+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9fjo | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
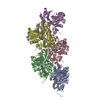
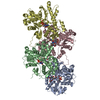
| Title | Structure of the undecorated pointed end of F-actin | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Actin, alpha skeletal muscle | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / actin / filament / pointed end | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament ...cytoskeletal motor activator activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / lamellipodium / cell body / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.05 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Boiero Sanders, M. / Oosterheert, W. / Hofnagel, O. / Bieling, P. / Raunser, S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 3items Germany, European Union, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Phalloidin and DNase I-bound F-actin pointed end structures reveal principles of filament stabilization and disassembly. Authors: Micaela Boiero Sanders / Wout Oosterheert / Oliver Hofnagel / Peter Bieling / Stefan Raunser /  Abstract: Actin filament turnover involves subunits binding to and dissociating from the filament ends, with the pointed end being the primary site of filament disassembly. Several molecules modulate filament ...Actin filament turnover involves subunits binding to and dissociating from the filament ends, with the pointed end being the primary site of filament disassembly. Several molecules modulate filament turnover, but the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Here, we present three cryo-EM structures of the F-actin pointed end in the presence and absence of phalloidin or DNase I. The two terminal subunits at the undecorated pointed end adopt a twisted conformation. Phalloidin can still bind and bridge these subunits, inducing a conformational shift to a flattened, F-actin-like state. This explains how phalloidin prevents depolymerization at the pointed end. Interestingly, two DNase I molecules simultaneously bind to the phalloidin-stabilized pointed end. In the absence of phalloidin, DNase I binding would disrupt the terminal actin subunit packing, resulting in filament disassembly. Our findings uncover molecular principles of pointed end regulation and provide structural insights into the kinetic asymmetry between the actin filament ends. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9fjo.cif.gz 9fjo.cif.gz | 287.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9fjo.ent.gz pdb9fjo.ent.gz | 232.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9fjo.json.gz 9fjo.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fj/9fjo https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fj/9fjo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fj/9fjo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fj/9fjo | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  50507MC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 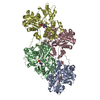
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 41875.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Rabbit skeletal alpha actin purified from frozen rabbit muscle acetone powder. Source: (natural)  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of actin subunits that form the pointed end of actin filaments. Type: COMPLEX Details: Alpha actin was purified from skeletal muscle. Actin filaments were polymerized in the presence of the formin INF2, which was purified separetely and added during polymerization prior to ...Details: Alpha actin was purified from skeletal muscle. Actin filaments were polymerized in the presence of the formin INF2, which was purified separetely and added during polymerization prior to cryo-EM grid preparation. Entity ID: #1 / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.1 Details: 12 mM HEPES pH 7.1, 100 mM KCl, 2.1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM TCEP, 0.2 mM ATP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 286 K / Details: 3 seconds, force 0. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS Details: 300 kV Titan Krios G3 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific). |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1300 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 20305 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Details: Gatan energy filter / Energyfilter slit width: 15 eV Spherical aberration corrector: 300 kV Titan Krios G3 microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific). |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1935707 / Details: Particles picked using SPHIRE-crYOLO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.05 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 206373 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Details: Real Space Refinement in Phenix. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 8A2T Accession code: 8A2T / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj