[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8efh: Helical reconstruction of the human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-myo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8efh | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Helical reconstruction of the human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-myosin complex in complex with ADP-Mg2+ | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / actin / tropomyosin / myosin / cardiac | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / bleb / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber ...regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / bleb / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber / myosin filament / ruffle organization / adult heart development / Striated Muscle Contraction / cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress / muscle filament sliding / myosin complex / myosin II complex / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / microfilament motor activity / heart contraction / myosin binding / regulation of heart contraction / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / myofibril / mesenchyme migration / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / Smooth Muscle Contraction / skeletal muscle contraction / striated muscle contraction / ATP metabolic process / cytoskeletal protein binding / cardiac muscle contraction / stress fiber / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of cell adhesion / regulation of heart rate / muscle contraction / negative regulation of cell migration / actin filament organization / sarcomere / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / actin filament / filopodium / wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / Z disc / actin filament binding / regulation of cell shape / lamellipodium / actin cytoskeleton / cell body / actin binding / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / positive regulation of gene expression / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Doran, M.H. / Lehman, W. / Rynkiewicz, M.J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Gen Physiol / Year: 2023 Journal: J Gen Physiol / Year: 2023Title: Conformational changes linked to ADP release from human cardiac myosin bound to actin-tropomyosin. Authors: Matthew H Doran / Michael J Rynkiewicz / David Rasicci / Skylar M L Bodt / Meaghan E Barry / Esther Bullitt / Christopher M Yengo / Jeffrey R Moore / William Lehman /  Abstract: Following binding to the thin filament, β-cardiac myosin couples ATP-hydrolysis to conformational rearrangements in the myosin motor that drive myofilament sliding and cardiac ventricular ...Following binding to the thin filament, β-cardiac myosin couples ATP-hydrolysis to conformational rearrangements in the myosin motor that drive myofilament sliding and cardiac ventricular contraction. However, key features of the cardiac-specific actin-myosin interaction remain uncertain, including the structural effect of ADP release from myosin, which is rate-limiting during force generation. In fact, ADP release slows under experimental load or in the intact heart due to the afterload, thereby adjusting cardiac muscle power output to meet physiological demands. To further elucidate the structural basis of this fundamental process, we used a combination of cryo-EM reconstruction methodologies to determine structures of the human cardiac actin-myosin-tropomyosin filament complex at better than 3.4 Å-resolution in the presence and in the absence of Mg2+·ADP. Focused refinements of the myosin motor head and its essential light chains in these reconstructions reveal that small changes in the nucleotide-binding site are coupled to significant rigid body movements of the myosin converter domain and a 16-degree lever arm swing. Our structures provide a mechanistic framework to understand the effect of ADP binding and release on human cardiac β-myosin, and offer insights into the force-sensing mechanism displayed by the cardiac myosin motor. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8efh.cif.gz 8efh.cif.gz | 513.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8efh.ent.gz pdb8efh.ent.gz | 419.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8efh.json.gz 8efh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ef/8efh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28082MC 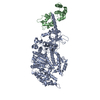 8efdC  8efeC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 99157.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYH7, MYHCB / Cell line (production host): C2C12 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYH7, MYHCB / Cell line (production host): C2C12 / Production host:  | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 42064.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 32763.621 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TPM1, C15orf13, TMSA / Production host:  #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / Has ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.13 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 15 mA was used in the Pelco Easiglow glow discharge machine Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 80000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 3.12 sec. / Electron dose: 53.7 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 4 / Num. of real images: 3961 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1_4122: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: -166.8 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 27.9 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 628787 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 131194 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6X5Z Accession code: 6X5Z / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj
















