+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7xzz | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
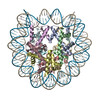
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the nucleosome in complex with p53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION/DNA / Transcription factor / Tumor-suppressor / GENE REGULATION-DNA COMPLEX | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of helicase activity / Loss of function of TP53 in cancer due to loss of tetramerization ability / Regulation of TP53 Expression / signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition / negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / Transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity ...negative regulation of helicase activity / Loss of function of TP53 in cancer due to loss of tetramerization ability / Regulation of TP53 Expression / signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of G1 to G0 transition / negative regulation of glucose catabolic process to lactate via pyruvate / Transcriptional activation of cell cycle inhibitor p21 / regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / ATP-dependent DNA/DNA annealing activity / Activation of NOXA and translocation to mitochondria / regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition / oligodendrocyte apoptotic process / negative regulation of miRNA processing / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hypoxia / positive regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / oxidative stress-induced premature senescence / regulation of tissue remodeling / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability / regulation of fibroblast apoptotic process / mRNA transcription / bone marrow development / circadian behavior / positive regulation of programmed necrotic cell death / T cell proliferation involved in immune response / regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability involved in apoptotic process / histone deacetylase regulator activity / germ cell nucleus / RUNX3 regulates CDKN1A transcription / homolactic fermentation / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Death Receptors and Ligands / TP53 regulates transcription of additional cell cycle genes whose exact role in the p53 pathway remain uncertain / Activation of PUMA and translocation to mitochondria / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Association with Co-factors / regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / mitochondrial DNA repair / T cell lineage commitment / Formation of Senescence-Associated Heterochromatin Foci (SAHF) / thymocyte apoptotic process / ER overload response / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Caspase Activators and Caspases / cardiac septum morphogenesis / entrainment of circadian clock by photoperiod / B cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of mitophagy / negative regulation of DNA replication / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / PI5P Regulates TP53 Acetylation / necroptotic process / negative regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / positive regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / SUMOylation of transcription factors / TP53 regulates transcription of several additional cell death genes whose specific roles in p53-dependent apoptosis remain uncertain / TFIID-class transcription factor complex binding / cellular response to actinomycin D / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process / rRNA transcription / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / cellular response to UV-C / viral process / general transcription initiation factor binding / replicative senescence / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / neuroblast proliferation / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / Pyroptosis / positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis / embryonic organ development / hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / chromosome organization / type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / response to X-ray / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / somitogenesis / hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / cellular response to glucose starvation / mitophagy / cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Acetylation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / 14-3-3 protein binding / negative regulation of proteolysis / response to salt stress / CENP-A containing nucleosome Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.07 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nishimura, M. / Nozawa, K. / Takizawa, Y. / Kurumizaka, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 10items Japan, 10items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PNAS Nexus / Year: 2022 Journal: PNAS Nexus / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for p53 binding to its nucleosomal target DNA sequence. Authors: Masahiro Nishimura / Yoshimasa Takizawa / Kayo Nozawa / Hitoshi Kurumizaka /  Abstract: The tumor suppressor p53 functions as a pioneer transcription factor that binds a nucleosomal target DNA sequence. However, the mechanism by which p53 binds to its target DNA in the nucleosome ...The tumor suppressor p53 functions as a pioneer transcription factor that binds a nucleosomal target DNA sequence. However, the mechanism by which p53 binds to its target DNA in the nucleosome remains elusive. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of the p53 DNA-binding domain and the full-length p53 protein complexed with a nucleosome containing the 20 base-pair target DNA sequence of p53 (p53BS). In the p53-nucleosome structures, the p53 DNA-binding domain forms a tetramer and specifically binds to the p53BS DNA, located near the entry/exit region of the nucleosome. The nucleosomal position of the p53BS DNA is within the genomic p21 promoter region. The p53 binding peels the DNA from the histone surface, and drastically changes the DNA path around the p53BS on the nucleosome. The C-terminal domain of p53 also binds to the DNA around the center and linker DNA regions of the nucleosome, as revealed by hydroxyl radical footprinting. These results provide important structural information for understanding the mechanism by which p53 binds the nucleosome and changes the chromatin structure for gene activation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7xzz.cif.gz 7xzz.cif.gz | 456.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7xzz.ent.gz pdb7xzz.ent.gz | 350.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7xzz.json.gz 7xzz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xz/7xzz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xz/7xzz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xz/7xzz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xz/7xzz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33535MC 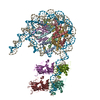 7xzxC  7xzyC 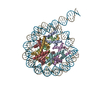 7y00C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 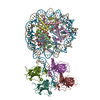
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 12 molecules AEBFCGDHKLMN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15719.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H3C1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H3C1 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11676.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: H4C1 / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14447.825 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AE / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AE / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 14217.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BJ / Production host:  #7: Protein | Mass: 43855.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TP53, P53 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TP53, P53 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 52032.137 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 52312.316 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.398 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.25 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 289.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2739901 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.07 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 92142 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj