+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8jd5 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
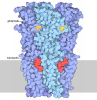
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Gi1-bound mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimer | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Complex structure / Gi1-bound mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimer | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationadenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of response to drug / group II metabotropic glutamate receptor activity / adenylate cyclase inhibiting G protein-coupled glutamate receptor activity / intracellular glutamate homeostasis / behavioral response to nicotine / neurotransmitter secretion / G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / astrocyte projection ...adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of response to drug / group II metabotropic glutamate receptor activity / adenylate cyclase inhibiting G protein-coupled glutamate receptor activity / intracellular glutamate homeostasis / behavioral response to nicotine / neurotransmitter secretion / G protein-coupled glutamate receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / astrocyte projection / Class C/3 (Metabotropic glutamate/pheromone receptors) / glutamate receptor activity / glutamate secretion / long-term synaptic depression / regulation of glutamate secretion / cellular response to stress / regulation of dopamine secretion / positive regulation of protein localization to cell cortex / Adenylate cyclase inhibitory pathway / T cell migration / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / D2 dopamine receptor binding / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / response to prostaglandin E / G protein-coupled serotonin receptor binding / adenylate cyclase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting serotonin receptor signaling pathway / calcium channel regulator activity / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / cellular response to forskolin / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / Regulation of insulin secretion / response to cocaine / positive regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process / G protein-coupled receptor binding / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-modulating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / response to peptide hormone / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / centriolar satellite / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / G-protein activation / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / photoreceptor disc membrane / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / GDP binding / G alpha (z) signalling events / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / GPER1 signaling / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / G-protein beta-subunit binding / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / sensory perception of taste / extracellular vesicle / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / presynapse / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / presynaptic membrane / G protein activity / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / retina development in camera-type eye / midbody / cell cortex / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / cytoplasmic vesicle / fibroblast proliferation / scaffold protein binding / G alpha (i) signalling events / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / gene expression / chemical synaptic transmission / G alpha (q) signalling events / postsynaptic membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, X. / Wang, M. / Xu, T. / Feng, Y. / Han, S. / Zhao, Q. / Wu, B. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 2items China, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2023Title: Structural insights into dimerization and activation of the mGlu2-mGlu3 and mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimers. Authors: Xinwei Wang / Mu Wang / Tuo Xu / Ye Feng / Qiang Shao / Shuo Han / Xiaojing Chu / Yechun Xu / Shuling Lin / Qiang Zhao / Beili Wu /  Abstract: Heterodimerization of the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlus) has shown importance in the functional modulation of the receptors and offers potential drug targets for treating central nervous ...Heterodimerization of the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGlus) has shown importance in the functional modulation of the receptors and offers potential drug targets for treating central nervous system diseases. However, due to a lack of molecular details of the mGlu heterodimers, understanding of the mechanisms underlying mGlu heterodimerization and activation is limited. Here we report twelve cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the mGlu2-mGlu3 and mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimers in different conformational states, including inactive, intermediate inactive, intermediate active and fully active conformations. These structures provide a full picture of conformational rearrangement of mGlu2-mGlu3 upon activation. The Venus flytrap domains undergo a sequential conformational change, while the transmembrane domains exhibit a substantial rearrangement from an inactive, symmetric dimer with diverse dimerization patterns to an active, asymmetric dimer in a conserved dimerization mode. Combined with functional data, these structures reveal that stability of the inactive conformations of the subunits and the subunit-G protein interaction pattern are determinants of asymmetric signal transduction of the heterodimers. Furthermore, a novel binding site for two mGlu4 positive allosteric modulators was observed in the asymmetric dimer interfaces of the mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimer and mGlu4 homodimer, and may serve as a drug recognition site. These findings greatly extend our knowledge about signal transduction of the mGlus. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8jd5.cif.gz 8jd5.cif.gz | 442.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8jd5.ent.gz pdb8jd5.ent.gz | 336.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8jd5.json.gz 8jd5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jd/8jd5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jd/8jd5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jd/8jd5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jd/8jd5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  36176MC  8jcuC  8jcvC  8jcwC  8jcxC  8jcyC  8jczC  8jd0C  8jd1C  8jd2C  8jd3C  8jd4C  8jd6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Metabotropic glutamate receptor ... , 2 types, 2 molecules 24
| #1: Protein | Mass: 95684.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRM2, GPRC1B, MGLUR2 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRM2, GPRC1B, MGLUR2Production host:  References: UniProt: Q14416 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 102560.789 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRM4, GPRC1D, MGLUR4 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GRM4, GPRC1D, MGLUR4Production host:  References: UniProt: Q14833 |
-Guanine nucleotide-binding protein ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #3: Protein | Mass: 40414.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAI1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAI1 / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P63096 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P63096 |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 38744.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P62873 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P62873 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 7861.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P59768 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P59768 |
-Antibody / Sugars , 2 types, 3 molecules H

| #11: Sugar | | #6: Antibody | | Mass: 27409.588 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 10 molecules 
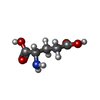







| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-HZR / | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #8: Chemical | | #9: Chemical | ChemComp-CLR / #10: Chemical | ChemComp-PEF / | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-BQI / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Gi1-bound mGlu2-mGlu4 heterodimer / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 70 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 939819 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 97.22 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 PDBj
PDBj