[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8th4: Structure of AT118-L Nanobody Antagonist in Complex with the Angi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8th4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of AT118-L Nanobody Antagonist in Complex with the Angiotensin II Type I Receptor and Losartan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / G protein-coupled receptor / nanobody / SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationangiotensin type I receptor activity / angiotensin type II receptor activity / phospholipase C-activating angiotensin-activated signaling pathway / regulation of renal sodium excretion / maintenance of blood vessel diameter homeostasis by renin-angiotensin / bradykinin receptor binding / renin-angiotensin regulation of aldosterone production / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis / positive regulation of cholesterol metabolic process / low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling ...angiotensin type I receptor activity / angiotensin type II receptor activity / phospholipase C-activating angiotensin-activated signaling pathway / regulation of renal sodium excretion / maintenance of blood vessel diameter homeostasis by renin-angiotensin / bradykinin receptor binding / renin-angiotensin regulation of aldosterone production / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis / positive regulation of cholesterol metabolic process / low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling / positive regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by renin-angiotensin / regulation of vasoconstriction / Rho protein signal transduction / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / blood vessel diameter maintenance / angiotensin-activated signaling pathway / cell chemotaxis / regulation of cell growth / kidney development / calcium-mediated signaling / electron transport chain / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / positive regulation of inflammatory response / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / regulation of cell population proliferation / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / regulation of inflammatory response / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / electron transfer activity / periplasmic space / iron ion binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / inflammatory response / protein heterodimerization activity / heme binding / symbiont entry into host cell / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Skiba, M.A. / Kruse, A.C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7items United States, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024Title: Antibodies expand the scope of angiotensin receptor pharmacology. Authors: Meredith A Skiba / Sarah M Sterling / Shaun Rawson / Shuhao Zhang / Huixin Xu / Haoran Jiang / Genevieve R Nemeth / Morgan S A Gilman / Joseph D Hurley / Pengxiang Shen / Dean P Staus / ...Authors: Meredith A Skiba / Sarah M Sterling / Shaun Rawson / Shuhao Zhang / Huixin Xu / Haoran Jiang / Genevieve R Nemeth / Morgan S A Gilman / Joseph D Hurley / Pengxiang Shen / Dean P Staus / Jihee Kim / Conor McMahon / Maria K Lehtinen / Howard A Rockman / Patrick Barth / Laura M Wingler / Andrew C Kruse /   Abstract: G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are key regulators of human physiology and are the targets of many small-molecule research compounds and therapeutic drugs. While most of these ligands bind to ...G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are key regulators of human physiology and are the targets of many small-molecule research compounds and therapeutic drugs. While most of these ligands bind to their target GPCR with high affinity, selectivity is often limited at the receptor, tissue and cellular levels. Antibodies have the potential to address these limitations but their properties as GPCR ligands remain poorly characterized. Here, using protein engineering, pharmacological assays and structural studies, we develop maternally selective heavy-chain-only antibody ('nanobody') antagonists against the angiotensin II type I receptor and uncover the unusual molecular basis of their receptor antagonism. We further show that our nanobodies can simultaneously bind to angiotensin II type I receptor with specific small-molecule antagonists and demonstrate that ligand selectivity can be readily tuned. Our work illustrates that antibody fragments can exhibit rich and evolvable pharmacology, attesting to their potential as next-generation GPCR modulators. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8th4.cif.gz 8th4.cif.gz | 196 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8th4.ent.gz pdb8th4.ent.gz | 120.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8th4.json.gz 8th4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/8th4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/8th4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/8th4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/th/8th4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41249MC 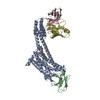 8th3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 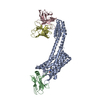
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49501.059 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.) Homo sapiens (human), (gene. exp.)  Gene: AGTR1, AGTR1A, AGTR1B, AT2R1, AT2R1B, cybC / Cell (production host): Expi293 Tet-R / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30556, UniProt: P0ABE7 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P30556, UniProt: P0ABE7 |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 24539.314 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #3: Antibody | Mass: 23541.164 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #4: Antibody | Mass: 15345.063 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-LSN / [ |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: AT118-L Nanobody Antagonist in Complex with the Angiotensin II Type I Receptor BRIL Fusion protein, Anti-BRIL Fab, Anti-Fab Nanobody, and Losartan Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293 Tet-R Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: Expi293 Tet-R |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 0.05% GDN, 0.005% CHS |
| Specimen | Conc.: 7 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 405950 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 238621 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 83.12 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj



















