA polymerase II transcription, poly(A)-coupled / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / protein phosphatase type 1 complex / volume-sensitive anion channel activity / glycogen granule / RNA polymerase II promoter clearance / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat S5 phosphatase activity ...cellular response to growth hormone stimulus / regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of termination of RNA polymerase II transcription, poly(A)-coupled / PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex / negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation / protein phosphatase type 1 complex / volume-sensitive anion channel activity / glycogen granule / RNA polymerase II promoter clearance / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat S5 phosphatase activity / nerve growth factor signaling pathway / cyclic-GMP-AMP transmembrane import across plasma membrane / cadherin binding involved in cell-cell adhesion / protein phosphatase 1 binding / regulation of translational initiation in response to stress / protein phosphatase regulator activity / SHOC2 M1731 mutant abolishes MRAS complex function / Gain-of-function MRAS complexes activate RAF signaling / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / dephosphorylation / positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / response to mineralocorticoid / GMP binding / forebrain astrocyte development / LRR domain binding / glycogen metabolic process / regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / protein dephosphorylation / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / negative regulation of epithelial cell differentiation / protein-serine/threonine phosphatase / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / response to isolation stress / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / Triglyceride catabolism / response to gravity / epithelial tube branching involved in lung morphogenesis / type I pneumocyte differentiation / protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity / Rac protein signal transduction / Maturation of hRSV A proteins / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / phosphatase activity / Signaling by RAS GAP mutants / Signaling by RAS GTPase mutants / regulation of MAPK cascade / Activation of RAS in B cells / positive regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / myoblast proliferation / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RAS signaling downstream of NF1 loss-of-function variants / transition metal ion binding / RUNX3 regulates p14-ARF / positive regulation of glial cell proliferation / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / SOS-mediated signalling / fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Activated NTRK3 signals through RAS / Activated NTRK2 signals through RAS / SHC1 events in ERBB4 signaling / DARPP-32 events / cardiac muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / Signalling to RAS / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / SHC-related events triggered by IGF1R / Activated NTRK2 signals through FRS2 and FRS3 / Estrogen-stimulated signaling through PRKCZ / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR3 / glial cell proliferation / MET activates RAS signaling / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR2 / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR4 / Signaling by PDGFRA transmembrane, juxtamembrane and kinase domain mutants / Signaling by PDGFRA extracellular domain mutants / PTK6 Regulates RHO GTPases, RAS GTPase and MAP kinases / Erythropoietin activates RAS / SHC-mediated cascade:FGFR1 / Signaling by FGFR4 in disease / Signaling by CSF3 (G-CSF) / FRS-mediated FGFR3 signaling / : / Signaling by FLT3 ITD and TKD mutants / FRS-mediated FGFR2 signaling / FRS-mediated FGFR4 signaling / p38MAPK events / FRS-mediated FGFR1 signaling / Signaling by FGFR3 in disease / protein-membrane adaptor activity / striated muscle cell differentiation / Tie2 Signaling / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Signaling by FGFR2 in disease / GRB2 events in EGFR signaling / Signaling by FLT3 fusion proteins / SHC1 events in EGFR signaling / FLT3 Signaling / Signaling by FGFR1 in disease / EGFR Transactivation by Gastrin Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Finci, L.I. / Bonsor, D.A. / Simanshu, D.K. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2026 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2026Title: Structure of SHOC2-KRAS-PP1C complex reveals RAS isoform-specific determinants and insights into targeting complex assembly by RAS inhibitors. Authors: Daniel A Bonsor / Lorenzo I Finci / Jacob R Potter / Lucy C Young / Vanessa E Wall / Ruby Goldstein de Salazar / Katie R Geis / Tyler Stephens / Joseph Finney / Dwight V Nissley / Frank ...Authors: Daniel A Bonsor / Lorenzo I Finci / Jacob R Potter / Lucy C Young / Vanessa E Wall / Ruby Goldstein de Salazar / Katie R Geis / Tyler Stephens / Joseph Finney / Dwight V Nissley / Frank McCormick / Dhirendra K Simanshu /  Abstract: RAF activation is essential for MAPK signaling and is mediated by RAS binding and the dephosphorylation of a conserved phosphoserine by the SHOC2-RAS-PP1C complex. MRAS forms a high-affinity SHOC2- ...RAF activation is essential for MAPK signaling and is mediated by RAS binding and the dephosphorylation of a conserved phosphoserine by the SHOC2-RAS-PP1C complex. MRAS forms a high-affinity SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C (SMP) complex, while canonical RAS isoforms (KRAS, HRAS, NRAS) form analogous but lower-affinity assemblies. Yet, cancers driven by oncogenic KRAS, HRAS, or NRAS remain strongly SHOC2-dependent, suggesting that these weaker complexes contribute to tumorigenesis. To elucidate how canonical RAS proteins form lower-affinity ternary complexes, the cryo-EM structure of the SHOC2-KRAS-PP1C (SKP) complex stabilized by Noonan syndrome mutations is described. The SKP architecture is similar to the SMP complex but forms fewer contacts and buries less surface area due to the absence of MRAS-specific structural features in KRAS that enhance complex stability. RAS inhibitors MRTX1133 and RMC-6236 alter Switch-I/II conformations, thereby blocking SKP assembly more effectively than they disrupt preformed complexes. These RAS inhibitors do not affect SMP formation because they do not bind MRAS. Since MRAS is upregulated in resistance to KRAS inhibition, we characterize a MRAS mutant capable of binding MRTX1133. This MRAS mutant can form an SMP complex, but MRTX1133 blocks its assembly, demonstrating the feasibility of dual SKP and SMP targeting. Overall, our findings define isoform-specific differences in SHOC2-RAS-PP1C complex formation and support a strategy to prevent both SKP and SMP assemblies to overcome resistance in RAS-driven cancers. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9o65.cif.gz 9o65.cif.gz | 199.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9o65.ent.gz pdb9o65.ent.gz | 151.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9o65.json.gz 9o65.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/9o65 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/9o65 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/9o65 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o6/9o65 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  70159MC  9o0nC  9o0oC  9o0pC  9o0qC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 64954.840 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: M173I Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SHOC2, KIAA0862 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SHOC2, KIAA0862 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UQ13 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UQ13 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 19300.824 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: Q61R Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KRAS, KRAS2, RASK2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KRAS, KRAS2, RASK2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P01116, small monomeric GTPase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P01116, small monomeric GTPase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 37543.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: P50R Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CA, PPP1A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PPP1CA, PPP1A / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P62136, protein-serine/threonine phosphatase |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 4 molecules 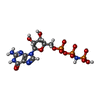



| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-GNP / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #6: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ternary complex of SHOC2, KRAS, and PP1CA / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.12 MDa / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.08 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2250 nm / Nominal defocus min: 750 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 52.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 518550 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 199681 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj