+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8h1t | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of BAP1-ASXL1 bound to chromatosome | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / nucleosome / histone deubiquitination / chromatin | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthrombocyte differentiation / nucleate erythrocyte differentiation / PR-DUB complex / platelet morphogenesis / histone H2A deubiquitinase activity / positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / lung saccule development / macrophage homeostasis / leukocyte proliferation / podocyte development ...thrombocyte differentiation / nucleate erythrocyte differentiation / PR-DUB complex / platelet morphogenesis / histone H2A deubiquitinase activity / positive regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / lung saccule development / macrophage homeostasis / leukocyte proliferation / podocyte development / negative regulation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / myeloid cell apoptotic process / neutrophil differentiation / regulation of kidney size / hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis / common myeloid progenitor cell proliferation / monoubiquitinated protein deubiquitination / tissue homeostasis / protein K48-linked deubiquitination / negative regulation of DNA recombination / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding / chromosome condensation / hypothalamus gonadotrophin-releasing hormone neuron development / bone marrow development / female meiosis I / positive regulation of protein monoubiquitination / positive regulation of protein targeting to mitochondrion / fat pad development / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / nucleosomal DNA binding / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / erythrocyte maturation / female gonad development / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation / seminiferous tubule development / regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / male meiosis I / hemopoiesis / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / homeostasis of number of cells / protein deubiquitination / response to retinoic acid / heart morphogenesis / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / heterochromatin / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / energy homeostasis / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / regulation of neuron apoptotic process / neuron projection morphogenesis / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / telomere organization / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Interleukin-7 signaling / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / Pexophagy / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ge, W. / Yu, C. / Xu, R.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4items China, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Basis of the H2AK119 specificity of the Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase. Authors: Weiran Ge / Cong Yu / Jingjing Li / Zhenyu Yu / Xiaorong Li / Yan Zhang / Chao-Pei Liu / Yingfeng Li / Changlin Tian / Xinzheng Zhang / Guohong Li / Bing Zhu / Rui-Ming Xu /  Abstract: Repression of gene expression by protein complexes of the Polycomb group is a fundamental mechanism that governs embryonic development and cell-type specification. The Polycomb repressive ...Repression of gene expression by protein complexes of the Polycomb group is a fundamental mechanism that governs embryonic development and cell-type specification. The Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex removes the ubiquitin moiety from monoubiquitinated histone H2A K119 (H2AK119ub1) on the nucleosome, counteracting the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) to facilitate the correct silencing of genes by Polycomb proteins and safeguard active genes from inadvertent silencing by PRC1 (refs. ). The intricate biological function of PR-DUB requires accurate targeting of H2AK119ub1, but PR-DUB can deubiquitinate monoubiquitinated free histones and peptide substrates indiscriminately; the basis for its exquisite nucleosome-dependent substrate specificity therefore remains unclear. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structure of human PR-DUB, composed of BAP1 and ASXL1, in complex with the chromatosome. We find that ASXL1 directs the binding of the positively charged C-terminal extension of BAP1 to nucleosomal DNA and histones H3-H4 near the dyad, an addition to its role in forming the ubiquitin-binding cleft. Furthermore, a conserved loop segment of the catalytic domain of BAP1 is situated near the H2A-H2B acidic patch. This distinct nucleosome-binding mode displaces the C-terminal tail of H2A from the nucleosome surface, and endows PR-DUB with the specificity for H2AK119ub1. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8h1t.cif.gz 8h1t.cif.gz | 471.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8h1t.ent.gz pdb8h1t.ent.gz | 353.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8h1t.json.gz 8h1t.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8h1t_validation.pdf.gz 8h1t_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8h1t_full_validation.pdf.gz 8h1t_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8h1t_validation.xml.gz 8h1t_validation.xml.gz | 58.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8h1t_validation.cif.gz 8h1t_validation.cif.gz | 90.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h1/8h1t https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h1/8h1t ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h1/8h1t ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/h1/8h1t | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  34431MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 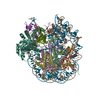
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 8 types, 12 molecules AEBFCGDHKLMN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15437.167 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14137.537 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC7, H2AFG, HIST1H2AD / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H2AC7, H2AFG, HIST1H2AD / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 13951.239 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H2BE, H2BFQ / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H2BE, H2BFQ / Production host:  #7: Protein | | Mass: 23190.926 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H1-4, H1F4, HIST1H1E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H1-4, H1F4, HIST1H1E / Production host:  #8: Protein | | Mass: 80456.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C91S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BAP1, KIAA0272, hucep-6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: BAP1, KIAA0272, hucep-6 / Production host:  #9: Protein | | Mass: 8576.831 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: UBB / Production host:  #10: Protein | | Mass: 41788.602 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASXL1, KIAA0978 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASXL1, KIAA0978 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 57438.527 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 58030.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of BAP1-ASXL1 bound to chromatosome / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 284 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20_4444: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 95225 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj























































