[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8sps: High resolution structure of ESRRB nucleosome bound OCT4 at site ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8sps | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | High resolution structure of ESRRB nucleosome bound OCT4 at site a and site b | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA / nucleosome / transcription factor / transcription / CHROMATIN BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex / GENE REGULATION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells ...cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells / Specification of the neural plate border / Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells / Germ layer formation at gastrulation / miRNA binding / somatic stem cell population maintenance / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / blastocyst development / anatomical structure morphogenesis / BMP signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / response to wounding / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / regulation of gene expression / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / transcription regulator complex / gene expression / sequence-specific DNA binding / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / chromosome, telomeric region Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lian, T. / Guan, R. / Bai, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: Structural mechanism of LIN28B nucleosome targeting by OCT4. Authors: Ruifang Guan / Tengfei Lian / Bing-Rui Zhou / David Wheeler / Yawen Bai /  Abstract: Pioneer transcription factors are essential for cell fate changes by targeting closed chromatin. OCT4 is a crucial pioneer factor that can induce cell reprogramming. However, the structural basis of ...Pioneer transcription factors are essential for cell fate changes by targeting closed chromatin. OCT4 is a crucial pioneer factor that can induce cell reprogramming. However, the structural basis of how pioneer factors recognize the in vivo nucleosomal DNA targets is unknown. Here, we determine the high-resolution structures of the nucleosome containing human LIN28B DNA and its complexes with the OCT4 DNA binding region. Three OCT4s bind the pre-positioned nucleosome by recognizing non-canonical DNA sequences. Two use their POUS domains while the other uses the POUS-loop-POUHD region; POUHD serves as a wedge to unwrap ∼25 base pair DNA. Our analysis of previous genomic data and determination of the ESRRB-nucleosome-OCT4 structure confirmed the generality of these structural features. Moreover, biochemical studies suggest that multiple OCT4s cooperatively open the H1-condensed nucleosome array containing the LIN28B nucleosome. Thus, our study suggests a mechanism of how OCT4 can target the nucleosome and open closed chromatin. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8sps.cif.gz 8sps.cif.gz | 446 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8sps.ent.gz pdb8sps.ent.gz | 332.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8sps.json.gz 8sps.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8sps_validation.pdf.gz 8sps_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8sps_full_validation.pdf.gz 8sps_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8sps_validation.xml.gz 8sps_validation.xml.gz | 50.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8sps_validation.cif.gz 8sps_validation.cif.gz | 78.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sp/8sps https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sp/8sps ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sp/8sps ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sp/8sps | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  40683MC 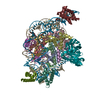 7u0gC 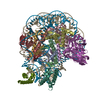 7u0iC 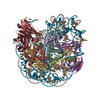 7u0jC  8dk5C  8spuC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 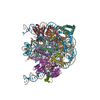
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #1: DNA chain | Mass: 52499.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 11094662 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 11094662 |
|---|---|
| #2: DNA chain | Mass: 51224.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 11094662 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 11094662 |
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules LMAEBFCGDH
| #3: Protein | Mass: 61285.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: malE, NCTC8450_00456, NCTC9775_03059, POU5F1, OCT3, OCT4, OTF3 Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A376KDN7, UniProt: Q01860 #4: Protein | Mass: 15437.167 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Production host:  References: UniProt: P68431 #5: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  References: UniProt: P62805 #6: Protein | Mass: 14017.428 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC20, H2AFQ, HIST2H2AC Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC20, H2AFQ, HIST2H2ACProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q16777 #7: Protein | Mass: 13951.239 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC21, H2BFQ, HIST2H2BE Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2BC21, H2BFQ, HIST2H2BEProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q16778 |
|---|
-Antibody , 1 types, 2 molecules KN
| #8: Antibody | Mass: 29030.146 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Production host:  |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of ESRRB nucleosome bound to OCT4 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.3 | ||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 53.8 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20rc2_4400: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 68790 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj














































