[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
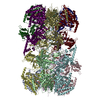
Yorodumi- PDB-8rig: Cryo-EM structure of an MCM helicase single hexamer loaded onto dsDNA. -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8rig | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of an MCM helicase single hexamer loaded onto dsDNA. | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION / MCM helicase / DNA replication | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / MCM complex binding / nuclear DNA replication / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / mitotic DNA replication ...MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / MCM complex binding / nuclear DNA replication / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / mitotic DNA replication / CMG complex / nuclear pre-replicative complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / nuclear replication fork / DNA replication origin binding / DNA replication initiation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / DNA helicase activity / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / heterochromatin formation / single-stranded DNA binding / DNA helicase / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.41 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Miller, T.C.R. / Lim, C.T. / Diffley, J.F.X. / Costa, A. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, United Kingdom, European Union,  Denmark, 6items Denmark, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Cell cycle regulation has shaped replication origins in budding yeast. Authors: Chew Theng Lim / Thomas C R Miller / Kang Wei Tan / Saurabh Talele / Anne Early / Philip East / Humberto Sánchez / Nynke H Dekker / Alessandro Costa / John F X Diffley /    Abstract: Eukaryotic DNA replication initiates from genomic loci known as origins. At budding yeast origins like ARS1, a double hexamer (DH) of the MCM replicative helicase is assembled by origin recognition ...Eukaryotic DNA replication initiates from genomic loci known as origins. At budding yeast origins like ARS1, a double hexamer (DH) of the MCM replicative helicase is assembled by origin recognition complex (ORC), Cdc6 and Cdt1 by sequential hexamer loading from two opposed ORC binding sites. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibits DH assembly, which prevents re-replication by restricting helicase loading to the G1 phase. Here, we show that an intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in the Orc2 subunit promotes interaction between ORC and the first loaded, closed-ring MCM hexamer (the MCM-ORC (MO) intermediate). CDK-dependent phosphorylation of this IDR blocks MO formation and DH assembly. We show that MO stabilizes ORC at lower-affinity binding sites required for second hexamer loading. Origins comprising two high-affinity ORC sites can assemble DH efficiently without MO by independently loading single hexamers. Strikingly, these origins escape CDK inhibition in vitro and in vivo. Our work reveals mechanistic plasticity in MCM loading with implications for understanding how CDK regulation has shaped yeast origin evolution and how natural, strong origins might escape cell cycle regulation. We also identify key steps common to loading pathways, with implications for understanding how MCM is loaded in other eukaryotes. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8rig.cif.gz 8rig.cif.gz | 714.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8rig.ent.gz pdb8rig.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8rig.json.gz 8rig.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ri/8rig https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ri/8rig ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ri/8rig ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ri/8rig | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  19187MC  8rifC  9i3iC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 5 types, 5 molecules 23467
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98911.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 111720.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: MCM3 contains a CBP-TEV tag at the N-terminus: KRRWKKNFIAVSAANRFKKISSSGALENLYFQG Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 105138.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 113110.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 95049.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules 5
| #4: Protein | Mass: 86505.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 5804.773 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 5211.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 17 molecules 






| #9: Chemical | | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #12: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Hexameric MCM helicase complex loaded onto duplex DNA / Type: COMPLEX Details: Structural intermediate on path to MCM-double hexamer formation during the process of origin licensing. Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.61 MDa |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Complete biochemical reaction containing the MCM helicase in complex with Cdt1, the helicase loader (the origin recognition complex), the co-factor Cdc6, an origin or replication (DNA) ...Details: Complete biochemical reaction containing the MCM helicase in complex with Cdt1, the helicase loader (the origin recognition complex), the co-factor Cdc6, an origin or replication (DNA) flanked by nucleosomes, the regulatory kinase CDK and an inhibitor of CDK (Sic1). The sample was incubated with ATP yielding a range of structural intermediates in the MCM loading pathway. |
| Specimen support | Details: Glow discharge at 40 mA for 5 minutes prior to applying graphene oxide. Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 51.2 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 24506 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 / Used frames/image: 1-40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 621909 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.41 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 396366 Details: Reported resolution obtained from maps after Relion 3D Refinement Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7P30 Accession code: 7P30 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj