+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8duj | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Global map in C1 of RyR1 particles in complex with ImperaCalcin | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / ryanodine receptor / ion channel / snake toxin / calcin / complex / toxin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATP-gated ion channel activity / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine receptor complex / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity ...ATP-gated ion channel activity / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine receptor complex / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / response to redox state / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / ossification involved in bone maturation / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / 'de novo' protein folding / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / negative regulation of heart rate / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / cellular response to caffeine / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / skin development / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / FK506 binding / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / organelle membrane / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / outflow tract morphogenesis / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / protein phosphatase activator activity / Long-term potentiation / Calcineurin activates NFAT / smooth muscle contraction / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / catalytic complex / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / toxic substance binding / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / T cell proliferation / striated muscle contraction / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / skeletal muscle fiber development / Ion homeostasis / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / eNOS activation / titin binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / calcium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / substantia nigra development / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / muscle contraction / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / cellular response to calcium ion / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / protein maturation / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcoplasmic reticulum / sarcomere Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)  Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Haji-Ghassemi, O. / Van Petegm, F. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 2items Canada, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM analysis of scorpion toxin binding to Ryanodine Receptors reveals subconductance that is abolished by PKA phosphorylation. Authors: Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Yu Seby Chen / Kellie Woll / Georgina B Gurrola / Carmen R Valdivia / Wenxuan Cai / Songhua Li / Hector H Valdivia / Filip Van Petegem /     Abstract: Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that ...Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that control release of Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcins target RyRs and induce long-lived subconductance states, whereby single-channel currents are decreased. We used cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the binding and structural effects of imperacalcin, showing that it opens the channel pore and causes large asymmetry throughout the cytosolic assembly of the tetrameric RyR. This also creates multiple extended ion conduction pathways beyond the transmembrane region, resulting in subconductance. Phosphorylation of imperacalcin by protein kinase A prevents its binding to RyR through direct steric hindrance, showing how posttranslational modifications made by the host organism can determine the fate of a natural toxin. The structure provides a direct template for developing calcin analogs that result in full channel block, with potential to treat RyR-related disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8duj.cif.gz 8duj.cif.gz | 2.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8duj.ent.gz pdb8duj.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8duj.json.gz 8duj.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8duj_validation.pdf.gz 8duj_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8duj_full_validation.pdf.gz 8duj_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8duj_validation.xml.gz 8duj_validation.xml.gz | 362.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8duj_validation.cif.gz 8duj_validation.cif.gz | 580.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duj https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duj ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/du/8duj | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27721MC  8drpC  8dtbC  8dveC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 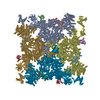
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules M
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3776.495 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) / References: UniProt: P59868 Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) / References: UniProt: P59868 |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 12 molecules GADJHBEKICFL
| #2: Protein | Mass: 565908.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 11667.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP1B, FKBP12.6, FKBP1L, FKBP9, OTK4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP1B, FKBP12.6, FKBP1L, FKBP9, OTK4 / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 16620.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Mutation: E32A, E68A, E105A, E141A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 16 molecules 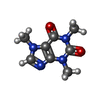






| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-CFF / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #7: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RyR1 in complex with ImperaCalcin in presence of Caffeine/CaM1234/Calcium/ATP Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 2.2 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 144529 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6M2W Accession code: 6M2W / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

























