[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-40683: High resolution structure of ESRRB nucleosome bound OCT4 at site ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
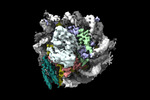
| Title | High resolution structure of ESRRB nucleosome bound OCT4 at site a and site b | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nucleosome / transcription factor / transcription / CHROMATIN BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex / GENE REGULATION / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells ...cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / heart induction / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells / Specification of the neural plate border / Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells / Germ layer formation at gastrulation / miRNA binding / blastocyst development / somatic stem cell population maintenance / carbohydrate transmembrane transporter activity / anatomical structure morphogenesis / BMP signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / telomere organization / Interleukin-7 signaling / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Meiotic synapsis / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / DNA methylation / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / innate immune response in mucosa / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / response to wounding / Meiotic recombination / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / nucleosome / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome assembly / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / outer membrane-bounded periplasmic space / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / chromatin organization / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / regulation of gene expression / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / transcription regulator complex / gene expression / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / chromosome, telomeric region Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lian T / Guan R / Bai Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: Structural mechanism of LIN28B nucleosome targeting by OCT4. Authors: Ruifang Guan / Tengfei Lian / Bing-Rui Zhou / David Wheeler / Yawen Bai /  Abstract: Pioneer transcription factors are essential for cell fate changes by targeting closed chromatin. OCT4 is a crucial pioneer factor that can induce cell reprogramming. However, the structural basis of ...Pioneer transcription factors are essential for cell fate changes by targeting closed chromatin. OCT4 is a crucial pioneer factor that can induce cell reprogramming. However, the structural basis of how pioneer factors recognize the in vivo nucleosomal DNA targets is unknown. Here, we determine the high-resolution structures of the nucleosome containing human LIN28B DNA and its complexes with the OCT4 DNA binding region. Three OCT4s bind the pre-positioned nucleosome by recognizing non-canonical DNA sequences. Two use their POUS domains while the other uses the POUS-loop-POUHD region; POUHD serves as a wedge to unwrap ∼25 base pair DNA. Our analysis of previous genomic data and determination of the ESRRB-nucleosome-OCT4 structure confirmed the generality of these structural features. Moreover, biochemical studies suggest that multiple OCT4s cooperatively open the H1-condensed nucleosome array containing the LIN28B nucleosome. Thus, our study suggests a mechanism of how OCT4 can target the nucleosome and open closed chromatin. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_40683.map.gz emd_40683.map.gz | 26.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-40683-v30.xml emd-40683-v30.xml emd-40683.xml emd-40683.xml | 22.9 KB 22.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_40683.png emd_40683.png | 68.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-40683.cif.gz emd-40683.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_40683_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40683_half_map_1.map.gz emd_40683_half_map_2.map.gz emd_40683_half_map_2.map.gz | 48.9 MB 48.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40683 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40683 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40683 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-40683 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_40683_validation.pdf.gz emd_40683_validation.pdf.gz | 910.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_40683_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_40683_full_validation.pdf.gz | 910 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_40683_validation.xml.gz emd_40683_validation.xml.gz | 11.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_40683_validation.cif.gz emd_40683_validation.cif.gz | 14 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40683 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40683 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40683 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-40683 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8spsMC  7u0gC  7u0iC  7u0jC  8dk5C  8spuC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_40683.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_40683.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
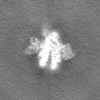
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.056 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
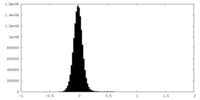
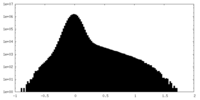
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_40683_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
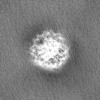
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
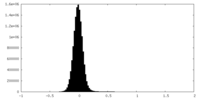
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_40683_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
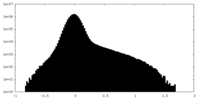
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of ESRRB nucleosome bound to OCT4
| Entire | Name: Complex of ESRRB nucleosome bound to OCT4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of ESRRB nucleosome bound to OCT4
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of ESRRB nucleosome bound to OCT4 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: DNA (168-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (168-MER) / type: dna / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.499562 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT) (DC)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC) GENBANK: GENBANK: AC016543.6 |
-Macromolecule #2: DNA (168-MER)
| Macromolecule | Name: DNA (168-MER) / type: dna / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.224516 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DT) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) ...String: (DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DC) (DT) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DG)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DG)(DA)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DT)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DT) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DT) GENBANK: GENBANK: AC016543.6 |
-Macromolecule #3: Maltodextrin-binding protein,POU domain, class 5, transcription f...
| Macromolecule | Name: Maltodextrin-binding protein,POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.285703 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKEAKIEEGK LVIWINGDKG YNGLAEVGKK FEKDTGIKVT VEHPDKLEEK FPQVAATGDG PDIIFWAHDR FGGYAQSGLL AEITPDKAF QDKLYPFTWD AVRYNGKLIA YPIAVEALSL IYNKDLLPNP PKTWEEIPAL DKELKAKGKS ALMFNLQEPY F TWPLIAAD ...String: MKEAKIEEGK LVIWINGDKG YNGLAEVGKK FEKDTGIKVT VEHPDKLEEK FPQVAATGDG PDIIFWAHDR FGGYAQSGLL AEITPDKAF QDKLYPFTWD AVRYNGKLIA YPIAVEALSL IYNKDLLPNP PKTWEEIPAL DKELKAKGKS ALMFNLQEPY F TWPLIAAD GGYAFKYENG KYDIKDVGVD NAGAKAGLTF LVDLIKNKHM NADTDYSIAE AAFNKGETAM TINGPWAWSN ID TSKVNYG VTVLPTFKGQ PSKPFVGVLS AGINAASPNK ELAKEFLENY LLTDEGLEAV NKDKPLGAVA LKSYEEELAK DPR IAATME NAQKGEIMPN IPQMSAFWYA VRTAVINAAS GRQTVDAALA AAQTNAGSEN LYFQGSVDSA AASDIKALQK ELEQ FAKLL KQKRITLGYT QADVGLTLGV LFGKVFSQTT ICRFEALQLS FKNMCKLRPL LQKWVEEADN NENLQEICKA ETLVQ ARKR KRTSIENRVR GNLENLFLQC PKPTLQQISH IAQQLGLEKD VVRVWFCNRR QKGKRSSSEF HHHHHH UniProtKB: Maltodextrin-binding protein, POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H3.1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.437167 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MARTKQTARK STGGKAPRKQ LATKAARKSA PATGGVKKPH RYRPGTVALR EIRRYQKSTE LLIRKLPFQR LVREIAQDFK TDLRFQSSA VMALQEACEA YLVGLFEDTN LCAIHAKRVT IMPKDIQLAR RIRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.1 |
-Macromolecule #5: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.394426 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKGGKG LGKGGAKRHR KVLRDNIQGI TKPAIRRLAR RGGVKRISGL IYEETRGVLK VFLENVIRDA VTYTEHAKRK TVTAMDVVY ALKRQGRTLY GFGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #6: Histone H2A type 2-C
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 2-C / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.017428 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSGRGKQGGK ARAKAKSRSS RAGLQFPVGR VHRLLRKGNY AERVGAGAPV YMAAVLEYLT AEILELAGNA ARDNKKTRII PRHLQLAIR NDEELNKLLG KVTIAQGGVL PNIQAVLLPK KTESHKAKSK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 2-C |
-Macromolecule #7: Histone H2B type 2-E
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 2-E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.951239 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPEPAKSAPA PKKGSKKAVT KAQKKDGKKR KRSRKESYSI YVYKVLKQVH PDTGISSKAM GIMNSFVNDI FERIAGEASR LAHYNKRST ITSREIQTAV RLLLPGELAK HAVSEGTKAV TKYTSSK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 2-E |
-Macromolecule #8: ScFv
| Macromolecule | Name: ScFv / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.030146 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MKSSHHHHHH ENLYFQSNAM EVQLQQSGPE LVEPGTSVKM PCKASGYTFT SYTIQWVKQT PRQGLEWIGY IYPYNAGTKY NEKFKGKAT LTSDKSSSTV YMELSSLTSE DSAVYYCARK SSRLRSTLDY WGQGTSVTVS SGGGGSGGGG SGGGGSMDIK M TQSPSSMH ...String: MKSSHHHHHH ENLYFQSNAM EVQLQQSGPE LVEPGTSVKM PCKASGYTFT SYTIQWVKQT PRQGLEWIGY IYPYNAGTKY NEKFKGKAT LTSDKSSSTV YMELSSLTSE DSAVYYCARK SSRLRSTLDY WGQGTSVTVS SGGGGSGGGG SGGGGSMDIK M TQSPSSMH ASLGERVTIT CKASQDIRSY LSWYQQKPWK SPKTLIYYAT SLADGVPSRF SGSGSGQDFS LTINNLESDD TA TYYCLQH GESPYTFGSG TKLEIKRA |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.3 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 53.8 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 68790 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)