[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
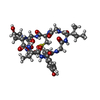
Yorodumi- PDB-8waw: De novo transcribing complex 13 (TC13), the early elongation comp... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8waw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | De novo transcribing complex 13 (TC13), the early elongation complex with Pol II positioned 13nt downstream of TSS | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / transcribing complex / de novo transcription initiation / early elongation complex (EEC) | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphosphatase activator activity / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / TFIIF-class transcription factor complex binding / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex ...phosphatase activator activity / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / TFIIF-class transcription factor complex binding / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / transcription factor TFIIF complex / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor binding / FGFR2 alternative splicing / Signaling by FGFR2 IIIa TM / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / transcription factor TFIID complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity / mRNA Capping / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA polymerase III activity / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / RNA polymerase II activity / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / RNA polymerase I activity / RNA polymerase I complex / RNA polymerase III complex / positive regulation of translational initiation / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / RNA polymerase II, core complex / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / translation initiation factor binding / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / negative regulation of protein binding / promoter-specific chromatin binding / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / P-body / response to virus / ribonucleoside binding / fibrillar center / DNA-directed 5'-3' RNA polymerase activity / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell junction / single-stranded DNA binding / toxin activity / protein phosphatase binding / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleic acid binding / single-stranded RNA binding / protein dimerization activity / protein domain specific binding / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Amanita phalloides (death cap) Amanita phalloides (death cap) synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.02 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, X. / Liu, W. / Wang, Q. / Wang, X. / Ren, Y. / Qu, X. / Li, W. / Xu, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2023 Journal: Science / Year: 2023Title: Structural visualization of transcription initiation in action. Authors: Xizi Chen / Weida Liu / Qianmin Wang / Xinxin Wang / Yulei Ren / Xuechun Qu / Wanjun Li / Yanhui Xu /  Abstract: Transcription initiation is a complex process, and its mechanism is incompletely understood. We determined the structures of de novo transcribing complexes TC2 to TC17 with RNA polymerase II halted ...Transcription initiation is a complex process, and its mechanism is incompletely understood. We determined the structures of de novo transcribing complexes TC2 to TC17 with RNA polymerase II halted on G-less promoters when nascent RNAs reach 2 to 17 nucleotides in length, respectively. Connecting these structures generated a movie and a working model. As initially synthesized RNA grows, general transcription factors (GTFs) remain bound to the promoter and the transcription bubble expands. Nucleoside triphosphate (NTP)-driven RNA-DNA translocation and template-strand accumulation in a nearly sealed channel may promote the transition from initially transcribing complexes (ITCs) (TC2 to TC9) to early elongation complexes (EECs) (TC10 to TC17). Our study shows dynamic processes of transcription initiation and reveals why ITCs require GTFs and bubble expansion for initial RNA synthesis, whereas EECs need GTF dissociation from the promoter and bubble collapse for promoter escape. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8waw.cif.gz 8waw.cif.gz | 852.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8waw.ent.gz pdb8waw.ent.gz | 669.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8waw.json.gz 8waw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8waw_validation.pdf.gz 8waw_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8waw_full_validation.pdf.gz 8waw_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8waw_validation.xml.gz 8waw_validation.xml.gz | 106.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8waw_validation.cif.gz 8waw_validation.cif.gz | 171.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8waw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8waw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8waw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wa/8waw | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37407MC  8wakC  8walC  8wanC  8waoC  8wapC  8waqC  8warC  8wasC 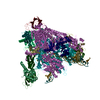 8watC  8wauC  8wavC  8waxC  8wayC  8wazC 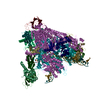 8wb0C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 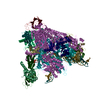
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-General transcription factor IIF subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules ST
| #2: Protein | Mass: 58343.578 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2F1, RAP74 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2F1, RAP74 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35269 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P35269 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 28427.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2F2, RAP30 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2F2, RAP30 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13984, DNA helicase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P13984, DNA helicase |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 30602.541 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 30482.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase ... , 9 types, 9 molecules opqrstuwy
| #7: Protein | Mass: 217450.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 134041.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: A0A4X1TVZ5, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 31439.074 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 16331.255 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 24644.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 14477.001 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 19314.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #15: Protein | Mass: 14541.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 13310.284 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules vx
| #14: Protein | Mass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #16: Protein | Mass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein/peptide / RNA chain / Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules NZz
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 10 molecules 




| #19: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #20: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | #21: Chemical | ChemComp-W0F / [[( | |
|---|
-Details
| Compound details | ALPHA-AMANITIN, AN AMATOXIN, IS A DI-CYCLIC PEPTIDE. HERE, ALPHA-AMANITIN IS REPRESENTED BY THE ...ALPHA-AMANITIN, AN AMATOXIN, IS A DI-CYCLIC PEPTIDE. HERE, ALPHA-AMANITIN IS REPRESENTE |
|---|---|
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293T Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293T | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.02 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 108001 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj