[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
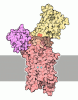
Yorodumi- PDB-8ox9: Cryo-EM structure of ATP8B1-CDC50A in E2P active conformation wit... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ox9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of ATP8B1-CDC50A in E2P active conformation with bound PC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / lipid transporter autoinhibition P-type ATPase P4-ATPase CDC50A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvestibulocochlear nerve formation / regulation of plasma membrane organization / regulation of microvillus assembly / phosphatidylcholine flippase activity / positive regulation of phospholipid translocation / aminophospholipid flippase activity / aminophospholipid transport / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / protein localization to endosome / phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex ...vestibulocochlear nerve formation / regulation of plasma membrane organization / regulation of microvillus assembly / phosphatidylcholine flippase activity / positive regulation of phospholipid translocation / aminophospholipid flippase activity / aminophospholipid transport / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / protein localization to endosome / phospholipid-translocating ATPase complex / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / phosphatidylcholine floppase activity / xenobiotic transmembrane transport / stereocilium / cardiolipin binding / bile acid metabolic process / P-type phospholipid transporter / inner ear receptor cell development / apical protein localization / phospholipid translocation / azurophil granule membrane / bile acid and bile salt transport / transport vesicle membrane / Golgi organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / specific granule membrane / regulation of chloride transport / trans-Golgi network / sensory perception of sound / positive regulation of neuron projection development / late endosome membrane / early endosome membrane / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / apical plasma membrane / nuclear body / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / Neutrophil degranulation / structural molecule activity / magnesium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dieudonne, T. / Kummerer, F. / Juknaviciute Laursen, M. / Stock, C. / Kock Flygaard, R. / Khalid, S. / Lenoir, G. / Lyons, J.A. / Lindorff-Larsen, K. / Nissen, P. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Denmark, Denmark,  France, France,  United Kingdom, 8items United Kingdom, 8items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Activation and substrate specificity of the human P4-ATPase ATP8B1. Authors: Thibaud Dieudonné / Felix Kümmerer / Michelle Juknaviciute Laursen / Charlott Stock / Rasmus Kock Flygaard / Syma Khalid / Guillaume Lenoir / Joseph A Lyons / Kresten Lindorff-Larsen / Poul Nissen /    Abstract: Asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in eukaryotic membranes is essential for cell integrity, signaling pathways, and vesicular trafficking. P4-ATPases, also known as flippases, participate in ...Asymmetric distribution of phospholipids in eukaryotic membranes is essential for cell integrity, signaling pathways, and vesicular trafficking. P4-ATPases, also known as flippases, participate in creating and maintaining this asymmetry through active transport of phospholipids from the exoplasmic to the cytosolic leaflet. Here, we present a total of nine cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human flippase ATP8B1-CDC50A complex at 2.4 to 3.1 Å overall resolution, along with functional and computational studies, addressing the autophosphorylation steps from ATP, substrate recognition and occlusion, as well as a phosphoinositide binding site. We find that the P4-ATPase transport site is occupied by water upon phosphorylation from ATP. Additionally, we identify two different autoinhibited states, a closed and an outward-open conformation. Furthermore, we identify and characterize the PI(3,4,5)P binding site of ATP8B1 in an electropositive pocket between transmembrane segments 5, 7, 8, and 10. Our study also highlights the structural basis of a broad lipid specificity of ATP8B1 and adds phosphatidylinositol as a transport substrate for ATP8B1. We report a critical role of the sn-2 ester bond of glycerophospholipids in substrate recognition by ATP8B1 through conserved S403. These findings provide fundamental insights into ATP8B1 catalytic cycle and regulation, and substrate recognition in P4-ATPases. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ox9.cif.gz 8ox9.cif.gz | 275.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ox9.ent.gz pdb8ox9.ent.gz | 213.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ox9.json.gz 8ox9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ox/8ox9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ox/8ox9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ox/8ox9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ox/8ox9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17261MC  8ox4C  8ox5C  8ox6C  8ox7C  8ox8C  8oxaC  8oxbC  8oxcC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 136283.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP8B1, ATPIC, FIC1, PFIC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATP8B1, ATPIC, FIC1, PFIC / Production host:  References: UniProt: O43520, P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 41085.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TMEM30A, C6orf67, CDC50A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TMEM30A, C6orf67, CDC50A / Production host:  |
-Sugars , 2 types, 3 molecules 
| #3: Polysaccharide | beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta- ...beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source |
|---|---|
| #8: Sugar |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 13 molecules 








| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-BEF / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( |
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-IP9 / ( |
| #9: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ATP8B1-CDC50A complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.185 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: 50 mM MOPS-Tris pH 7, 100 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 5 mM MgCl2 supplemented with 0.03 mg.mL-1 LMNG, 0.003 mg.mL-1 CHS, PI(3,4,5)P3 0.0015 mg.mL-1 and 1 mM BeCl3 + 4 mM KF and 0.003 mg.mL-1 POPC |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1900 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.72 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 256001 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7PY4 Accession code: 7PY4 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj