+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8eza | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | NHEJ Long-range complex with PAXX | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / Complex / Kinase / NHEJ / DNA BINDING PROTEIN / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / positive regulation of platelet formation / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA double-strand break attachment to nuclear envelope / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex ...FHA domain binding / positive regulation of chromosome organization / positive regulation of ligase activity / DNA ligase IV complex / DNA ligase activity / positive regulation of platelet formation / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / DNA double-strand break attachment to nuclear envelope / DNA ligase (ATP) / Ku70:Ku80 complex / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of t-circle formation / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA end binding / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nonhomologous end joining complex / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / single strand break repair / immature B cell differentiation / V(D)J recombination / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / cellular response to X-ray / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / isotype switching / nuclear telomere cap complex / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / protein localization to site of double-strand break / telomere capping / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / recombinational repair / regulation of telomere maintenance / positive regulation of neurogenesis / U3 snoRNA binding / protein localization to chromosome, telomeric region / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / T cell lineage commitment / cellular response to lithium ion / DNA biosynthetic process / cellular hyperosmotic salinity response / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / 2-LTR circle formation / B cell lineage commitment / response to ionizing radiation / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / AMP binding / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / ligase activity / telomeric repeat DNA binding / DNA 3'-5' helicase / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of protein kinase activity / T cell differentiation / somatic stem cell population maintenance / 5'-deoxyribose-5-phosphate lyase activity / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / chromosome organization / response to X-ray / somitogenesis / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / telomere maintenance via telomerase / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / site of DNA damage / condensed chromosome / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / DNA polymerase binding / neurogenesis / activation of innate immune response / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / DNA helicase activity / telomere maintenance / B cell differentiation / cyclin binding / DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase / stem cell proliferation / central nervous system development / positive regulation of translation / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / cellular response to ionizing radiation / response to gamma radiation / protein modification process / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / small-subunit processome / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / protein-DNA complex / cellular response to gamma radiation / regulation of circadian rhythm / brain development / base-excision repair Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.39 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, S. / He, Y. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM visualization of DNA-PKcs structural intermediates in NHEJ. Authors: Siyu Chen / Alex Vogt / Linda Lee / Tasmin Naila / Ryan McKeown / Alan E Tomkinson / Susan P Lees-Miller / Yuan He /   Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), one of the most cytotoxic forms of DNA damage, can be repaired by the tightly regulated nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) machinery (Stinson and Loparo and Zhao ). ...DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), one of the most cytotoxic forms of DNA damage, can be repaired by the tightly regulated nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) machinery (Stinson and Loparo and Zhao ). Core NHEJ factors form an initial long-range (LR) synaptic complex that transitions into a DNA-PKcs (DNA-dependent protein kinase, catalytic subunit)-free, short-range state to align the DSB ends (Chen ). Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, we have visualized three additional key NHEJ complexes representing different transition states, with DNA-PKcs adopting distinct dimeric conformations within each of them. Upon DNA-PKcs autophosphorylation, the LR complex undergoes a substantial conformational change, with both Ku and DNA-PKcs rotating outward to promote DNA break exposure and DNA-PKcs dissociation. We also captured a dimeric state of catalytically inactive DNA-PKcs, which resembles structures of other PIKK (Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase) family kinases, revealing a model of the full regulatory cycle of DNA-PKcs during NHEJ. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8eza.cif.gz 8eza.cif.gz | 2.1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8eza.ent.gz pdb8eza.ent.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8eza.json.gz 8eza.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ez/8eza https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ez/8eza ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ez/8eza ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ez/8eza | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28732MC  8ez9C 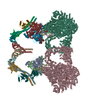 8ezbC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 12 molecules STLCHIFGOPXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21663.498 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAXX, C9orf142, XLS / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PAXX, C9orf142, XLS / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 469673.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P78527 Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: UniProt: P78527#8: Protein | Mass: 33372.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NHEJ1, XLF / Production host:  #9: Protein | Mass: 38337.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XRCC4 / Production host:  #10: Protein | Mass: 104124.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: LIG4 / Production host:  |
|---|
-X-ray repair cross-complementing protein ... , 2 types, 4 molecules JAKB
| #2: Protein | Mass: 69945.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P12956 unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P12956#3: Protein | Mass: 82812.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P13010 unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P13010 |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 4 molecules MDNE
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 9510.159 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#7: DNA chain | Mass: 9236.976 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Protein/peptide / Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules RQ

| #11: Chemical | | #5: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1720.111 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line: HELA / References: non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: NHEJ Long-range complex with PAXX / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7, #9-#10, #8 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.75 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 302 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 60000 X / Calibrated magnification: 60000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 2000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 4000 nm / Cs: 2 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 70 K / Temperature (min): 70 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4 sec. / Electron dose: 65 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 11006 |
| Image scans | Width: 5760 / Height: 4092 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1101255 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.39 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 138252 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj