+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7tbh | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
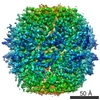
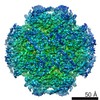
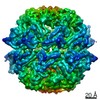
| Title | cryo-EM structure of MBP-KIX-apoferritin complex with peptide 7 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Protein Engineering / Simulation / Peptide Therapeutics / Acute Myeloid Leukemia | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationIron uptake and transport / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / peptide lactyltransferase (CoA-dependent) activity / NFE2L2 regulating ER-stress associated genes / NFE2L2 regulating inflammation associated genes / Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity ...Iron uptake and transport / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / peptide lactyltransferase (CoA-dependent) activity / NFE2L2 regulating ER-stress associated genes / NFE2L2 regulating inflammation associated genes / Activation of the TFAP2 (AP-2) family of transcription factors / histone H3K18 acetyltransferase activity / N-terminal peptidyl-lysine acetylation / LRR FLII-interacting protein 1 (LRRFIP1) activates type I IFN production / histone H3K27 acetyltransferase activity / NFE2L2 regulates pentose phosphate pathway genes / regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / NFE2L2 regulating MDR associated enzymes / MRF binding / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of myeloid cells / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / Regulation of FOXO transcriptional activity by acetylation / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Regulation of NFE2L2 gene expression / Nuclear events mediated by NFE2L2 / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation / NFE2L2 regulating tumorigenic genes / NFE2L2 regulating anti-oxidant/detoxification enzymes / embryonic digit morphogenesis / protein-lysine-acetyltransferase activity / protein acetylation / negative regulation of ferroptosis / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / acetyltransferase activity / ferroxidase / homeostatic process / FOXO-mediated transcription of cell death genes / stimulatory C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway / Zygotic genome activation (ZGA) / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in Cytochrome C Release / autolysosome / ferroxidase activity / histone acetyltransferase complex / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Attenuation phase / cellular response to nutrient levels / histone acetyltransferase activity / histone acetyltransferase / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of cellular response to heat / : / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / Neutrophil degranulation / endocytic vesicle lumen / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / ferric iron binding / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian expression / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / autophagosome / iron ion transport / Heme signaling / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / PPARA activates gene expression / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / chromatin DNA binding / protein destabilization / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / tau protein binding / transcription coactivator binding / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / p53 binding / cellular response to UV / : / transcription corepressor activity / rhythmic process / HATs acetylate histones / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / protein-containing complex assembly / TRAF3-dependent IRF activation pathway / transcription regulator complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / DNA-binding transcription factor binding / damaged DNA binding / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / response to hypoxia / transcription coactivator activity / immune response Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, K. / Horikoshi, N. / Li, S. / Powers, A. / Hameedi, M. / Pintilie, G. / Chae, H. / Khan, Y. / Suomivuori, C. / Dror, R. ...Zhang, K. / Horikoshi, N. / Li, S. / Powers, A. / Hameedi, M. / Pintilie, G. / Chae, H. / Khan, Y. / Suomivuori, C. / Dror, R. / Sakamoto, K. / Chiu, W. / Wakatsuki, S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ACS Cent Sci / Year: 2022 Journal: ACS Cent Sci / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM, Protein Engineering, and Simulation Enable the Development of Peptide Therapeutics against Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Authors: Kaiming Zhang / Naoki Horikoshi / Shanshan Li / Alexander S Powers / Mikhail A Hameedi / Grigore D Pintilie / Hee-Don Chae / Yousuf A Khan / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Ron O Dror / Kathleen M ...Authors: Kaiming Zhang / Naoki Horikoshi / Shanshan Li / Alexander S Powers / Mikhail A Hameedi / Grigore D Pintilie / Hee-Don Chae / Yousuf A Khan / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Ron O Dror / Kathleen M Sakamoto / Wah Chiu / Soichi Wakatsuki /    Abstract: Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has emerged as a viable structural tool for molecular therapeutics development against human diseases. However, it remains a challenge to determine structures ...Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has emerged as a viable structural tool for molecular therapeutics development against human diseases. However, it remains a challenge to determine structures of proteins that are flexible and smaller than 30 kDa. The 11 kDa KIX domain of CREB-binding protein (CBP), a potential therapeutic target for acute myeloid leukemia and other cancers, is a protein which has defied structure-based inhibitor design. Here, we develop an experimental approach to overcome the size limitation by engineering a protein double-shell to sandwich the KIX domain between apoferritin as the inner shell and maltose-binding protein as the outer shell. To assist homogeneous orientations of the target, disulfide bonds are introduced at the target-apoferritin interface, resulting in a cryo-EM structure at 2.6 Å resolution. We used molecular dynamics simulations to design peptides that block the interaction of the KIX domain of CBP with the intrinsically disordered pKID domain of CREB. The double-shell design allows for fluorescence polarization assays confirming the binding between the KIX domain in the double-shell and these interacting peptides. Further cryo-EM analysis reveals a helix-helix interaction between a single KIX helix and the best peptide, providing a possible strategy for developments of next-generation inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7tbh.cif.gz 7tbh.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7tbh.ent.gz pdb7tbh.ent.gz | 911.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7tbh.json.gz 7tbh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/7tbh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/7tbh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/7tbh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tb/7tbh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25799MC  7tb3C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 30408.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 24 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CREBBP, CBP, Fth1, Fth Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CREBBP, CBP, Fth1, FthProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q92793, UniProt: P09528, histone acetyltransferase, Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2272.457 Da / Num. of mol.: 24 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MBP-KIX-apoferritin complex with peptide 7 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.7 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: MBP-KIX-apoferritin complex with peptide 7 |
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 300 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 6 sec. / Electron dose: 43.8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2490 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 124114 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 35613 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Target criteria: Q-score |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj

























