+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8b1r | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | RecBCD in complex with the phage protein gp5.9 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Homologous recombination / DNA repair / phage / Helicase / Nuclease / Inhibitor / Protein complex / Enzyme / DNA mimic | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexodeoxyribonuclease V / exodeoxyribonuclease V activity / exodeoxyribonuclease V complex / clearance of foreign intracellular DNA / DNA 5'-3' helicase / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / recombinational repair / DNA 3'-5' helicase / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / DNA helicase activity ...exodeoxyribonuclease V / exodeoxyribonuclease V activity / exodeoxyribonuclease V complex / clearance of foreign intracellular DNA / DNA 5'-3' helicase / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / recombinational repair / DNA 3'-5' helicase / 3'-5' DNA helicase activity / DNA helicase activity / response to radiation / helicase activity / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / 5'-3' DNA helicase activity / DNA recombination / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / DNA damage response / magnesium ion binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |    Escherichia phage T7 (virus) Escherichia phage T7 (virus) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wilkinson, M. / Wilkinson, O.J. / Feyerherm, C. / Fletcher, E.E. / Wigley, D.B. / Dillingham, M.S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2022 Journal: Elife / Year: 2022Title: Structures of RecBCD in complex with phage-encoded inhibitor proteins reveal distinctive strategies for evasion of a bacterial immunity hub. Authors: Martin Wilkinson / Oliver J Wilkinson / Connie Feyerherm / Emma E Fletcher / Dale B Wigley / Mark S Dillingham /  Abstract: Following infection of bacterial cells, bacteriophage modulate double-stranded DNA break repair pathways to protect themselves from host immunity systems and prioritise their own recombinases. Here, ...Following infection of bacterial cells, bacteriophage modulate double-stranded DNA break repair pathways to protect themselves from host immunity systems and prioritise their own recombinases. Here, we present biochemical and structural analysis of two phage proteins, gp5.9 and Abc2, which target the DNA break resection complex RecBCD. These exemplify two contrasting mechanisms for control of DNA break repair in which the RecBCD complex is either inhibited or co-opted for the benefit of the invading phage. Gp5.9 completely inhibits RecBCD by preventing it from binding to DNA. The RecBCD-gp5.9 structure shows that gp5.9 acts by substrate mimicry, binding predominantly to the RecB arm domain and competing sterically for the DNA binding site. Gp5.9 adopts a parallel coiled-coil architecture that is unprecedented for a natural DNA mimic protein. In contrast, binding of Abc2 does not substantially affect the biochemical activities of isolated RecBCD. The RecBCD-Abc2 structure shows that Abc2 binds to the Chi-recognition domains of the RecC subunit in a position that might enable it to mediate the loading of phage recombinases onto its single-stranded DNA products. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8b1r.cif.gz 8b1r.cif.gz | 495.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8b1r.ent.gz pdb8b1r.ent.gz | 395.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8b1r.json.gz 8b1r.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b1/8b1r https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b1/8b1r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b1/8b1r ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b1/8b1r | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15803MC  8b1tC  8b1uC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 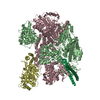
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 134110.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: recB, BHS81_16925, BJI68_00835, BON89_01565, BON93_20715, BvCmsHHP056_02020, C5N07_06355, C5Y87_19730, C9114_10810, DAH36_05180, DAH37_01130, E2134_07940, E5M02_13555, E5P30_22870, E5P31_10440, ...Gene: recB, BHS81_16925, BJI68_00835, BON89_01565, BON93_20715, BvCmsHHP056_02020, C5N07_06355, C5Y87_19730, C9114_10810, DAH36_05180, DAH37_01130, E2134_07940, E5M02_13555, E5P30_22870, E5P31_10440, E5P32_13260, E5P36_03520, E5P40_11525, E5P51_08340, E5S39_06465, E5S44_07560, EI021_14360, ELX85_18530, EYV17_10125, EYV18_15060, F0L67_06605, F2N31_08115, F9V24_07045, FOI11_01100, FOI11_022080, GF699_18635, GKF89_09600, GRW05_08565, HMV95_04145, HX136_04845, IH772_15520, JNP96_21695, NCTC13216_00866, NCTC9117_01550, NCTC9706_03254, RG28_07470 Plasmid: pETduet / Production host:  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 128974.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   | ||||
| #3: Protein | Mass: 66990.367 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   | ||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 6049.601 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Escherichia phage T7 (virus) / Gene: 5.9 / Plasmid: pACEBAC1 / Cell line (production host): High Five / Production host: Escherichia phage T7 (virus) / Gene: 5.9 / Plasmid: pACEBAC1 / Cell line (production host): High Five / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P20406 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P20406#5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: RecBCD mixed with T7 gp5.9 protein prior to making grids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Mixture of graphene oxide with 0.3 mM DDM detergent applied directly to grids twice before application of sample Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Details: 1.5s blot time |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 4.3 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 5064 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1458124 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 141458 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 89.5 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5MBV Accession code: 5MBV / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj






