[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
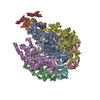
Yorodumi- PDB-7tkf: Yeast ATP synthase State 2binding(b) with 10 mM ATP backbone model -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7tkf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Yeast ATP synthase State 2binding(b) with 10 mM ATP backbone model | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / F1-ATPase / ATP Synthase / Nanomotor | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcristae formation / Mitochondrial protein degradation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / mitochondrial nucleoid / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase ...cristae formation / Mitochondrial protein degradation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / mitochondrial nucleoid / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport / ADP binding / mitochondrial intermembrane space / protein-containing complex assembly / mitochondrial inner membrane / lipid binding / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.1 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guo, H. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 3items Canada, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structure of ATP synthase under strain during catalysis. Authors: Hui Guo / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: ATP synthases are macromolecular machines consisting of an ATP-hydrolysis-driven F motor and a proton-translocation-driven F motor. The F and F motors oppose each other's action on a shared rotor ...ATP synthases are macromolecular machines consisting of an ATP-hydrolysis-driven F motor and a proton-translocation-driven F motor. The F and F motors oppose each other's action on a shared rotor subcomplex and are held stationary relative to each other by a peripheral stalk. Structures of resting mitochondrial ATP synthases revealed a left-handed curvature of the peripheral stalk even though rotation of the rotor, driven by either ATP hydrolysis in F or proton translocation through F, would apply a right-handed bending force to the stalk. We used cryoEM to image yeast mitochondrial ATP synthase under strain during ATP-hydrolysis-driven rotary catalysis, revealing a large deformation of the peripheral stalk. The structures show how the peripheral stalk opposes the bending force and suggests that during ATP synthesis proton translocation causes accumulation of strain in the stalk, which relaxes by driving the relative rotation of the rotor through six sub-steps within F, leading to catalysis. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7tkf.cif.gz 7tkf.cif.gz | 600 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7tkf.ent.gz pdb7tkf.ent.gz | 371.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7tkf.json.gz 7tkf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tk/7tkf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tk/7tkf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tk/7tkf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tk/7tkf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25967MC  7tjsC  7tjtC  7tjuC  7tjvC  7tjwC  7tjxC  7tjyC  7tjzC  7tk0C  7tk1C  7tk2C  7tk3C  7tk4C  7tk5C  7tk6C  7tk7C  7tk8C  7tk9C  7tkaC  7tkbC  7tkcC  7tkdC  7tkeC  7tkgC  7tkhC  7tkiC  7tkjC  7tkkC  7tklC  7tkmC  7tknC  7tkoC  7tkpC  7tkqC  7tkrC  7tksC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 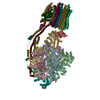
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 13 types, 26 molecules 0123456789ABCDEFGHIOTUVWXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 7762.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 55007.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 51181.082 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P00830, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #4: Protein | | Mass: 30657.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | | Mass: 14565.385 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | | Mass: 6618.359 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | | Mass: 20901.139 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 27900.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 23194.498 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | | Mass: 19709.424 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | | Mass: 10584.166 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | | Mass: 10417.298 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | | Mass: 6696.771 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules Z
| #14: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5825.215 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Yeast ATP synthase State 2binding(b) with 10 mM ATPv backbone model Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.61 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Homemade |
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 59000 X / Calibrated magnification: 103896 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1100 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 11.9 sec. / Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 10037 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: UCSF ChimeraX / Version: 1.2/v9 / Classification: model building / URL: https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ / Os: macOS / Type: package | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2534488 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 9157 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: RECIPROCAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 2HLD Accession code: 2HLD / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



















































 PDBj
PDBj