[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28082: Helical reconstruction of the human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-myo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Helical reconstruction of the human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-myosin complex in complex with ADP-Mg2+ | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Primary map used for model building of the helical reconstruction of the actin-tropomyosin-B-cardiac myosin II complex with ADP-Mg2 bound. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | actin / tropomyosin / myosin / cardiac / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / bleb / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber ...regulation of slow-twitch skeletal muscle fiber contraction / regulation of the force of skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of heart rate by epinephrine / muscle thin filament tropomyosin / actin-myosin filament sliding / muscle myosin complex / regulation of muscle contraction / bleb / regulation of the force of heart contraction / transition between fast and slow fiber / myosin filament / ruffle organization / adult heart development / Striated Muscle Contraction / muscle filament sliding / cardiac muscle hypertrophy in response to stress / myosin complex / myosin II complex / structural constituent of muscle / sarcomere organization / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue morphogenesis / microfilament motor activity / heart contraction / myosin binding / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / regulation of heart contraction / myofibril / mesenchyme migration / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / Smooth Muscle Contraction / striated muscle contraction / ATP metabolic process / skeletal muscle contraction / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / cytoskeletal protein binding / stress fiber / cytoskeleton organization / positive regulation of cell adhesion / regulation of heart rate / muscle contraction / negative regulation of cell migration / actin filament organization / sarcomere / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / actin filament / filopodium / wound healing / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / ruffle membrane / Z disc / actin filament binding / regulation of cell shape / lamellipodium / actin cytoskeleton / actin binding / cell body / cytoskeleton / calmodulin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / positive regulation of gene expression / protein homodimerization activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
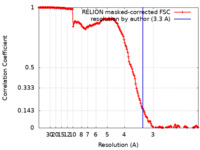
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Doran MH / Lehman W / Rynkiewicz MJ | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Gen Physiol / Year: 2023 Journal: J Gen Physiol / Year: 2023Title: Conformational changes linked to ADP release from human cardiac myosin bound to actin-tropomyosin. Authors: Matthew H Doran / Michael J Rynkiewicz / David Rasicci / Skylar M L Bodt / Meaghan E Barry / Esther Bullitt / Christopher M Yengo / Jeffrey R Moore / William Lehman /  Abstract: Following binding to the thin filament, β-cardiac myosin couples ATP-hydrolysis to conformational rearrangements in the myosin motor that drive myofilament sliding and cardiac ventricular ...Following binding to the thin filament, β-cardiac myosin couples ATP-hydrolysis to conformational rearrangements in the myosin motor that drive myofilament sliding and cardiac ventricular contraction. However, key features of the cardiac-specific actin-myosin interaction remain uncertain, including the structural effect of ADP release from myosin, which is rate-limiting during force generation. In fact, ADP release slows under experimental load or in the intact heart due to the afterload, thereby adjusting cardiac muscle power output to meet physiological demands. To further elucidate the structural basis of this fundamental process, we used a combination of cryo-EM reconstruction methodologies to determine structures of the human cardiac actin-myosin-tropomyosin filament complex at better than 3.4 Å-resolution in the presence and in the absence of Mg2+·ADP. Focused refinements of the myosin motor head and its essential light chains in these reconstructions reveal that small changes in the nucleotide-binding site are coupled to significant rigid body movements of the myosin converter domain and a 16-degree lever arm swing. Our structures provide a mechanistic framework to understand the effect of ADP binding and release on human cardiac β-myosin, and offer insights into the force-sensing mechanism displayed by the cardiac myosin motor. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28082.map.gz emd_28082.map.gz | 181.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28082-v30.xml emd-28082-v30.xml emd-28082.xml emd-28082.xml | 24.8 KB 24.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_28082_fsc.xml emd_28082_fsc.xml | 15.6 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_28082.png emd_28082.png | 69.2 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_28082_msk_1.map emd_28082_msk_1.map | 325 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28082.cif.gz emd-28082.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28082_additional_1.map.gz emd_28082_additional_1.map.gz emd_28082_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28082_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28082_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28082_half_map_2.map.gz | 297.8 MB 259.4 MB 259.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28082 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28082 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28082 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8efhMC  8efdC  8efeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28082.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28082.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 325 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Primary map used for model building of the helical reconstruction of the actin-tropomyosin-B-cardiac myosin II complex with ADP-Mg2 bound. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
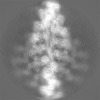
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.078 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
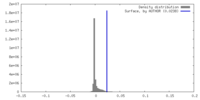
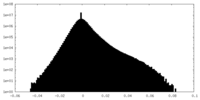
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_28082_msk_1.map emd_28082_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
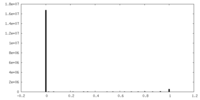
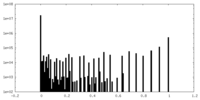
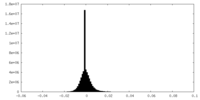
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Non-locally-filtered map associated with primary map.
| File | emd_28082_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Non-locally-filtered map associated with primary map. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1.
| File | emd_28082_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2.
| File | emd_28082_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-beta-myosin II complex bound to A...
| Entire | Name: Human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-beta-myosin II complex bound to ADPMg2+. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-beta-myosin II complex bound to A...
