+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8qr1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human Tip60 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Eukaryotic transcription / Histone acetyltransferase / chromatin remodeling / Complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpiccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / sperm DNA condensation / histone chaperone activity / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / cellular response to cytochalasin B ...piccolo histone acetyltransferase complex / promoter-enhancer loop anchoring activity / telomerase RNA localization to Cajal body / positive regulation of norepinephrine uptake / regulation of DNA strand elongation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / sperm DNA condensation / histone chaperone activity / establishment of protein localization to chromatin / cellular response to cytochalasin B / R2TP complex / bBAF complex / npBAF complex / regulation of transepithelial transport / nBAF complex / dynein axonemal particle / brahma complex / morphogenesis of a polarized epithelium / neural retina development / protein localization to adherens junction / postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / Swr1 complex / structural constituent of postsynaptic actin cytoskeleton / protein antigen binding / GBAF complex / Formation of annular gap junctions / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / Tat protein binding / Gap junction degradation / regulation of G0 to G1 transition / Folding of actin by CCT/TriC / dense body / Cell-extracellular matrix interactions / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / Ino80 complex / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / Prefoldin mediated transfer of substrate to CCT/TriC / RSC-type complex / apical protein localization / regulation of double-strand break repair / blastocyst formation / box C/D snoRNP assembly / adherens junction assembly / RHOF GTPase cycle / Adherens junctions interactions / tight junction / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / protein folding chaperone complex / Interaction between L1 and Ankyrins / SWI/SNF complex / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / regulation of norepinephrine uptake / apical junction complex / transporter regulator activity / nitric-oxide synthase binding / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / spinal cord development / regulation of chromosome organization / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / establishment or maintenance of cell polarity / cortical cytoskeleton / spermatid development / RUNX1 interacts with co-factors whose precise effect on RUNX1 targets is not known / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / Transcriptional Regulation by E2F6 / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in pigmentation / Recycling pathway of L1 / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of DNA replication / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / brush border / regulation of embryonic development / MLL1 complex / kinesin binding / somatic stem cell population maintenance / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells / negative regulation of cell differentiation / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of DNA repair / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA helicase activity / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / TBP-class protein binding / cytoskeleton organization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / substantia nigra development / calyx of Held Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Li, C. / Smirnova, E. / Schnitzler, C. / Crucifix, C. / Concordet, J.P. / Brion, A. / Poterszman, A. / Schultz, P. / Papai, G. / Ben-Shem, A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1items France, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structure of the human TIP60-C histone exchange and acetyltransferase complex. Authors: Changqing Li / Ekaterina Smirnova / Charlotte Schnitzler / Corinne Crucifix / Jean Paul Concordet / Alice Brion / Arnaud Poterszman / Patrick Schultz / Gabor Papai / Adam Ben-Shem /  Abstract: Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two ...Chromatin structure is a key regulator of DNA transcription, replication and repair. In humans, the TIP60-EP400 complex (TIP60-C) is a 20-subunit assembly that affects chromatin structure through two enzymatic activities: ATP-dependent exchange of histone H2A-H2B for H2A.Z-H2B, and histone acetylation. In yeast, however, these activities are performed by two independent complexes-SWR1 and NuA4, respectively. How the activities of the two complexes are merged into one supercomplex in humans, and what this association entails for the structure and mechanism of the proteins and their recruitment to chromatin, are unknown. Here we describe the structure of the endogenous human TIP60-C. We find a three-lobed architecture composed of SWR1-like (SWR1L) and NuA4-like (NuA4L) parts, which associate with a TRRAP activator-binding module. The huge EP400 subunit contains the ATPase motor, traverses the junction between SWR1L and NuA4L twice and constitutes the scaffold of the three-lobed architecture. NuA4L is completely rearranged compared with its yeast counterpart. TRRAP is flexibly tethered to NuA4L-in stark contrast to its robust connection to the completely opposite side of NuA4 in yeast. A modelled nucleosome bound to SWR1L, supported by tests of TIP60-C activity, suggests that some aspects of the histone exchange mechanism diverge from what is seen in yeast. Furthermore, a fixed actin module (as opposed to the mobile actin subcomplex in SWR1; ref. ), the flexibility of TRRAP and the weak effect of extranucleosomal DNA on exchange activity lead to a different, activator-based mode of enlisting TIP60-C to chromatin. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8qr1.cif.gz 8qr1.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8qr1.ent.gz pdb8qr1.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8qr1.json.gz 8qr1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qr/8qr1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qr/8qr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qr/8qr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qr/8qr1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18611MC  8qriC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 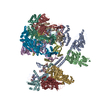
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 8 types, 13 molecules ACFSBGKLIEHDJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 343867.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562References: UniProt: Q96L91, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 93589.172 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9H2F5 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9H2F5 | ||||||
| #3: Protein | Mass: 53090.699 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9NPF5 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9NPF5 | ||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 40658.363 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q15906 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q15906 | ||||||
| #5: Protein | Mass: 41782.660 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: P60709 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: P60709#6: Protein | | Mass: 47509.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: O96019 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: O96019#7: Protein | Mass: 50296.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9Y265, DNA helicase Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9Y265, DNA helicase#8: Protein | Mass: 51222.465 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9Y230, DNA helicase Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: K562 / References: UniProt: Q9Y230, DNA helicase |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Tip60 complex / Type: CELL / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 / Cellular location: nucleus Homo sapiens (human) / Strain: K562 / Cellular location: nucleus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS | ||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | ||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE | ||||||||||||
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER | ||||||||||||
| Image recording |
|
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 284286 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 180397 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj



























