[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-46464: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | kinase / degrader / ternary complex / CDK2 / CELL CYCLE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / negative regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / UV-damage excision repair / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont ...positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation / homologous chromosome pairing at meiosis / negative regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / RHOBTB3 ATPase cycle / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / UV-damage excision repair / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / WD40-repeat domain binding / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / limb development / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / regulation of heterochromatin organization / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / G2 Phase / Y chromosome / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / positive regulation of heterochromatin formation / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / X chromosome / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / G1/S-Specific Transcription / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / centriole replication / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / microtubule organizing center / locomotory exploration behavior / centrosome duplication / G0 and Early G1 / viral release from host cell / cullin family protein binding / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / DNA replication initiation / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / cyclin-dependent kinase / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / Cajal body / positive regulation of viral genome replication / negative regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / proteasomal protein catabolic process / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / condensed chromosome / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / sperm end piece / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / cellular response to nitric oxide / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / post-translational protein modification / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / telomere maintenance / sperm principal piece / cyclin binding / positive regulation of DNA replication / male germ cell nucleus / meiotic cell cycle / nucleotide-excision repair / potassium ion transport / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / regulation of circadian rhythm / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / Meiotic recombination / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Wnt signaling pathway / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / Orc1 removal from chromatin Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.95 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kwiatkowski N / Liang T / Sha Z / Collier PN / Yang A / Sathappa M / Paul A / Su L / Zheng X / Aversa R ...Kwiatkowski N / Liang T / Sha Z / Collier PN / Yang A / Sathappa M / Paul A / Su L / Zheng X / Aversa R / Li K / Mehovic R / Breitkopf SB / Chen D / Howarth CL / Yuan K / Jo H / Growney JD / Weiss M / Williams J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell Chem Biol / Year: 2025Title: CDK2 heterobifunctional degraders co-degrade CDK2 and cyclin E resulting in efficacy in CCNE1-amplified and overexpressed cancers. Authors: Nicholas Kwiatkowski / Tong Liang / Zhe Sha / Philip N Collier / Annan Yang / Murugappan Sathappa / Atanu Paul / Lijing Su / Xiaozhang Zheng / Robert Aversa / Kunhua Li / Revonda Mehovic / ...Authors: Nicholas Kwiatkowski / Tong Liang / Zhe Sha / Philip N Collier / Annan Yang / Murugappan Sathappa / Atanu Paul / Lijing Su / Xiaozhang Zheng / Robert Aversa / Kunhua Li / Revonda Mehovic / Christina Kolodzy / Susanne B Breitkopf / Dapeng Chen / Charles L Howarth / Karen Yuan / Hakryul Jo / Joseph D Growney / Matthew Weiss / Juliet Williams /  Abstract: CCNE1 amplification drives aberrant CDK2-cyclin E1 activity in cancer. Despite activity of CDK2 inhibitors, their therapeutic margins are limited by poor CDK selectivity. We developed a degrader with ...CCNE1 amplification drives aberrant CDK2-cyclin E1 activity in cancer. Despite activity of CDK2 inhibitors, their therapeutic margins are limited by poor CDK selectivity. We developed a degrader with high selectivity for CDK2 over CDK1 that also unexpectedly led to cyclin E1 degradation and potent and complete suppression of RB phosphorylation at concentrations with low CDK2 occupancy and negligible CDK1 degradation. Co-depletion of CDK2 and cyclin E1 also resensitized palbociclib-adapted breast cancer cells to cell cycle blockade. Overall, the improved potency and selectivity of the degrader for CDK2 over small-molecule inhibitors drives antiproliferative activity with greater specificity for CCNE1 cancer cells and RB dependency. Using an orally administered degrader, we demonstrate deep and sustained RB pathway suppression, which is needed to induce stasis in CCNE1 tumors. These results highlight the potential of this modality to target CDK2 potently and selectivity in this biomarker-defined patient population with high unmet need. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_46464.map.gz emd_46464.map.gz | 154.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-46464-v30.xml emd-46464-v30.xml emd-46464.xml emd-46464.xml | 22.8 KB 22.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_46464_fsc.xml emd_46464_fsc.xml | 11.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_46464.png emd_46464.png | 47.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-46464.cif.gz emd-46464.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_46464_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46464_half_map_1.map.gz emd_46464_half_map_2.map.gz emd_46464_half_map_2.map.gz | 154.5 MB 154.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46464 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46464 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46464 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-46464 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 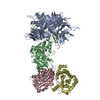 9d0wMC  9d0uC  9d0vC 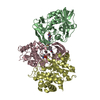 9d0xC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_46464.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_46464.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 166.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.04873 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_46464_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_46464_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4
| Entire | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4
| Supramolecule | Name: Cryo-EM structure of CDK2/CyclinE1 in complex with CRBN/DDB1 and Cpd 4 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA damage-binding protein 1
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA damage-binding protein 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 128.139578 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSYNYVVTAQ KPTAVNGCVT GHFTSAEDLN LLIAKNTRLE IYVVTAEGLR PVKEVGMYGK IAVMELFRPK GESKDLLFIL TAKYNACIL EYKQSGESID IITRAHGNVQ DRIGRPSETG IIGIIDPECR MIGLRLYDGL FKVIPLDRDN KELKAFNIRL E ELHVIDVK ...String: MSYNYVVTAQ KPTAVNGCVT GHFTSAEDLN LLIAKNTRLE IYVVTAEGLR PVKEVGMYGK IAVMELFRPK GESKDLLFIL TAKYNACIL EYKQSGESID IITRAHGNVQ DRIGRPSETG IIGIIDPECR MIGLRLYDGL FKVIPLDRDN KELKAFNIRL E ELHVIDVK FLYGCQAPTI CFVYQDPQGR HVKTYEVSLR EKEFNKGPWK QENVEAEASM VIAVPEPFGG AIIIGQESIT YH NGDKYLA IAPPIIKQST IVCHNRVDPN GSRYLLGDME GRLFMLLLEK EEQMDGTVTL KDLRVELLGE TSIAECLTYL DNG VVFVGS RLGDSQLVKL NVDSNEQGSY VVAMETFTNL GPIVDMCVVD LERQGQGQLV TCSGAFKEGS LRIIRNGIGI HEHA SIDLP GIKGLWPLRS DPNRETDDTL VLSFVGQTRV LMLNGEEVEE TELMGFVDDQ QTFFCGNVAH QQLIQITSAS VRLVS QEPK ALVSEWKEPQ AKNISVASCN SSQVVVAVGR ALYYLQIHPQ ELRQISHTEM EHEVACLDIT PLGDSNGLSP LCAIGL WTD ISARILKLPS FELLHKEMLG GEIIPRSILM TTFESSHYLL CALGDGALFY FGLNIETGLL SDRKKVTLGT QPTVLRT FR SLSTTNVFAC SDRPTVIYSS NHKLVFSNVN LKEVNYMCPL NSDGYPDSLA LANNSTLTIG TIDEIQKLHI RTVPLYES P RKICYQEVSQ CFGVLSSRIE VQDTSGGTTA LRPSASTQAL SSSVSSSKLF SSSTAPHETS FGEEVEVHNL LIIDQHTFE VLHAHQFLQN EYALSLVSCK LGKDPNTYFI VGTAMVYPEE AEPKQGRIVV FQYSDGKLQT VAEKEVKGAV YSMVEFNGKL LASINSTVR LYEWTTEKEL RTECNHYNNI MALYLKTKGD FILVGDLMRS VLLLAYKPME GNFEEIARDF NPNWMSAVEI L DDDNFLGA ENAFNLFVCQ KDSAATTDEE RQHLQEVGLF HLGEFVNVFC HGSLVMQNLG ETSTPTQGSV LFGTVNGMIG LV TSLSESW YNLLLDMQNR LNKVIKSVGK IEHSFWRSFH TERKTEPATG FIDGDLIESF LDISRPKMQE VVANLQYDDG SGM KREATA DDLIKVVEEL TRIHWSHPQF EK UniProtKB: DNA damage-binding protein 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Protein cereblon
| Macromolecule | Name: Protein cereblon / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.465375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GSEAKKPNII NFDTSLPTSH TYLGADMEEF HGRTLHDDDS CQVIPVLPQV MMILIPGQTL PLQLFHPQEV SMVRNLIQKD RTFAVLAYS NVQEREAQFG TTAEIYAYRE EQDFGIEIVK VKAIGRQRFK VLELRTQSDG IQQAKVQILP ECVLPSTMSA V QLESLNKC ...String: GSEAKKPNII NFDTSLPTSH TYLGADMEEF HGRTLHDDDS CQVIPVLPQV MMILIPGQTL PLQLFHPQEV SMVRNLIQKD RTFAVLAYS NVQEREAQFG TTAEIYAYRE EQDFGIEIVK VKAIGRQRFK VLELRTQSDG IQQAKVQILP ECVLPSTMSA V QLESLNKC QIFPSKPVSR EDQCSYKWWQ KYQKRKFHCA NLTSWPRWLY SLYDAETLMD RIKKQLREWD ENLKDDSLPS NP IDFSYRV AACLPIDDVL RIQLLKIGSA IQRLRCELDI MNKCTSLCCK QCQETEITTK NEIFSLSLCG PMAAYVNPHG YVH ETLTVY KACNLNLIGR PSTEHSWFPG YAWTVAQCKI CASHIGWKFT ATKKDMSPQK FWGLTRSALL PTIPDTEDEI SPDK VILCL UniProtKB: Protein cereblon |
-Macromolecule #3: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: cyclin-dependent kinase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.056469 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MENFQKVEKI GEGTYGVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKLYLVF EFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPVRTY (TPO)HEVVTLWY ...String: MENFQKVEKI GEGTYGVVYK ARNKLTGEVV ALKKIRLDTE TEGVPSTAIR EISLLKELNH PNIVKLLDVI HTENKLYLVF EFLHQDLKK FMDASALTGI PLPLIKSYLF QLLQGLAFCH SHRVLHRDLK PQNLLINTEG AIKLADFGLA RAFGVPVRTY (TPO)HEVVTLWY RAPEILLGCK YYSTAVDIWS LGCIFAEMVT RRALFPGDSE IDQLFRIFRT LGTPDEVVWP GVTSMPD YK PSFPKWARQD FSKVVPPLDE DGRSLLSQML HYDPNKRISA KAALAHPFFQ DVTKPVPHLR L UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
-Macromolecule #4: G1/S-specific cyclin-E1
| Macromolecule | Name: G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.140578 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SGSIIAPSRG SPLPVLSWAN REEVWKIMLN KEKTYLRDQH FLEQHPLLQP KMRAILLDWL MEVCEVYKLH RETFYLAQDF FDRYMATQE NVVKTLLQLI GISSLFIAAK LEEIYPPKLH QFAYVTDGAC SGDEILTMEL MIMKALKWRL SPLTIVSWLN V YMQVAYLN ...String: SGSIIAPSRG SPLPVLSWAN REEVWKIMLN KEKTYLRDQH FLEQHPLLQP KMRAILLDWL MEVCEVYKLH RETFYLAQDF FDRYMATQE NVVKTLLQLI GISSLFIAAK LEEIYPPKLH QFAYVTDGAC SGDEILTMEL MIMKALKWRL SPLTIVSWLN V YMQVAYLN DLHEVLLPQY PQQIFIQIAE LLDLCVLDVD CLEFPYGILA ASALYHFSSS ELMQKVSGYQ WCDIENCVKW MV PFAMVIR ETGSSKLKHF RGVADEDAHN IQTHRDSLDL LDKARAKKA UniProtKB: G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 |
-Macromolecule #5: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: (3R)-3-(5-{4-[(2-{4-[(8-cyclopentyl-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d...
| Macromolecule | Name: (3R)-3-(5-{4-[(2-{4-[(8-cyclopentyl-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)amino]-3-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl}-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonan-7-yl)methyl]piperidin-1-yl}-4-fluoro-3-methyl-2-oxo-2,3- ...Name: (3R)-3-(5-{4-[(2-{4-[(8-cyclopentyl-7-oxo-7,8-dihydropyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-2-yl)amino]-3-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl}-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonan-7-yl)methyl]piperidin-1-yl}-4-fluoro-3-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,3-benzimidazol-1-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1A1I |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 880.041 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOCONTINUUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)