+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8q4d | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | IstA-IstB(E167Q) Strand Transfer Complex | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA transposition / DNA integration / transposon / transpososome / holo-transpososome / insertion sequence / IS21 / IstA / IstB / DDE transposase / DDE domain / AAA+ ATPase / DNA strand transfer complex / STC | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtransposition / DNA strand exchange activity / DNA integration / DNA replication / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.62 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | de la Gandara, A. / Spinola-Amilibia, M. / Araujo-Bazan, L. / Nunez-Ramirez, R. / Berger, J.M. / Arias-Palomo, E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Spain, 2items Spain, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Molecular basis for transposase activation by a dedicated AAA+ ATPase. Authors: Álvaro de la Gándara / Mercedes Spínola-Amilibia / Lidia Araújo-Bazán / Rafael Núñez-Ramírez / James M Berger / Ernesto Arias-Palomo /   Abstract: Transposases drive chromosomal rearrangements and the dissemination of drug-resistance genes and toxins. Although some transposases act alone, many rely on dedicated AAA+ ATPase subunits that ...Transposases drive chromosomal rearrangements and the dissemination of drug-resistance genes and toxins. Although some transposases act alone, many rely on dedicated AAA+ ATPase subunits that regulate site selectivity and catalytic function through poorly understood mechanisms. Using IS21 as a model transposase system, we show how an ATPase regulator uses nucleotide-controlled assembly and DNA deformation to enable structure-based site selectivity, transposase recruitment, and activation and integration. Solution and cryogenic electron microscopy studies show that the IstB ATPase self-assembles into an autoinhibited pentamer of dimers that tightly curves target DNA into a half-coil. Two of these decamers dimerize, which stabilizes the target nucleic acid into a kinked S-shaped configuration that engages the IstA transposase at the interface between the two IstB oligomers to form an approximately 1 MDa transpososome complex. Specific interactions stimulate regulator ATPase activity and trigger a large conformational change on the transposase that positions the catalytic site to perform DNA strand transfer. These studies help explain how AAA+ ATPase regulators-which are used by classical transposition systems such as Tn7, Mu and CRISPR-associated elements-can remodel their substrate DNA and cognate transposases to promote function. | |||||||||
| History |
|
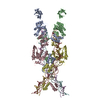
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8q4d.cif.gz 8q4d.cif.gz | 2.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8q4d.ent.gz pdb8q4d.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8q4d.json.gz 8q4d.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4d https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4d ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q4/8q4d | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18144MC  8q3wC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 24 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWX
| #1: Protein | Mass: 44012.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria)Plasmid: 2-Cc-T Details (production host): TEV cleavable MBP-His6 tag at the C-terminus Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 28817.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 20 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: E167Q mutant Source: (gene. exp.)   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria)Plasmid: pHMKS Details (production host): TEV cleavable MBP-His6 tag at the N-terminus Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 1 types, 2 molecules ad
| #3: DNA chain | Mass: 36524.391 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: complete sequence of the right terminal inverted repeat (TIR) covalently bound to a target DNA Source: (synth.)   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1801971458 Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1801971458 |
|---|
-DNA (58-MER) / ... , 2 types, 4 molecules becf
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 17767.412 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: complementary sequence of the right terminal inverted repeat (TIR) Source: (synth.)   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1190175513 Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1190175513#5: DNA chain | Mass: 17836.412 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Details: complementary sequence of the target DNA / Source: (synth.)   Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1801971458 Geobacillus stearothermophilus (bacteria) / References: GenBank: 1801971458 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 40 molecules 




| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #7: Chemical | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.952 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.1 sec. / Electron dose: 51.3 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: Super-resolution counting mode | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 4102640 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.62 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 272218 / Num. of class averages: 3 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 91.21 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj









































