[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-9d0x: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9d0x | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4 (local mask) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / kinase / degrader / ternary complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / negative regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / limb development / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / regulation of heterochromatin organization / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex ...positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / negative regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / limb development / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / regulation of heterochromatin organization / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / G2 Phase / Y chromosome / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / positive regulation of heterochromatin formation / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / X chromosome / G1/S-Specific Transcription / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / centriole replication / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / microtubule organizing center / locomotory exploration behavior / centrosome duplication / G0 and Early G1 / DNA replication initiation / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / cyclin-dependent kinase / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Cajal body / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / condensed chromosome / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / cellular response to nitric oxide / post-translational protein modification / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance / cyclin binding / positive regulation of DNA replication / male germ cell nucleus / meiotic cell cycle / potassium ion transport / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Meiotic recombination / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / Wnt signaling pathway / Orc1 removal from chromatin / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / kinase activity / cellular senescence / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / nuclear envelope / regulation of protein localization / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / regulation of gene expression / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / transcription regulator complex / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / Potential therapeutics for SARS / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Ras protein signal transduction / transmembrane transporter binding / DNA replication / protein phosphorylation / chromosome, telomeric region / endosome / protein ubiquitination / chromatin remodeling / protein domain specific binding / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / DNA repair / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / positive regulation of cell population proliferation Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.84 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kwiatkowski, N. / Liang, T. / Sha, Z. / Collier, P.N. / Yang, A. / Sathappa, M. / Paul, A. / Su, L. / Zheng, X. / Aversa, R. ...Kwiatkowski, N. / Liang, T. / Sha, Z. / Collier, P.N. / Yang, A. / Sathappa, M. / Paul, A. / Su, L. / Zheng, X. / Aversa, R. / Li, K. / Mehovic, R. / Breitkopf, S.B. / Chen, D. / Howarth, C.L. / Yuan, K. / Jo, H. / Growney, J.D. / Weiss, M. / Williams, J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2025Title: CDK2 heterobifunctional degraders co-degrade CDK2 and cyclin E resulting in efficacy in CCNE1-amplified and overexpressed cancers. Authors: Nicholas Kwiatkowski / Tong Liang / Zhe Sha / Philip N Collier / Annan Yang / Murugappan Sathappa / Atanu Paul / Lijing Su / Xiaozhang Zheng / Robert Aversa / Kunhua Li / Revonda Mehovic / ...Authors: Nicholas Kwiatkowski / Tong Liang / Zhe Sha / Philip N Collier / Annan Yang / Murugappan Sathappa / Atanu Paul / Lijing Su / Xiaozhang Zheng / Robert Aversa / Kunhua Li / Revonda Mehovic / Christina Kolodzy / Susanne B Breitkopf / Dapeng Chen / Charles L Howarth / Karen Yuan / Hakryul Jo / Joseph D Growney / Matthew Weiss / Juliet Williams /  Abstract: CCNE1 amplification drives aberrant CDK2-cyclin E1 activity in cancer. Despite activity of CDK2 inhibitors, their therapeutic margins are limited by poor CDK selectivity. We developed a degrader with ...CCNE1 amplification drives aberrant CDK2-cyclin E1 activity in cancer. Despite activity of CDK2 inhibitors, their therapeutic margins are limited by poor CDK selectivity. We developed a degrader with high selectivity for CDK2 over CDK1 that also unexpectedly led to cyclin E1 degradation and potent and complete suppression of RB phosphorylation at concentrations with low CDK2 occupancy and negligible CDK1 degradation. Co-depletion of CDK2 and cyclin E1 also resensitized palbociclib-adapted breast cancer cells to cell cycle blockade. Overall, the improved potency and selectivity of the degrader for CDK2 over small-molecule inhibitors drives antiproliferative activity with greater specificity for CCNE1 cancer cells and RB dependency. Using an orally administered degrader, we demonstrate deep and sustained RB pathway suppression, which is needed to induce stasis in CCNE1 tumors. These results highlight the potential of this modality to target CDK2 potently and selectivity in this biomarker-defined patient population with high unmet need. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9d0x.cif.gz 9d0x.cif.gz | 197.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9d0x.ent.gz pdb9d0x.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9d0x.json.gz 9d0x.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d0/9d0x https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d0/9d0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d0/9d0x ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d0/9d0x | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  46465MC  9d0uC  9d0vC 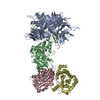 9d0wC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 46465.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRBN, AD-006 / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CRBN, AD-006 / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 34056.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK2, CDKN2 / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK2, CDKN2 / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 33140.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CCNE1, CCNE / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CCNE1, CCNE / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  |
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-A1A1I / ( Mass: 880.041 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C46H54FN9O6S / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN and Cpd 4 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOCONTINUUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.84 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 537511 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj















