[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9dmi: Structure of the C-terminal half of LRRK2 bound to RN277 (Type-II... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9dmi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
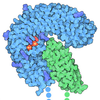
| Title | Structure of the C-terminal half of LRRK2 bound to RN277 (Type-II inhibitor) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN BINDING / GTPase / Kinase / inhibitors | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcaveola neck / : / beta-catenin destruction complex binding / regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve / Wnt signalosome assembly / regulation of kidney size / regulation of cell projection organization / tangential migration from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb / GTP-dependent protein kinase activity / regulation of SNARE complex assembly ...caveola neck / : / beta-catenin destruction complex binding / regulation of branching morphogenesis of a nerve / Wnt signalosome assembly / regulation of kidney size / regulation of cell projection organization / tangential migration from the subventricular zone to the olfactory bulb / GTP-dependent protein kinase activity / regulation of SNARE complex assembly / regulation of neuroblast proliferation / regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum exit site / peroxidase inhibitor activity / negative regulation of late endosome to lysosome transport / regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / : / positive regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / amphisome / regulation of synaptic vesicle transport / regulation of lysosomal lumen pH / regulation of CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / co-receptor binding / negative regulation of GTPase activity / regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of microglial cell activation / regulation of neuron maturation / regulation of retrograde transport, endosome to Golgi / positive regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / cytoplasmic side of mitochondrial outer membrane / negative regulation of autophagosome assembly / olfactory bulb development / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / JUN kinase kinase kinase activity / neuron projection arborization / striatum development / multivesicular body, internal vesicle / negative regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of dendritic spine morphogenesis / mitochondrion localization / protein localization to mitochondrion / cellular response to dopamine / positive regulation of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization involved in apoptotic signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum organization / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / Wnt signalosome / negative regulation of protein processing / positive regulation of programmed cell death / GTP metabolic process / regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / syntaxin-1 binding / regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / lysosome organization / Golgi-associated vesicle / clathrin binding / PTK6 promotes HIF1A stabilization / negative regulation of macroautophagy / regulation of mitochondrial fission / protein kinase A binding / regulation of locomotion / neuromuscular junction development / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / Golgi organization / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / microvillus / exploration behavior / endoplasmic reticulum exit site / autolysosome / locomotory exploration behavior / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / MAP kinase kinase kinase activity / canonical Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / Rho protein signal transduction / presynaptic cytosol / neuron projection morphogenesis / phagocytic vesicle / cellular response to manganese ion / JNK cascade / positive regulation of autophagy / dendrite cytoplasm / tubulin binding / GTPase activator activity / cellular response to starvation / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / SNARE binding / determination of adult lifespan / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / mitochondrion organization / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / trans-Golgi network / calcium-mediated signaling / regulation of protein stability / regulation of autophagy / autophagy / small GTPase binding / mitochondrial membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Sanz-Murillo, M. / Leschziner, A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2025Title: Type II kinase inhibitors that target Parkinson's disease-associated LRRK2. Authors: Nicolai D Raig / Katherine J Surridge / Marta Sanz-Murillo / Verena Dederer / Andreas Krämer / Martin P Schwalm / Nicholas M Lattal / Lewis Elson / Deep Chatterjee / Sebastian Mathea / ...Authors: Nicolai D Raig / Katherine J Surridge / Marta Sanz-Murillo / Verena Dederer / Andreas Krämer / Martin P Schwalm / Nicholas M Lattal / Lewis Elson / Deep Chatterjee / Sebastian Mathea / Thomas Hanke / Andres E Leschziner / Samara L Reck-Peterson / Stefan Knapp /   Abstract: Increased kinase activity of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is associated with Parkinson's disease (PD). Numerous LRRK2-selective type I kinase inhibitors have been developed, and some have ...Increased kinase activity of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is associated with Parkinson's disease (PD). Numerous LRRK2-selective type I kinase inhibitors have been developed, and some have entered clinical trials. Here, to our knowledge, we present the first type II kinase inhibitors that target LRRK2. Targeting the inactive conformation of LRRK2 is functionally distinct from targeting the active-like conformation using type I inhibitors. We designed these inhibitors with a combinatorial chemistry approach fusing selective LRRK2 type I and promiscuous type II inhibitors using iterative cycles of synthesis supported by structural biology and activity testing. Our lead compounds are selective and potent toward both LRRK2 and LRRK1, a close relative of LRRK2. Through cellular assays, cryo-electron microscopy structural analysis, and in vitro motility assays, we show that our inhibitors stabilize the open, inactive LRRK2 kinase conformation. These new conformation-specific compounds will be invaluable as tools to study LRRK2's function and regulation and expand the potential therapeutic options for PD. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9dmi.cif.gz 9dmi.cif.gz | 227.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9dmi.ent.gz pdb9dmi.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9dmi.json.gz 9dmi.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dm/9dmi https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dm/9dmi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dm/9dmi ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dm/9dmi | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  47006MC  9ez3C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 136174.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LRRK2, PARK8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LRRK2, PARK8 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q5S007, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 19766.912 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Some loops are missing due to the lack of cryo-EM density Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-A1A7Q / Mass: 585.099 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C31H33ClN8O2 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: C-terminal half of LRRK2 bound to RN277 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.137 MDa / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 616.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K / Details: Blot time 4s Blot force 5 Waiting time 20s |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 13972 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 226172 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6VP7 Pdb chain-ID: A / Accession code: 6VP7 / Chain residue range: 1333-2527 / Pdb chain residue range: 1333-2527 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.35 Å Stereochemistry target values: REAL-SPACE (WEIGHTED MAP SUM AT ATOM CENTERS) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj