+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8wry | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
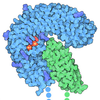
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of Mouse TLR4/MD-2/DLAM3 Complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / Innate immune system / Toll-like receptors / TLR4 agonist / Vaccine adjuvants / Disaccharide-based Lipid A Mimetics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMyD88-independent TLR4 cascade / Caspase activation via Death Receptors in the presence of ligand / Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade / Heme signaling / nitric oxide production involved in inflammatory response / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / MHC class II biosynthetic process / TRIF-mediated programmed cell death / positive regulation of cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex ...MyD88-independent TLR4 cascade / Caspase activation via Death Receptors in the presence of ligand / Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade / Heme signaling / nitric oxide production involved in inflammatory response / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / MHC class II biosynthetic process / TRIF-mediated programmed cell death / positive regulation of cellular response to macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulus / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / lipopolysaccharide immune receptor activity / positive regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway / positive regulation of matrix metallopeptidase secretion / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Toll-like receptor 4 binding / mast cell activation / detection of lipopolysaccharide / positive regulation of lymphocyte proliferation / regulation of dendritic cell cytokine production / lipopolysaccharide receptor complex / negative regulation of interleukin-23 production / cellular response to oxidised low-density lipoprotein particle stimulus / wound healing involved in inflammatory response / B cell proliferation involved in immune response / lymphocyte proliferation / nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 1 signaling pathway / positive regulation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of stress-activated MAPK cascade / activation of NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activity / intestinal epithelial structure maintenance / positive regulation of interleukin-13 production / positive regulation of interleukin-1 production / TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway / macrophage activation / astrocyte development / microglia differentiation / nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of MHC class II biosynthetic process / NAD+ nucleosidase activity, cyclic ADP-ribose generating / positive regulation of platelet activation / positive regulation of macrophage activation / negative regulation of interleukin-17 production / positive regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production / negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell migration / MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway / toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / toll-like receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of macrophage cytokine production / positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly / cellular response to lipoteichoic acid / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / negative regulation of type II interferon production / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / B cell proliferation / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / phagocytosis / stress-activated MAPK cascade / phagocytic cup / positive regulation of chemokine production / cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor stimulus / ruffle / positive regulation of B cell proliferation / JNK cascade / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / neurogenesis / nitric oxide biosynthetic process / positive regulation of interleukin-12 production / positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / activation of innate immune response / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / positive regulation of interleukin-8 production / positive regulation of JNK cascade / response to bacterium / lipopolysaccharide binding / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / : / negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / cellular response to type II interferon / positive regulation of type II interferon production / cellular response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / cellular response to lipopolysaccharide / regulation of inflammatory response / response to lipopolysaccharide Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fu, Y. / Kim, H. / Zamyatina, A. / Kim, H.M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Korea, Republic Of, 1items Korea, Republic Of, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Structural insight into TLR4/MD-2 activation by synthetic LPS mimetics with distinct binding modes. Authors: Yaoyao Fu / Hyojin Kim / Dong Sun Lee / Ah-Reum Han / Holger Heine / Alla Zamyatina / Ho Min Kim /    Abstract: The mammalian pattern-recognition receptor TLR4/MD-2 (Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor-2) can be activated by a wide variety of pathogen-associated and endogenous molecules, with ...The mammalian pattern-recognition receptor TLR4/MD-2 (Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor-2) can be activated by a wide variety of pathogen-associated and endogenous molecules, with Gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) being the primary natural TLR4 agonist. Activation of TLR4 triggers cellular signaling that enables the beneficial innate immune responses and enhances adaptive immunity, thereby emphasizing the potential of TLR4 agonists for the management of diseases with an immunopathological background and for use as vaccine adjuvants. Given the challenges associated with LPS-derived products, including structural complexity, heterogeneity, toxicity, and species specificity, synthetic molecules targeting TLR4/MD-2 offer a promising alternative. Here, we elucidate the structural basis for the recognition of synthetic LPS-mimicking glycolipids, Disaccharide Lipid A Mimetics (DLAMs), by human and mouse TLR4/MD-2 through cryo-EM structures of six dimeric [TLR4/MD-2/ligand] complexes resolved at 2.2-3.1 Å. We reveal that the specific binding modes of DLAMs, distinct from those of LPS, are essential for the species-independent TLR4 agonistic activity. DLAMs function as a molecular bridge, effectively induce the dimerization of TLR4/MD-2 complexes through specific carbohydrate structure-relevant ligand-protein interactions. Our findings reveal the distinct molecular modes of TLR4 activation, and provide a structural basis for the rationale design and development of innovative, highly potent TLR4-targeting immunotherapeutics and adjuvants. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8wry.cif.gz 8wry.cif.gz | 282.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8wry.ent.gz pdb8wry.ent.gz | 225.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8wry.json.gz 8wry.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wr/8wry https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wr/8wry ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wr/8wry ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wr/8wry | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37794MC  8wo1C  8wqtC  8wsaC  8wtaC  9j03C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 4 molecules CDBA
| #1: Protein | Mass: 16411.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9JHF9 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9JHF9#2: Protein | Mass: 68651.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9QUK6 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9QUK6 |
|---|
-Sugars , 4 types, 26 molecules 
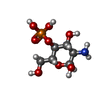

| #3: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #6: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #7: Sugar | #8: Sugar | Type: D-saccharide, alpha linking / Mass: 188.135 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C7H8O6 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 6 molecules 
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-2IL / ( #5: Chemical | Mass: 454.726 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C28H54O4 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: mouse TLR4/MD2/DLAM3 complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #2, #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 10mA / Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 58963 X / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 66.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 18733 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 625831 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 3VQ2 Accession code: 3VQ2 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 2.6 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj