+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ebs | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Initial DNA-lesion (Cy5) binding by XPC and TFIIH | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN/DNA / Protein-DNA complex / DNA BINDING PROTEIN-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationXPC complex / 9+2 motile cilium / MMXD complex / core TFIIH complex portion of holo TFIIH complex / photoreceptor connecting cilium / Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly / DNA damage sensor activity / central nervous system myelin formation / transcription export complex 2 / heterotrimeric G-protein binding ...XPC complex / 9+2 motile cilium / MMXD complex / core TFIIH complex portion of holo TFIIH complex / photoreceptor connecting cilium / Cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly / DNA damage sensor activity / central nervous system myelin formation / transcription export complex 2 / heterotrimeric G-protein binding / regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of mitotic recombination / hair cell differentiation / hair follicle maturation / nucleotide-excision repair factor 3 complex / nucleotide-excision repair, preincision complex assembly / nuclear pore nuclear basket / CAK-ERCC2 complex / embryonic cleavage / DNA 5'-3' helicase / UV protection / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / transcription factor TFIIH core complex / transcription factor TFIIH holo complex / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / nuclear thyroid hormone receptor binding / cellular response to interleukin-7 / transcription preinitiation complex / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / DNA 3'-5' helicase / RNA polymerase II general transcription initiation factor activity / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / transcription factor TFIID complex / erythrocyte maturation / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / spinal cord development / hematopoietic stem cell proliferation / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / proteasome binding / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / bone mineralization / mRNA Capping / centriole replication / ATPase activator activity / DNA topological change / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / glial cell projection / embryonic organ development / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / mRNA transport / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / response to UV / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / hormone-mediated signaling pathway / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / extracellular matrix organization / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / centriole / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling pathway / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / DNA helicase activity / proteasome complex / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / ubiquitin binding / Josephin domain DUBs / regulation of cytokinesis / post-embryonic development / determination of adult lifespan / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / nucleotide-excision repair / chromosome segregation / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / promoter-specific chromatin binding / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / cellular response to gamma radiation / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kim, J. / Yang, W. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Japan, 3items Japan, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Lesion recognition by XPC, TFIIH and XPA in DNA excision repair. Authors: Jinseok Kim / Chia-Lung Li / Xuemin Chen / Yanxiang Cui / Filip M Golebiowski / Huaibin Wang / Fumio Hanaoka / Kaoru Sugasawa / Wei Yang /     Abstract: Nucleotide excision repair removes DNA lesions caused by ultraviolet light, cisplatin-like compounds and bulky adducts. After initial recognition by XPC in global genome repair or a stalled RNA ...Nucleotide excision repair removes DNA lesions caused by ultraviolet light, cisplatin-like compounds and bulky adducts. After initial recognition by XPC in global genome repair or a stalled RNA polymerase in transcription-coupled repair, damaged DNA is transferred to the seven-subunit TFIIH core complex (Core7) for verification and dual incisions by the XPF and XPG nucleases. Structures capturing lesion recognition by the yeast XPC homologue Rad4 and TFIIH in transcription initiation or DNA repair have been separately reported. How two different lesion recognition pathways converge and how the XPB and XPD helicases of Core7 move the DNA lesion for verification are unclear. Here we report on structures revealing DNA lesion recognition by human XPC and DNA lesion hand-off from XPC to Core7 and XPA. XPA, which binds between XPB and XPD, kinks the DNA duplex and shifts XPC and the DNA lesion by nearly a helical turn relative to Core7. The DNA lesion is thus positioned outside of Core7, as would occur with RNA polymerase. XPB and XPD, which track the lesion-containing strand but translocate DNA in opposite directions, push and pull the lesion-containing strand into XPD for verification. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ebs.cif.gz 8ebs.cif.gz | 728.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ebs.ent.gz pdb8ebs.ent.gz | 566.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ebs.json.gz 8ebs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eb/8ebs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eb/8ebs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eb/8ebs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/eb/8ebs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27996MC  8ebtC  8ebuC  8ebvC  8ebwC  8ebxC  8ebyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules ABHIJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 89404.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC3, XPB, XPBC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC3, XPB, XPBC / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 88018.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC2, XPD, XPDC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC2, XPD, XPDC / Production host:  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 107437.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XPC, hCG_27237 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: XPC, hCG_27237 / Production host:  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 44275.055 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD23B / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAD23B / Production host:  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 19769.486 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CETN2, CALT, CEN2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CETN2, CALT, CEN2 / Production host:  |
-General transcription factor IIH subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules CDEFG
| #3: Protein | Mass: 62116.492 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H1, BTF2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H1, BTF2 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 52245.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H4 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 46926.648 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H2, BTF2P44 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H2, BTF2P44 / Production host:  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 34416.008 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H3 / Production host:  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 8060.362 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H5, C6orf175, TTDA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GTF2H5, C6orf175, TTDA / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules LM
| #11: DNA chain | Mass: 16345.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #12: DNA chain | Mass: 16219.405 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 8 molecules 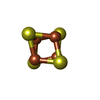




| #13: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 / | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #14: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #15: Chemical | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: bulky DNA lesion recognition complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#12 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.58 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1600 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.5 sec. / Electron dose: 54.1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 6243 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1645921 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 278447 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6NMI Accession code: 6NMI / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj