[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-27721: Global map in C1 of RyR1 particles in complex with ImperaCalcin -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Global map in C1 of RyR1 particles in complex with ImperaCalcin | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ryanodine receptor / ion channel / snake toxin / calcin / complex / membrane protein / toxin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATP-gated ion channel activity / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / ryanodine receptor complex ...ATP-gated ion channel activity / positive regulation of sequestering of calcium ion / negative regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / negative regulation of insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / neuronal action potential propagation / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / insulin secretion involved in cellular response to glucose stimulus / terminal cisterna / ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / ryanodine receptor complex / CaM pathway / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / response to redox state / ossification involved in bone maturation / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / negative regulation of heart rate / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / cellular response to caffeine / 'de novo' protein folding / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / skin development / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / FK506 binding / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / organelle membrane / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / smooth endoplasmic reticulum / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / outflow tract morphogenesis / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / smooth muscle contraction / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / toxic substance binding / catalytic complex / T cell proliferation / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / striated muscle contraction / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cellular response to interferon-beta / skeletal muscle fiber development / presynaptic cytosol / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / eNOS activation / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / sperm midpiece / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane / regulation of heart rate / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / cellular response to calcium ion / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / muscle contraction / calyx of Held / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein maturation / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) / Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Haji-Ghassemi O / Van Petegm F | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 2 items Canada, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM analysis of scorpion toxin binding to Ryanodine Receptors reveals subconductance that is abolished by PKA phosphorylation. Authors: Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Yu Seby Chen / Kellie Woll / Georgina B Gurrola / Carmen R Valdivia / Wenxuan Cai / Songhua Li / Hector H Valdivia / Filip Van Petegem /     Abstract: Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that ...Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that control release of Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcins target RyRs and induce long-lived subconductance states, whereby single-channel currents are decreased. We used cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the binding and structural effects of imperacalcin, showing that it opens the channel pore and causes large asymmetry throughout the cytosolic assembly of the tetrameric RyR. This also creates multiple extended ion conduction pathways beyond the transmembrane region, resulting in subconductance. Phosphorylation of imperacalcin by protein kinase A prevents its binding to RyR through direct steric hindrance, showing how posttranslational modifications made by the host organism can determine the fate of a natural toxin. The structure provides a direct template for developing calcin analogs that result in full channel block, with potential to treat RyR-related disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27721.map.gz emd_27721.map.gz | 321.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27721-v30.xml emd-27721-v30.xml emd-27721.xml emd-27721.xml | 25.4 KB 25.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27721_fsc.xml emd_27721_fsc.xml | 14.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27721.png emd_27721.png | 82.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27721.cif.gz emd-27721.cif.gz | 10.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27721_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27721_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27721_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27721_half_map_2.map.gz | 318.2 MB 318.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27721 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27721 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27721 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27721 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dujMC  8drpC  8dtbC  8dveC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27721.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27721.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
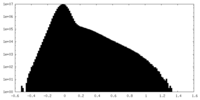
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_27721_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
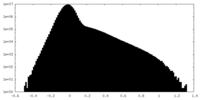
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_27721_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : RyR1 in complex with ImperaCalcin in presence of Caffeine/CaM1234...
| Entire | Name: RyR1 in complex with ImperaCalcin in presence of Caffeine/CaM1234/Calcium/ATP |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: RyR1 in complex with ImperaCalcin in presence of Caffeine/CaM1234...
| Supramolecule | Name: RyR1 in complex with ImperaCalcin in presence of Caffeine/CaM1234/Calcium/ATP type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.2 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Imperacalcin
| Macromolecule | Name: Imperacalcin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) Pandinus imperator (emperor scorpion) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 3.776495 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GDCLPHLKRC KADNDCCGKK CKRRGTNAEK RCR UniProtKB: Imperacalcin |
-Macromolecule #2: Ryanodine receptor 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Ryanodine receptor 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 565.908625 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MGDGGEGEDE VQFLRTDDEV VLQCSATVLK EQLKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE PTSNAQNVPP DLAICCFTLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEAG VESSQGGGHR TLLYGHAILL RHAHSRMYLS CLTTSRSMTD KLAFDVGLQE DATGEACWWT MHPASKQRSE G EKVRVGDD ...String: MGDGGEGEDE VQFLRTDDEV VLQCSATVLK EQLKLCLAAE GFGNRLCFLE PTSNAQNVPP DLAICCFTLE QSLSVRALQE MLANTVEAG VESSQGGGHR TLLYGHAILL RHAHSRMYLS CLTTSRSMTD KLAFDVGLQE DATGEACWWT MHPASKQRSE G EKVRVGDD LILVSVSSER YLHLSTASGE LQVDASFMQT LWNMNPICSC CEEGYVTGGH VLRLFHGHMD ECLTISAADS DD QRRLVYY EGGAVCTHAR SLWRLEPLRI SWSGSHLRWG QPLRIRHVTT GRYLALTEDQ GLVVVDACKA HTKATSFCFR VSK EKLDTA PKRDVEGMGP PEIKYGESLC FVQHVASGLW LTYAAPDPKA LRLGVLKKKA ILHQEGHMDD ALFLTRCQQE ESQA ARMIH STAGLYNQFI KGLDSFSGKP RGSGPPAGPA LPIEAVILSL QDLIGYFEPP SEELQHEEKQ SKLRSLRNRQ SLFQE EGML SLVLNCIDRL NVYTTAAHFA EYAGEEAAES WKEIVNLLYE LLASLIRGNR ANCALFSTNL DWVVSKLDRL EASSGI LEV LYCVLIESPE VLNIIQENHI KSIISLLDKH GRNHKVLDVL CSLCVCNGVA VRSNQDLITE NLLPGRELLL QTNLINY VT SIRPNIFVGR AEGSTQYGKW YFEVMVDEVV PFLTAQATHL RVGWALTEGY SPYPGGGEGW GGNGVGDDLY SYGFDGLH L WTGHVARPVT SPGQHLLAPE DVVSCCLDLS VPSISFRING CPVQGVFEAF NLDGLFFPVV SFSAGVKVRF LLGGRHGEF KFLPPPGYAP CHEAVLPRER LRLEPIKEYR REGPRGPHLV GPSRCLSHTD FVPCPVDTVQ IVLPPHLERI REKLAENIHE LWALTRIEQ GWTYGPVRDD NKRLHPCLVN FHSLPEPERN YNLQMSGETL KTLLALGCHV GMADEKAEDN LKKTKLPKTY M MSNGYKPA PLDLSHVRLT PAQTTLVDRL AENGHNVWAR DRVAQGWSYS AVQDIPARRN PRLVPYRLLD EATKRSNRDS LC QAVRTLL GYGYNIEPPD QEPSQVENQS RWDRVRIFRA EKSYTVQSGR WYFEFEAVTT GEMRVGWARP ELRPDVELGA DEL AYVFNG HRGQRWHLGS EPFGRPWQSG DVVGCMIDLT ENTIIFTLNG EVLMSDSGSE TAFREIEIGD GFLPVCSLGP GQVG HLNLG QDVSSLRFFA ICGLQEGFEP FAINMQRPVT TWFSKSLPQF EPVPPEHPHY EVARMDGTVD TPPCLRLAHR TWGSQ NSLV EMLFLRLSLP VQFHQHFRCT AGATPLAPPG LQPPAEDEAR AAEPDPDYEN LRRSAGGWGE AEGGKEGTAK EGTPGG TPQ PGVEAQPVRA ENEKDATTEK NKKRGFLFKA KKAAMMTQPP ATPALPRLPH DVVPADNRDD PEIILNTTTY YYSVRVF AG QEPSCVWVGW VTPDYHQHDM NFDLSKVRAV TVTMGDEQGN VHSSLKCSNC YMVWGGDFVS PGQQGRISHT DLVIGCLV D LATGLMTFTA NGKESNTFFQ VEPNTKLFPA VFVLPTHQNV IQFELGKQKN IMPLSAAMFL SERKNPAPQC PPRLEVQML MPVSWSRMPN HFLQVETRRA GERLGWAVQC QDPLTMMALH IPEENRCMDI LELSERLDLQ RFHSHTLRLY RAVCALGNNR VAHALCSHV DQAQLLHALE DAHLPGPLRA GYYDLLISIH LESACRSRRS MLSEYIVPLT PETRAITLFP PGRKGGNARR H GLPGVGVT TSLRPPHHFS PPCFVAALPA AGVAEAPARL SPAIPLEALR DKALRMLGEA VRDGGQHARD PVGGSVEFQF VP VLKLVST LLVMGIFGDE DVKQILKMIE PEVFTEEEEE EEEEEEEEEE EEEDEEEKEE DEEEEEKEDA EKEEEEAPEG EKE DLEEGL LQMKLPESVK LQMCNLLEYF CDQELQHRVE SLAAFAERYV DKLQANQRSR YALLMRAFTM SAAETARRTR EFRS PPQEQ INMLLHFKDE ADEEDCPLPE DIRQDLQDFH QDLLAHCGIQ LEGEEEEPEE ETSLSSRLRS LLETVRLVKK KEEKP EEEL PAEEKKPQSL QELVSHMVVR WAQEDYVQSP ELVRAMFSLL HRQYDGLGEL LRALPRAYTI SPSSVEDTMS LLECLG QIR SLLIVQMGPQ EENLMIQSIG NIMNNKVFYQ HPNLMRALGM HETVMEVMVN VLGGGETKEI RFPKMVTSCC RFLCYFC RI SRQNQRSMFD HLSYLLENSG IGLGMQGSTP LDVAAASVID NNELALALQE QDLEKVVSYL AGCGLQSCPM LLAKGYPD I GWNPCGGERY LDFLRFAVFV NGESVEENAN VVVRLLIRKP ECFGPALRGE GGSGLLAAIE EAIRISEDPA RDGPGVRRD RRREHFGEEP PEENRVHLGH AIMSFYAALI DLLGRCAPEM HLIQAGKGEA LRIRAILRSL VPLDDLVGII SLPLQIPTLG KDGALVQPK MSASFVPDHK ASMVLFLDRV YGIENQDFLL HVLDVGFLPD MRAAASLDTA TFSTTEMALA LNRYLCLAVL P LITKCAPL FAGTEHRAIM VDSMLHTVYR LSRGRSLTKA QRDVIEDCLM ALCRYIRPSM LQHLLRRLVF DVPILNEFAK MP LKLLTNH YERCWKYYCL PTGWANFGVT SEEELHLTRK LFWGIFDSLA HKKYDQELYR MAMPCLCAIA GALPPDYVDA SYS SKAEKK ATVDAEGNFD PRPVETLNVI IPEKLDSFIN KFAEYTHEKW AFDKIQNNWS YGENVDEELK THPMLRPYKT FSEK DKEIY RWPIKESLKA MIAWEWTIEK AREGEEERTE KKKTRKISQT AQTYDPREGY NPQPPDLSGV TLSRELQAMA EQLAE NYHN TWGRKKKQEL EAKGGGTHPL LVPYDTLTAK EKARDREKAQ ELLKFLQMNG YAVTRGLKDM ELDTSSIEKR FAFGFL QQL LRWMDISQEF IAHLEAVVSS GRVEKSPHEQ EIKFFAKILL PLINQYFTNH CLYFLSTPAK VLGSGGHASN KEKEMIT SL FCKLAALVRH RVSLFGTDAP AVVNCLHILA RSLDARTVMK SGPEIVKAGL RSFFESASED IEKMVENLRL GKVSQART Q VKGVGQNLTY TTVALLPVLT TLFQHIAQHQ FGDDVILDDV QVSCYRTLCS IYSLGTTKNT YVEKLRPALG ECLARLAAA MPVAFLEPQL NEYNACSVYT TKSPRERAIL GLPNSVEEMC PDIPVLDRLM ADIGGLAESG ARYTEMPHVI EITLPMLCSY LPRWWERGP EAPPPALPAG APPPCTAVTS DHLNSLLGNI LRIIVNNLGI DEATWMKRLA VFAQPIVSRA RPELLHSHFI P TIGRLRKR AGKVVAEEEQ LRLEAKAEAE EGELLVRDEF SVLCRDLYAL YPLLIRYVDN NRAHWLTEPN ANAEELFRMV GE IFIYWSK SHNFKREEQN FVVQNEINNM SFLTADSKSK MAKAGDAQSG GSDQERTKKK RRGDRYSVQT SLIVATLKKM LPI GLNMCA PTDQDLIMLA KTRYALKDTD EEVREFLQNN LHLQGKVEGS PSLRWQMALY RGLPGREEDA DDPEKIVRRV QEVS AVLYH LEQTEHPYKS KKAVWHKLLS KQRRRAVVAC FRMTPLYNLP THRACNMFLE SYKAAWILTE DHSFEDRMID DLSKA GEQE EEEEEVEEKK PDPLHQLVLH FSRTALTEKS KLDEDYLYMA YADIMAKSCH LEEGGENGEA EEEEVEVSFE EKEMEK QRL LYQQSRLHTR GAAEMVLQMI SACKGETGAM VSSTLKLGIS ILNGGNAEVQ QKMLDYLKDK KEVGFFQSIQ ALMQTCS VL DLNAFERQNK AEGLGMVNED GTVINRQNGE KVMADDEFTQ DLFRFLQLLC EGHNNDFQNY LRTQTGNTTT INIIICTV D YLLRLQESIS DFYWYYSGKD VIEEQGKRNF SKAMSVAKQV FNSLTEYIQG PCTGNQQSLA HSRLWDAVVG FLHVFAHMM MKLAQDSSQI ELLKELLDLQ KDMVVMLLSL LEGNVVNGMI ARQMVDMLVE SSSNVEMILK FFDMFLKLKD IVGSEAFQDY VTDPRGLIS KKDFQKAMDS QKQFTGPEIQ FLLSCSEADE NEMINFEEFA NRFQEPARDI GFNVAVLLTN LSEHVPHDPR L RNFLELAE SILEYFRPYL GRIEIMGASR RIERIYFEIS ETNRAQWEMP QVKESKRQFI FDVVNEGGEA EKMELFVSFC ED TIFEMQI AAQISEPEGE PEADEDEGMG EAAAEGAEEG AAGAEGAAGT VAAGATARLA AAAARALRGL SYRSLRRRVR RLR RLTARE AATALAALLW AVVARAGAAG AGAAAGALRL LWGSLFGGGL VEGAKKVTVT ELLAGMPDPT SDEVHGEQPA GPGG DADGA GEGEGEGDAA EGDGDEEVAG HEAGPGGAEG VVAVADGGPF RPEGAGGLGD MGDTTPAEPP TPEGSPILKR KLGVD GEEE ELVPEPEPEP EPEPEKADEE NGEKEEVPEA PPEPPKKAPP SPPAKKEEAG GAGMEFWGEL EVQRVKFLNY LSRNFY TLR FLALFLAFAI NFILLFYKVS DSPPGEDDME GSAAGDLAGA GSGGGSGWGS GAGEEAEGDE DENMVYYFLE ESTGYME PA LWCLSLLHTL VAFLCIIGYN CLKVPLVIFK REKELARKLE FDGLYITEQP GDDDVKGQWD RLVLNTPSFP SNYWDKFV K RKVLDKHGDI FGRERIAELL GMDLASLEIT AHNERKPDPP PGLLTWLMSI DVKYQIWKFG VIFTDNSFLY LGWYMVMSL LGHYNNFFFA AHLLDIAMGV KTLRTILSSV THNGKQLVMT VGLLAVVVYL YTVVAFNFFR KFYNKSEDED EPDMKCDDMM TCYLFHMYV GVRAGGGIGD EIEDPAGDEY ELYRVVFDIT FFFFVIVILL AIIQGLIIDA FGELRDQQEQ VKEDMETKCF I CGIGSDYF DTTPHGFETH TLEEHNLANY MFFLMYLINK DETEHTGQES YVWKMYQERC WDFFPAGDCF RKQYEDQLS UniProtKB: Ryanodine receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B
| Macromolecule | Name: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: peptidylprolyl isomerase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.667305 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GVEIETISPG DGRTFPKKGQ TCVVHYTGML QNGKKFDSSR DRNKPFKFRI GKQEVIKGFE EGAAQMSLGQ RAKLTCTPDV AYGATGHPG VIPPNATLIF DVELLNLE UniProtKB: Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B |
-Macromolecule #4: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.620402 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KALGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPAFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAALRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EAFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #5: CAFFEINE
| Macromolecule | Name: CAFFEINE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CFF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 194.191 Da |
| Chemical component information | 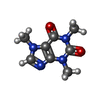 ChemComp-CFF: |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Macromolecule #7: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Macromolecule #8: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 10 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 4096 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 4096 pixel / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)