| Supramolecule | Name: Human cardiac actin-tropomyosin-beta-myosin II complex bound to ADPMg2+. type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 Details: Cardiac actomyosin-tropomyosin complex with ADPMg2+ bound to the myosin motor head. |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Cardiac F-actin complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Cardiac F-actin complex / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 / Details: F-actin forms the backbone of the complex |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Human beta-cardiac myosin II
| Supramolecule | Name: Human beta-cardiac myosin II / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: The motor domain of the myosin saturates the actin filament. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: Human cardiac tropomyosin
| Supramolecule | Name: Human cardiac tropomyosin / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 / Details: Tropomyosin wraps around the F-actin core. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: beta-cardiac myosin II
| Macromolecule | Name: beta-cardiac myosin II / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 99.157695 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGDSEMAVFG AAAPYLRKSE KERLEAQTRP FDLKKDVFVP DDKQEFVKAK IVSREGGKVT AETEYGKTVT VKEDQVMQQN PPKFDKIED MAMLTFLHEP AVLYNLKDRY GSWMIYTYSG LFCVTVNPYK WLPVYTPEVV AAYRGKKRSE APPHIFSISD N AYQYMLTD ...String: MGDSEMAVFG AAAPYLRKSE KERLEAQTRP FDLKKDVFVP DDKQEFVKAK IVSREGGKVT AETEYGKTVT VKEDQVMQQN PPKFDKIED MAMLTFLHEP AVLYNLKDRY GSWMIYTYSG LFCVTVNPYK WLPVYTPEVV AAYRGKKRSE APPHIFSISD N AYQYMLTD RENQSILITG ESGAGKTVNT KRVIQYFAVI AAIGDRSKKD QSPGKGTLED QIIQANPALE AFGNAKTVRN DN SSRFGKF IRIHFGATGK LASADIETYL LEKSRVIFQL KAERDYHIFY QILSNKKPEL LDMLLITNNP YDYAFISQGE TTV ASIDDA EELMATDNAF DVLGFTSEEK NSMYKLTGAI MHFGNMKFKL KQREEQAEPD GTEEADKSAY LMGLNSADLL KGLC HPRVK VGNEYVTKGQ NVQQVIYATG ALAKAVYERM FNWMVTRINA TLETKQPRQY FIGVLDIAGF EIFDFNSFEQ LCINF TNEK LQQFFNHHMF VLEQEEYKKE GIEWTFIDFG MDLQACIDLI EKPMGIMSIL EEECMFPKAT DMTFKAKLFD NHLGKS ANF QKPRNIKGKP EAHFSLIHYA GIVDYNIIGW LQKNKDPLNE TVVGLYQKSS LKLLSTLFAN YAGADAPIEK GKGKAKK GS SFQTVSALHR ENLNKLMTNL RSTHPHFVRC IIPNETKSPG VMDNPLVMHQ LRCNGVLEGI RICRKGFPNR ILYGDFRQ R YRILNPAAIP EGQFIDSRKG AEKLLSSLDI DHNQYKFGHT KVFFKAGLLG LLEEMRDERL SRIITRIQAQ SRGVLARME YKKLLERRDS LLVIQWNIRA FMGVKNWPWM KLYFKIKPLL KSGLNDIFEA QKIEWHEDYK DDDDK UniProtKB: Myosin-7 |
-Macromolecule #2: Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.064891 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCDDEETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY ...String: MCDDEETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY EGYALPHAIM RLDLAGRDLT DYLMKILTER GYSFVTTAER EIVRDIKEKL CYVALDFENE MATAASSSSL EK SYELPDG QVITIGNERF RCPETLFQPS FIGMESAGIH ETTYNSIMKC DIDIRKDLYA NNVLSGGTTM YPGIADRMQK EIT ALAPST MKIKIIAPPE RKYSVWIGGS ILASLSTFQQ MWISKQEYDE AGPSIVHRKC F UniProtKB: Actin alpha cardiac muscle 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.763621 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDAIKKKMQM LKLDKENALD RAEQAEADKK AAEDRSKQLE DELVSLQKKL KGTEDELDKY SEALKDAQEK LELAEKKATD AEADVASLN RRIQLVEEEL DRAQERLATA LQKLEEAEKA ADESERGMKV IESRAQKDEE KMEIQEIQLK EAKHIAEDAD R KYEEVARK ...String: MDAIKKKMQM LKLDKENALD RAEQAEADKK AAEDRSKQLE DELVSLQKKL KGTEDELDKY SEALKDAQEK LELAEKKATD AEADVASLN RRIQLVEEEL DRAQERLATA LQKLEEAEKA ADESERGMKV IESRAQKDEE KMEIQEIQLK EAKHIAEDAD R KYEEVARK LVIIESDLER AEERAELSEG KCAELEEELK TVTNNLKSLE AQAEKYSQKE DRYEEEIKVL SDKLKEAETR AE FAERSVT KLEKSIDDLE DELYAQKLKY KAISEELDHA LNDMTSI UniProtKB: Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.13 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. Details: 15 mA was used in the Pelco Easiglow glow discharge machine |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 4 / Number real images: 3961 / Average exposure time: 3.12 sec. / Average electron dose: 53.7 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.7000000000000001 µm / Nominal magnification: 80000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)